Modern Physics (PHY 251) Lecture 18
... Example: What’s the de Broglie’s wavelength (in meters) of a) a baseball of m=1kg moving at a speed of v=10m/s? b) an electron whose kinetic energy is 100 eV (i.e. non-relativistic)? m0= 0.511 MeV/c 2 ...
... Example: What’s the de Broglie’s wavelength (in meters) of a) a baseball of m=1kg moving at a speed of v=10m/s? b) an electron whose kinetic energy is 100 eV (i.e. non-relativistic)? m0= 0.511 MeV/c 2 ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... where n is an integer, h is Planck’s constant and ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation absorbed or emitted. 2. Energy is in fact quantized and can only occur in discrete units of size hv. Each of these small "packets" of energy is called a quantum (or a photon when we are talking abou ...
... where n is an integer, h is Planck’s constant and ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation absorbed or emitted. 2. Energy is in fact quantized and can only occur in discrete units of size hv. Each of these small "packets" of energy is called a quantum (or a photon when we are talking abou ...
Physics 1020 Ch 10-12 Practice Exam (2).
... b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of electrons occupying an orbital as long as enough energy is provided. d. no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state. 11. The A ...
... b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of electrons occupying an orbital as long as enough energy is provided. d. no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state. 11. The A ...
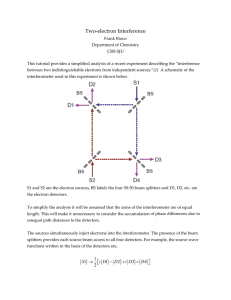
constructive - Purdue Physics
... the formula was derived by Einstein nine years before the first experiment that actually verified it!. (It was known that the energy of the electrons increased with frequency but not this simple formula). ...
... the formula was derived by Einstein nine years before the first experiment that actually verified it!. (It was known that the energy of the electrons increased with frequency but not this simple formula). ...
QUANTUM THEORY OF ATOMS AND MOLECULES
... Problems 2 1. Show that the function = N sin nx/L satisfies the Schrodinger equation for a particle in a 1-D box between x = 0 and x = L and calculate the value of the normalisation factor N. Evaluate the probability of finding the particle between 0.4L and 0.6L when n = 1 and when n = 2. What wo ...
... Problems 2 1. Show that the function = N sin nx/L satisfies the Schrodinger equation for a particle in a 1-D box between x = 0 and x = L and calculate the value of the normalisation factor N. Evaluate the probability of finding the particle between 0.4L and 0.6L when n = 1 and when n = 2. What wo ...
particles - Prof.Dr.Ümit Demir
... amount of energy reduction depended on the angle at which the x-rays were scattered. The change in wavelength between a scattered x-ray and an incident x-ray is called the Compton shift. In order to explain this effect, Compton assumed that if a photon behaves like a particle, its collision with oth ...
... amount of energy reduction depended on the angle at which the x-rays were scattered. The change in wavelength between a scattered x-ray and an incident x-ray is called the Compton shift. In order to explain this effect, Compton assumed that if a photon behaves like a particle, its collision with oth ...
28_lecture_acl
... §28.1 Wave-Particle Duality Light is both wave-like (interference & diffraction) and particle-like (photoelectric effect). Double slit experiment: allow only 1 photon at a time, but: • still makes interference pattern! • can’t determine which slit it will pass thru • can’t determine where it will h ...
... §28.1 Wave-Particle Duality Light is both wave-like (interference & diffraction) and particle-like (photoelectric effect). Double slit experiment: allow only 1 photon at a time, but: • still makes interference pattern! • can’t determine which slit it will pass thru • can’t determine where it will h ...
Homework No. 09 (Spring 2014) PHYS 530A: Quantum Mechanics II
... 4. (Schwinger’s QM book, Prob. 3-4a.) Iso(topic) spin T : The nucleon is a particle of isospin T = 12 ; the state with T3 = 21 is the proton (p), the state with T3 = − 12 is the neutron (n). Electric charge of a nucleon is given by Q = 12 + T3 . The π meson, or pion, has isospin T = 1, and electric ...
... 4. (Schwinger’s QM book, Prob. 3-4a.) Iso(topic) spin T : The nucleon is a particle of isospin T = 12 ; the state with T3 = 21 is the proton (p), the state with T3 = − 12 is the neutron (n). Electric charge of a nucleon is given by Q = 12 + T3 . The π meson, or pion, has isospin T = 1, and electric ...
Class25_review - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... states (integer n) are solutions • Each state has one allowed energy, so energy is again quantized • Energy depends on well width a (confinement width) |c(x)|2 ...
... states (integer n) are solutions • Each state has one allowed energy, so energy is again quantized • Energy depends on well width a (confinement width) |c(x)|2 ...
Lecture 9
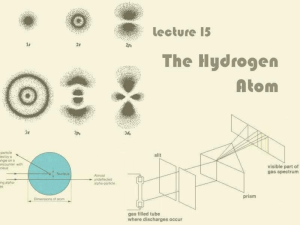
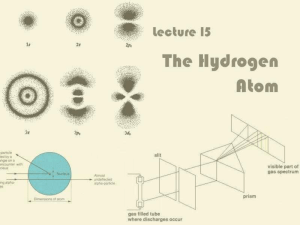
... diffraction glasses. They work just like a prism and break up light into its components. Notice the dark spots between the “lines” of the different colors. The number and positions of the lines are the unique signature of the elements. A lab experiment. Note the number and color of the lines. See if ...
... diffraction glasses. They work just like a prism and break up light into its components. Notice the dark spots between the “lines” of the different colors. The number and positions of the lines are the unique signature of the elements. A lab experiment. Note the number and color of the lines. See if ...
Chapter40_VGO
... 1. First treat photons as waves and calculate the classical wave fields for a wave of frequency w=2pf E(x) B(x) 2. Calculate the classical intensity 1 e0 ...
... 1. First treat photons as waves and calculate the classical wave fields for a wave of frequency w=2pf E(x) B(x) 2. Calculate the classical intensity 1 e0 ...
energy levels
... • Taking part in the Manhattan Project. Bohr’s theory of hydrogen (1913): • An obsolete theory which has been replaced by quantum mechanics. • The model can still be used to develop ideas of energy and angular momentum quantization in atomic-sized systems. Assumption 1: The electron moves in circula ...
... • Taking part in the Manhattan Project. Bohr’s theory of hydrogen (1913): • An obsolete theory which has been replaced by quantum mechanics. • The model can still be used to develop ideas of energy and angular momentum quantization in atomic-sized systems. Assumption 1: The electron moves in circula ...















![L 35 Modern Physics [1] - University of Iowa Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000679677_1-b925cf8c8f031b0f2b0c09a806312d20-300x300.png)
![L 35 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001558975_1-84d6e03bc786b63795533f59711ce2f4-300x300.png)




