Introduction: what is quantum field theory ?
... Yet another reason to treat fields as the fundamental physical quantity is that all particles of the same type are the same. This is much more serious than it initially sounds. For example, two electrons are identical in every way, regardless of where they came from and what they’ve been through. Th ...
... Yet another reason to treat fields as the fundamental physical quantity is that all particles of the same type are the same. This is much more serious than it initially sounds. For example, two electrons are identical in every way, regardless of where they came from and what they’ve been through. Th ...
Maxwell*s Equation*s in integral form
... electrodes separated by a narrow gap The discharge between the electrodes exhibits an oscillatory behavior at a very high frequency Sparks were induced across the gap of the receiving electrodes when the frequency of the receiver was adjusted to match that of the transmitter In a series of other exp ...
... electrodes separated by a narrow gap The discharge between the electrodes exhibits an oscillatory behavior at a very high frequency Sparks were induced across the gap of the receiving electrodes when the frequency of the receiver was adjusted to match that of the transmitter In a series of other exp ...
Document
... ______ 12. Stated that energy is emitted or absorbed in discrete pieces called quanta. ______ 13. Used Planck’s idea of quantization to explain the line spectrum of hydrogen. ______ 14. Stated that the position and momentum of a moving object cannot be simultaneously measured and known exactly. ____ ...
... ______ 12. Stated that energy is emitted or absorbed in discrete pieces called quanta. ______ 13. Used Planck’s idea of quantization to explain the line spectrum of hydrogen. ______ 14. Stated that the position and momentum of a moving object cannot be simultaneously measured and known exactly. ____ ...
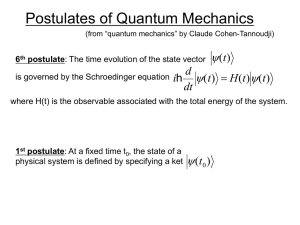
chem6V19_postulates
... where H(t) is the observable associated with the total energy of the system. ...
... where H(t) is the observable associated with the total energy of the system. ...
Physics IV - Exam - Winter 2007/08 Please note:
... (a) In an electric field E, an electron experiences a force F = −eE, where e is the electron charge. Assuming that the time τ between collisions of free electrons is unaffected by the accelerating electric field, show that the average, or ‘drift’ velocity vd of the electrons is ...
... (a) In an electric field E, an electron experiences a force F = −eE, where e is the electron charge. Assuming that the time τ between collisions of free electrons is unaffected by the accelerating electric field, show that the average, or ‘drift’ velocity vd of the electrons is ...
Quantum Science for Energy Healers
... chemical bonds. These charged species are called ions and the bond is ionic. d) atoms may also share electrons to form covalent bonds…these substances are typically insulators i.e. do not conduct electricity. e) Moving electrons generate an electrical and a magnetic field. Magnetic fields are ...
... chemical bonds. These charged species are called ions and the bond is ionic. d) atoms may also share electrons to form covalent bonds…these substances are typically insulators i.e. do not conduct electricity. e) Moving electrons generate an electrical and a magnetic field. Magnetic fields are ...
Quantum Potpourri
... and the Superposition Principle Electrons in atoms or molecules are characterized by their entire distributions, called wave functions or orbitals, rather than by instantaneous positions and velocities: an electron may be considered always to be, with appropriate probability, at all points of its di ...
... and the Superposition Principle Electrons in atoms or molecules are characterized by their entire distributions, called wave functions or orbitals, rather than by instantaneous positions and velocities: an electron may be considered always to be, with appropriate probability, at all points of its di ...
Lecture 14
... complications. In this theory the basic vertex involves particles A, B and C. In this toy theory as in the full Feynman theory we will construct matrix elements based on a simple set of rules. 1) rules for defining –iM 2) For each vertex write a factor of the coupling constant –ig. g has units of mo ...
... complications. In this theory the basic vertex involves particles A, B and C. In this toy theory as in the full Feynman theory we will construct matrix elements based on a simple set of rules. 1) rules for defining –iM 2) For each vertex write a factor of the coupling constant –ig. g has units of mo ...
Exam 2-1
... Einstein’s explanation of the photoelectric effect. Rutherford’s experiment with a beam of α particles passing through gold foil. Boer’s model of the atom. Faraday’s experiment of the electroplating of metals. Binnig and Rohrer’s demonstration of the scanning tunneling microscope. ...
... Einstein’s explanation of the photoelectric effect. Rutherford’s experiment with a beam of α particles passing through gold foil. Boer’s model of the atom. Faraday’s experiment of the electroplating of metals. Binnig and Rohrer’s demonstration of the scanning tunneling microscope. ...
PPT | 345.5 KB - Joint Quantum Institute
... wavelengths. The researchers found, however, that by beaming a carefully tuned laser at the dot, the wavelength difference was suppressed and the emitted photons were entangled. The technique may someday enable more compact and convenient sources of entangled photon pairs than presently available fo ...
... wavelengths. The researchers found, however, that by beaming a carefully tuned laser at the dot, the wavelength difference was suppressed and the emitted photons were entangled. The technique may someday enable more compact and convenient sources of entangled photon pairs than presently available fo ...
BWilliamsPaper - FSU High Energy Physics
... earth, and the earth in orbit around the sun, and so on. He was able to write a mathematical expression which quantified the force, called gravity, relating the attractive force between two objects to the product of their masses divided by the square of the distance between them. Newton also develo ...
... earth, and the earth in orbit around the sun, and so on. He was able to write a mathematical expression which quantified the force, called gravity, relating the attractive force between two objects to the product of their masses divided by the square of the distance between them. Newton also develo ...
Lecture IV : Feb 8, 2016 Learning from Two Hole Experiment (A
... of electron diffraction in two independent experiments. At the University of Aberdeen George Paget Thomson passed a beam of electrons through a thin metal film and observed the predicted interference patterns. At Bell Labs Clinton Joseph Davisson and Lester Halbert Germer guided their beam through a ...
... of electron diffraction in two independent experiments. At the University of Aberdeen George Paget Thomson passed a beam of electrons through a thin metal film and observed the predicted interference patterns. At Bell Labs Clinton Joseph Davisson and Lester Halbert Germer guided their beam through a ...