digestion of carbohydrates - KSU Faculty Member websites
... 1F Active transport : galactose and glucose are transported into the mucosal cells by an active , **** requiring that involves a specific transport protein ( carrier ) and requires a concurrent uptake of sodium ions . The carrier binds glucose and sodium at separate sites and transports them through ...
... 1F Active transport : galactose and glucose are transported into the mucosal cells by an active , **** requiring that involves a specific transport protein ( carrier ) and requires a concurrent uptake of sodium ions . The carrier binds glucose and sodium at separate sites and transports them through ...
Molecular basis of G6PD deficiency
... stress require glutathione and the products of the G6PD oxidative shunt for optimal growth. Not unlike the sickle cell trait which utilises an independent mechanism of protection against malaria, G6PD deficiency creates an inhospitable environment for the malarial parasites and discourage lodging o ...
... stress require glutathione and the products of the G6PD oxidative shunt for optimal growth. Not unlike the sickle cell trait which utilises an independent mechanism of protection against malaria, G6PD deficiency creates an inhospitable environment for the malarial parasites and discourage lodging o ...
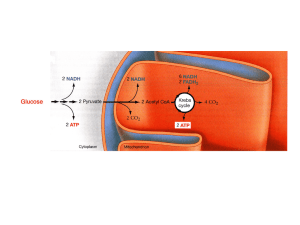
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... evolved much later, after the appearance of cyanobacteria. The metabolic activities of cyanobacteria account for the rise of oxygen levels in the earth’s atmosphere, a dramatic turning point in evolutionary history. We consider first the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl groups, then the entry of tho ...
... evolved much later, after the appearance of cyanobacteria. The metabolic activities of cyanobacteria account for the rise of oxygen levels in the earth’s atmosphere, a dramatic turning point in evolutionary history. We consider first the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl groups, then the entry of tho ...
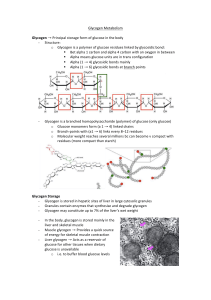
Glycogen!Metabolism! ! Glycogen$→!Principal!storage!form!of
... o AMP!(present!significantly!when!ATP!is!depleted)!activates!glycogen! phosphorylase!(R!conformation!enhanced)!and!glycogen!breakdown!is! activated!bc!more!energy!is!needed! o ATP!and!G6P!inhibit!glycogen!phosphorylase!(enhance!the!T!conformation)! ! ∴!glycogen!breakdown!is!inhibited!when!ATP!and!gl ...
... o AMP!(present!significantly!when!ATP!is!depleted)!activates!glycogen! phosphorylase!(R!conformation!enhanced)!and!glycogen!breakdown!is! activated!bc!more!energy!is!needed! o ATP!and!G6P!inhibit!glycogen!phosphorylase!(enhance!the!T!conformation)! ! ∴!glycogen!breakdown!is!inhibited!when!ATP!and!gl ...
Review Report
... If I understood the paper correctly, the hypothesis is that there were ancestral RNA molecules that both bound amino acids and catalyzed peptide bond formation, but only for what the author calls “bulky” amino acids. Preceding this combined role, the original RNA-AA binding may have been to increase ...
... If I understood the paper correctly, the hypothesis is that there were ancestral RNA molecules that both bound amino acids and catalyzed peptide bond formation, but only for what the author calls “bulky” amino acids. Preceding this combined role, the original RNA-AA binding may have been to increase ...
Improving penicillin biosynthesis in Penicillium chrysogenum
... DS17690 (Harris et al., 2006) was used as a high PEN production strain of P. chrysogenum. Sporulation of mycelia was stimulated by growth on R agar (Bartoszewska et al., 2011) at 25 1C for 10–11 days. For production of PEN V, spores were inoculated in 50 ml PEN production medium (Nijland et al., 201 ...
... DS17690 (Harris et al., 2006) was used as a high PEN production strain of P. chrysogenum. Sporulation of mycelia was stimulated by growth on R agar (Bartoszewska et al., 2011) at 25 1C for 10–11 days. For production of PEN V, spores were inoculated in 50 ml PEN production medium (Nijland et al., 201 ...
Enhancement of the Essential Amino Acid Composition of Food
... the flow of carbon intermediary compounds through glycolysis and citric acid cycle is regulated at the enzyme level by feedback substrate inhibition specific to the enzyme. On the other hand, reaction steps with near zero free energy changes catalyzed especially by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydro ...
... the flow of carbon intermediary compounds through glycolysis and citric acid cycle is regulated at the enzyme level by feedback substrate inhibition specific to the enzyme. On the other hand, reaction steps with near zero free energy changes catalyzed especially by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydro ...
Chapter 3
... • Others can be converted to metabolic intermediates – Contribute as a fuel in muscle • Overall, protein is not a primary energy source during exercise ...
... • Others can be converted to metabolic intermediates – Contribute as a fuel in muscle • Overall, protein is not a primary energy source during exercise ...
File
... In order to raise the temperature of water, the average molecular speed has to increase. It takes much more energy to raise the temperature of water compared to other solvents because hydrogen bonds hold the water molecules together! Water has a high heat capacity. “The specific heat is the amou ...
... In order to raise the temperature of water, the average molecular speed has to increase. It takes much more energy to raise the temperature of water compared to other solvents because hydrogen bonds hold the water molecules together! Water has a high heat capacity. “The specific heat is the amou ...
Mistranslation and its control by tRNA synthetases
... specificity, because of the subtle variations in the substrate recognition site created by the statistical ensemble of sequences, an enzymatic activity associated with a statistical protein could act on a variety of closely similar substrates. In addition, statistical proteins can explore a larger a ...
... specificity, because of the subtle variations in the substrate recognition site created by the statistical ensemble of sequences, an enzymatic activity associated with a statistical protein could act on a variety of closely similar substrates. In addition, statistical proteins can explore a larger a ...
Biochemical and genetic analysis of leucine-, isoleucine
... lyzes the first specific step in the biosynthesis of isoleucine, was one of the first examples of feed-back inhibition to . be analyzed directly at the enzyme level. ...
... lyzes the first specific step in the biosynthesis of isoleucine, was one of the first examples of feed-back inhibition to . be analyzed directly at the enzyme level. ...
The Science of Onion Flavor Onions are one of the most widely used
... meaty sensation. Fairly recent research (J Agric. Food Chem. 2004; 52: 27972802) has shown that heating the tear-producing compound PSO converts it to a new sulfur-containing compound called 3-mercapto-2-methylpentan-1-ol, or MMP for short. MMP tastes like meat broth. Chopping onions in a food proce ...
... meaty sensation. Fairly recent research (J Agric. Food Chem. 2004; 52: 27972802) has shown that heating the tear-producing compound PSO converts it to a new sulfur-containing compound called 3-mercapto-2-methylpentan-1-ol, or MMP for short. MMP tastes like meat broth. Chopping onions in a food proce ...
Diversity in P-loop Structure of A-ATP Synthase
... A-, F-ATP synthases and V-ATPases are fascinating enzymes, which arose from a common ancestor and are present in every life form. They are essential for life and are known as the coupling factors which convert the electrochemical ion gradient across the membrane to the synthesis of adenosine triphos ...
... A-, F-ATP synthases and V-ATPases are fascinating enzymes, which arose from a common ancestor and are present in every life form. They are essential for life and are known as the coupling factors which convert the electrochemical ion gradient across the membrane to the synthesis of adenosine triphos ...
Practice Problems on Amino Acids and Peptides
... Biological molecules often have phosphate or pyrophosphate monoester groups. Which one of the following statements regarding this is least correct? A) The phosphate or pyrophosphate provides a handle for electrostatic binding of the molecule by an enzyme B) Phosphates or pyrophosphates will accept h ...
... Biological molecules often have phosphate or pyrophosphate monoester groups. Which one of the following statements regarding this is least correct? A) The phosphate or pyrophosphate provides a handle for electrostatic binding of the molecule by an enzyme B) Phosphates or pyrophosphates will accept h ...
Substrate Specificity and Mechanism from the Structure of
... interactions made by galactose in Pf GalK are similar to those made by galactose in L. lactis GalK.21 Comparison with other GHMP kinase family members The overall structure of GalK is very similar to the structures of the other GHMP kinase superfamily that have been solved to date, even though overa ...
... interactions made by galactose in Pf GalK are similar to those made by galactose in L. lactis GalK.21 Comparison with other GHMP kinase family members The overall structure of GalK is very similar to the structures of the other GHMP kinase superfamily that have been solved to date, even though overa ...
Properties of ATP - BioWiki
... (along with Pi). These constituents are readily interconvertible. We actually break down an amount of ATP each day equal to about our body weight. Likewise we make about the same amount from the turnover products. When energy is needed, carbohydrates and lipids are oxidized and ATP is produced, whic ...
... (along with Pi). These constituents are readily interconvertible. We actually break down an amount of ATP each day equal to about our body weight. Likewise we make about the same amount from the turnover products. When energy is needed, carbohydrates and lipids are oxidized and ATP is produced, whic ...
Eram_SeyedMohammad - UWSpace
... active catalytic (large) subunit was responsible for both synthase and decarboxylase activities, which were 134±30 and 16.7±3.4 Umg-1, respectively. The activity had an optimal pH of 7.0 and an optimal temperature of 85°C for both activities, and was stable at 80°C (t1/2≥ 24 hours). The enzyme conta ...
... active catalytic (large) subunit was responsible for both synthase and decarboxylase activities, which were 134±30 and 16.7±3.4 Umg-1, respectively. The activity had an optimal pH of 7.0 and an optimal temperature of 85°C for both activities, and was stable at 80°C (t1/2≥ 24 hours). The enzyme conta ...
TCA Cycle - eCurriculum
... Catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase, enzyme directly linked to the electron transport chain. )G 0 ’= 0. Uses FAD because the free energy change is not enough to generate NADH. 7) fumarate + H2O ↔ malate Catalyzed by fumarase. )G 0 ’= 0. 8) malate + NAD + ↔ oxaloacetate + NADH Catalyzed ...
... Catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase, enzyme directly linked to the electron transport chain. )G 0 ’= 0. Uses FAD because the free energy change is not enough to generate NADH. 7) fumarate + H2O ↔ malate Catalyzed by fumarase. )G 0 ’= 0. 8) malate + NAD + ↔ oxaloacetate + NADH Catalyzed ...
File
... 26) Cows can derive nutrients from cellulose because A) they produce the enzymes that break down cellulose. B) they chew their food so thoroughly that cellulose fibers are broken down. C) their intestinal tract contains cellulose-hydrolyzing microorganisms. D) they convert cellulose into starch, whi ...
... 26) Cows can derive nutrients from cellulose because A) they produce the enzymes that break down cellulose. B) they chew their food so thoroughly that cellulose fibers are broken down. C) their intestinal tract contains cellulose-hydrolyzing microorganisms. D) they convert cellulose into starch, whi ...
bio- chemistry
... That is why blood samples are taken at pathology labs to determine the amount of vitamins or cell counts in our bodies. Clinical biochemistry uses biochemical methods to study diseases using body fluids such as urine, blood samples, etc. Biochemistry is focused on learning such dynamic cycles and th ...
... That is why blood samples are taken at pathology labs to determine the amount of vitamins or cell counts in our bodies. Clinical biochemistry uses biochemical methods to study diseases using body fluids such as urine, blood samples, etc. Biochemistry is focused on learning such dynamic cycles and th ...
CHARACTERIZATION OF B-LACTAMASES FROM TWO B
... The results showed in Fig. 1 (a,b) revealed that 80% saturation of ammonium sulphate gave maximal value of protein and p-lactamase activity in the two studied P.aeruginosa isolates (Z 33 and Z 90), where the maximum P-lactamase activities were 5.8 and 2.9 u mol/min/ml for the two isolates, respecti ...
... The results showed in Fig. 1 (a,b) revealed that 80% saturation of ammonium sulphate gave maximal value of protein and p-lactamase activity in the two studied P.aeruginosa isolates (Z 33 and Z 90), where the maximum P-lactamase activities were 5.8 and 2.9 u mol/min/ml for the two isolates, respecti ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.