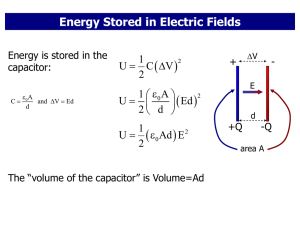
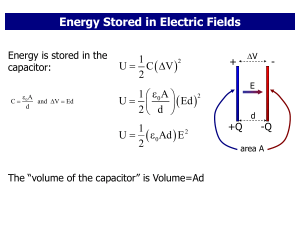
Wave Particle Duality
... Maxwell discovered that light was actually an electromagnetic wave – a wave of oscillating magnetic and electric fields. This was proven experimentally by Heinrich Hertz. ...
... Maxwell discovered that light was actually an electromagnetic wave – a wave of oscillating magnetic and electric fields. This was proven experimentally by Heinrich Hertz. ...
Quantum physics
... • Photocurrent I = (n/t)e, where (n/t) = rate of emission of electrons • Why rate of emission of electrons << rate of incidence of photons {for f>f0}: • Not every photon would collide with an electron; most are reflected by the metal or miss hitting any electron. • On the way out to the metal surfac ...
... • Photocurrent I = (n/t)e, where (n/t) = rate of emission of electrons • Why rate of emission of electrons << rate of incidence of photons {for f>f0}: • Not every photon would collide with an electron; most are reflected by the metal or miss hitting any electron. • On the way out to the metal surfac ...
Lecture 13: Heisenberg and Uncertainty
... Quantum Mechanics The observer is not objective and passive The act of observation changes the physical system irrevocably This is known as subjective reality ...
... Quantum Mechanics The observer is not objective and passive The act of observation changes the physical system irrevocably This is known as subjective reality ...
Quantum theory
... • Scientists are unable to describe the exact structure of an atom due to this • But it can be determined with probability • Can determine with high probability where an e- is most likely to be found in the energy levels of an atom at any one given time ...
... • Scientists are unable to describe the exact structure of an atom due to this • But it can be determined with probability • Can determine with high probability where an e- is most likely to be found in the energy levels of an atom at any one given time ...
PHYSICS GRADUATE SCHOOL QUALIFYING
... inner one of adjustable radius a. The space between the spheres is filled with air, which has a breakdown electric field strength ...
... inner one of adjustable radius a. The space between the spheres is filled with air, which has a breakdown electric field strength ...
January 2006
... the ground state is N0 (T ) = N (1 − (T /TE )α ), where TE is the Einstein condensation temperature. Determine the exponent α and an expression for TE . You may encounter a dimensionless integral whose value is not readily evaluated; you may give your answers in terms of this integral. For TE to rem ...
... the ground state is N0 (T ) = N (1 − (T /TE )α ), where TE is the Einstein condensation temperature. Determine the exponent α and an expression for TE . You may encounter a dimensionless integral whose value is not readily evaluated; you may give your answers in terms of this integral. For TE to rem ...
Slide 1
... “The energy in electromagnetic phenomena is the same as mechanical energy. The only question is, ‘Where does it reside?’ In the old theories, it resides in electrified bodies. In our theory, it resides in the electromagnetic field, in the space surrounding the electrified bodies.”—James Maxwell ...
... “The energy in electromagnetic phenomena is the same as mechanical energy. The only question is, ‘Where does it reside?’ In the old theories, it resides in electrified bodies. In our theory, it resides in the electromagnetic field, in the space surrounding the electrified bodies.”—James Maxwell ...
The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
... Electromagnetic waves are produced by the vibrations or oscillations of charged particles. The frequency is the number of times a particle vibrates per second. The vibrations produce a wave with a wavelength inversely proportional to the frequency (one vibration = one wavelength). The wave moves awa ...
... Electromagnetic waves are produced by the vibrations or oscillations of charged particles. The frequency is the number of times a particle vibrates per second. The vibrations produce a wave with a wavelength inversely proportional to the frequency (one vibration = one wavelength). The wave moves awa ...
quantumwaves
... •We are talking about one particle – but it is not at one location in space •If we measured its position, where would we be likely to find it? The Wave Function is also called the probability amplitude •Clearly, where the wave function is small (or zero), you wouldn’t expect to find the particle •Wh ...
... •We are talking about one particle – but it is not at one location in space •If we measured its position, where would we be likely to find it? The Wave Function is also called the probability amplitude •Clearly, where the wave function is small (or zero), you wouldn’t expect to find the particle •Wh ...
The Bohr Theory, Matter Waves, and Quantum Theory
... Here, light impinges on a surface and electrons may be emitted. Classically, the energy of the light is controlled by the intensity of the light. Energy conservation products that there should be no dependence on wavelength of light. If the intensity of the light is increased, the kinetic energy of ...
... Here, light impinges on a surface and electrons may be emitted. Classically, the energy of the light is controlled by the intensity of the light. Energy conservation products that there should be no dependence on wavelength of light. If the intensity of the light is increased, the kinetic energy of ...
Homework No. 07 (Spring 2015) PHYS 530A: Quantum Mechanics II
... (b) Beginning with |5/2, 5/2i use the lowering operator to build five other states with j = 5/2. (c) Construct |3/2, 3/2i state by requiring it to be orthogonal to |5/2, 3/2i, and be normalized. (d) Beginning with |3/2, 3/2i use the lowering operator to build three other states with j = 3/2. ...
... (b) Beginning with |5/2, 5/2i use the lowering operator to build five other states with j = 5/2. (c) Construct |3/2, 3/2i state by requiring it to be orthogonal to |5/2, 3/2i, and be normalized. (d) Beginning with |3/2, 3/2i use the lowering operator to build three other states with j = 3/2. ...