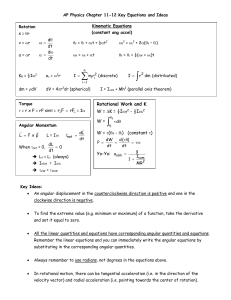
AP Physics Chapter 11-12 Key Equations and Ideas Rotation s = qr
... A body will freely rotate about an axis that always passes through the center of mass of the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
... A body will freely rotate about an axis that always passes through the center of mass of the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
Quantum Number, n. - Lyndhurst Schools
... Quantized Energy and Photons The Photoelectric Effect and Photons When light of a sufficiently high energy strikes a metal surface, electrons are knocked off its surface. • Einstein assumed that light traveled in energy packets called photons. • The energy of one photon is: ...
... Quantized Energy and Photons The Photoelectric Effect and Photons When light of a sufficiently high energy strikes a metal surface, electrons are knocked off its surface. • Einstein assumed that light traveled in energy packets called photons. • The energy of one photon is: ...
Quantum Numbers
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
Mass of an Electromagnetic Wave
... speed [2]. Thus it has been argued that electromagnetic waves or photons must be massless, as these by definition travel at the speed of light when in a vacuum. In this paper we will use some relativity equations to show that a photon does have mass, but that the amount of mass varies with its speed ...
... speed [2]. Thus it has been argued that electromagnetic waves or photons must be massless, as these by definition travel at the speed of light when in a vacuum. In this paper we will use some relativity equations to show that a photon does have mass, but that the amount of mass varies with its speed ...
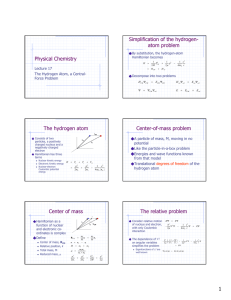
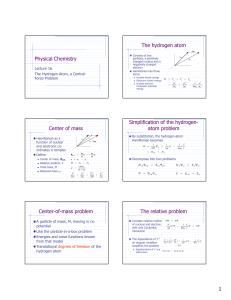
Physical Chemistry The hydrogen atom Center of mass
... with only Coulombic interaction The dependence of 2 on angular variables simplifies the problem ...
... with only Coulombic interaction The dependence of 2 on angular variables simplifies the problem ...
Chapter 41: Quantization of Angular Momentum and of Energy Values
... Example: if = 1 ( L = ), then Lz can have three values corresponding to m = 1, 0, or -1 ...
... Example: if = 1 ( L = ), then Lz can have three values corresponding to m = 1, 0, or -1 ...
Light and Energy AP Style
... Matter and energy were seen as different from each other in fundamental ways Matter was particles Energy could come in waves, with any frequency. Max Planck found that the cooling of hot objects couldn’t be explained by viewing energy as a wave. ...
... Matter and energy were seen as different from each other in fundamental ways Matter was particles Energy could come in waves, with any frequency. Max Planck found that the cooling of hot objects couldn’t be explained by viewing energy as a wave. ...
incident angle
... the dominant reflected polarization while allowing the other polarization to pass through. ...
... the dominant reflected polarization while allowing the other polarization to pass through. ...
pacing guide - Tallapoosa County Schools
... These content standards are what the Alabama State Board of Education has identified as what students should know and be able to do at the end of the grade level. Therefore, teaching these standards to mastery is the goal for each classroom in Alabama. ...
... These content standards are what the Alabama State Board of Education has identified as what students should know and be able to do at the end of the grade level. Therefore, teaching these standards to mastery is the goal for each classroom in Alabama. ...
Which scientist developed the quantum mechanical model of the
... What is the correct number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an oxygen atom? A) B) C) D) ...
... What is the correct number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an oxygen atom? A) B) C) D) ...