bio- chemistry
... That is why blood samples are taken at pathology labs to determine the amount of vitamins or cell counts in our bodies. Clinical biochemistry uses biochemical methods to study diseases using body fluids such as urine, blood samples, etc. Biochemistry is focused on learning such dynamic cycles and th ...
... That is why blood samples are taken at pathology labs to determine the amount of vitamins or cell counts in our bodies. Clinical biochemistry uses biochemical methods to study diseases using body fluids such as urine, blood samples, etc. Biochemistry is focused on learning such dynamic cycles and th ...
Supporting Information - Royal Society of Chemistry
... For determining the Ki values of complexes 2-4, the concentrations of different compounds required to achieve about 50% inhibition of the enzyme (2.5 M) in the presence of 75 M substrate (p-nitrophenyl acetate) were first determined (25 mM HEPES buffer, pH = 7.0; absorbance followed at 450 nm). Th ...
... For determining the Ki values of complexes 2-4, the concentrations of different compounds required to achieve about 50% inhibition of the enzyme (2.5 M) in the presence of 75 M substrate (p-nitrophenyl acetate) were first determined (25 mM HEPES buffer, pH = 7.0; absorbance followed at 450 nm). Th ...
Chapter 18 Homework Assignment Chapter 18 Amino Acid
... These and other proteases are activated and digest most proteins to free amino acids (some fibrous proteins like keratin are resistant) ...
... These and other proteases are activated and digest most proteins to free amino acids (some fibrous proteins like keratin are resistant) ...
glucose-6-P - WordPress.com
... normal conditions, and so acts at a constant rate to provide glucose 6-phosphate to meet the cell's need. Liver cells also contain an isoenzyme of hexokinase, glucokinase, which has a Km very much higher than the normal intracellular concentration of glucose. The function of glucokinase in the liver ...
... normal conditions, and so acts at a constant rate to provide glucose 6-phosphate to meet the cell's need. Liver cells also contain an isoenzyme of hexokinase, glucokinase, which has a Km very much higher than the normal intracellular concentration of glucose. The function of glucokinase in the liver ...
questions for self-preparation GENERAL CHARACTERISTIC OF
... carrying out biological transformations. The microbic transformations called by also microbiological transformations are possible to carry out by means of growing or not growing or even the dried-up cells, and also dispute. The essence of such transformations is to turn one substance into another, r ...
... carrying out biological transformations. The microbic transformations called by also microbiological transformations are possible to carry out by means of growing or not growing or even the dried-up cells, and also dispute. The essence of such transformations is to turn one substance into another, r ...
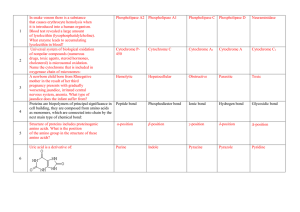
Beverage Treatment Products Technical Data Sheet Pure
... For more information, please email us at [email protected] or visit www.eaton.com/filtration © 2015 Eaton. All rights reserved. All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. All information and recommendations appearing in this brochure concerning the use o ...
... For more information, please email us at [email protected] or visit www.eaton.com/filtration © 2015 Eaton. All rights reserved. All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. All information and recommendations appearing in this brochure concerning the use o ...
respiration revision quiz
... In the reactions of respiration, coenzymes become …………………. as substrates become …………………….. . These are necessary because the reactions are catalysed by inefficient dehydrogenase ………………… . Hydrogen ATO ...
... In the reactions of respiration, coenzymes become …………………. as substrates become …………………….. . These are necessary because the reactions are catalysed by inefficient dehydrogenase ………………… . Hydrogen ATO ...
... primary structure of TAP the loops before and after the ~-sheets differ extensively in conformation from the prototype BPTI-fold (Antuch eI a/. 1994). It was show n that TAP is a tight-binding competitive inhibitor of fXa that binds to fXa via a two-step mechanism that involves a secondary binding-s ...
What is respiration?
... by yeast, without understanding that glycolysis was involved. In the second half of the nineteenth century, scientists investigated the mechanism. Pasteur established that alcoholic fermentation is caused by microorganisms. Buchner showed that extracts from yeast cells could also cause fermentation. ...
... by yeast, without understanding that glycolysis was involved. In the second half of the nineteenth century, scientists investigated the mechanism. Pasteur established that alcoholic fermentation is caused by microorganisms. Buchner showed that extracts from yeast cells could also cause fermentation. ...
Student Book (Unit 1 Module 4) - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... by yeast, without understanding that glycolysis was involved. In the second half of the nineteenth century, scientists investigated the mechanism. Pasteur established that alcoholic fermentation is caused by microorganisms. Buchner showed that extracts from yeast cells could also cause fermentation. ...
... by yeast, without understanding that glycolysis was involved. In the second half of the nineteenth century, scientists investigated the mechanism. Pasteur established that alcoholic fermentation is caused by microorganisms. Buchner showed that extracts from yeast cells could also cause fermentation. ...
... The interaction that is being disrupted by the salt is electrostatic, positively charged Lys and/or Arg residues on the protein are interacting with negatively charged phosphate groups on the DNA ( 3 1/2 pts). The protein still binds with high salt, so there must be additional interactions, i.e. hyd ...
Ethylene
... layer induces cells to produce enzymes that digest the cellulose and other components of cell walls ...
... layer induces cells to produce enzymes that digest the cellulose and other components of cell walls ...
Understanding fatty acid synthesis in developing - Shachar
... been shown to have a critical role in fatty acid synthesis since it maintains optimal rates of fatty acid synthesis on isolated plastids (Fuhrmann et al., 1994; Möhlmann et al., 1994; Qi et al., 1994). Besides ATP, fatty acids synthesis also requires large amounts of reducing equivalents in the for ...
... been shown to have a critical role in fatty acid synthesis since it maintains optimal rates of fatty acid synthesis on isolated plastids (Fuhrmann et al., 1994; Möhlmann et al., 1994; Qi et al., 1994). Besides ATP, fatty acids synthesis also requires large amounts of reducing equivalents in the for ...
Steady sucrose degradation is a prerequisite for
... and 380 mM acetaldehyde (Kogawara et al. 2006). The reactions were started by the addition of acetaldehyde. All reactions were performed at 30 °C. Enzyme activities were calculated from NADP reduction or NADH oxidation, monitored as the change in absorbance at 340 nm on a spectrophotometer (MPS-2450 ...
... and 380 mM acetaldehyde (Kogawara et al. 2006). The reactions were started by the addition of acetaldehyde. All reactions were performed at 30 °C. Enzyme activities were calculated from NADP reduction or NADH oxidation, monitored as the change in absorbance at 340 nm on a spectrophotometer (MPS-2450 ...
Sample Chapter 5: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... that protein. The ability of each type of the tens of thousands of different proteins to perform its functions is specified by its unique amino acid sequence. During synthesis each polypeptide molecule bends in three-dimensional space as its amino acid components (called amino acid residues) interac ...
... that protein. The ability of each type of the tens of thousands of different proteins to perform its functions is specified by its unique amino acid sequence. During synthesis each polypeptide molecule bends in three-dimensional space as its amino acid components (called amino acid residues) interac ...
Inhibitors are structural analogs of true substrate
... In cases of chronic pancreatitis a decrease of trypsin Cleavage of production and secretion is observed. Digestion and proteins absorption of what substances is injured in this case? After the addition of an extract of pancreatic gland to the tube with starch solution, a blue coloration of the sampl ...
... In cases of chronic pancreatitis a decrease of trypsin Cleavage of production and secretion is observed. Digestion and proteins absorption of what substances is injured in this case? After the addition of an extract of pancreatic gland to the tube with starch solution, a blue coloration of the sampl ...
"Fermentation Pathways". In: Microbial Physiology (Fourth Edition)
... ethanol in the presence of NADH and serves to maintain the redox balance of glucose fermentation occurring in the cytoplasm of yeast cells. During ethanol oxidation, ADH2 catalyzes the formation of acetaldehyde. Oxidative utilization of ethanol in the mitochondrion involves ADH3. The inner mitochond ...
... ethanol in the presence of NADH and serves to maintain the redox balance of glucose fermentation occurring in the cytoplasm of yeast cells. During ethanol oxidation, ADH2 catalyzes the formation of acetaldehyde. Oxidative utilization of ethanol in the mitochondrion involves ADH3. The inner mitochond ...
View/Open
... Metabolism can be defined as the sum total of all chemical transformations that occur in cells (Stanier, Adelberg & Ingraham 1980). Fermentation is a metabolic process in which carbohydrates and related compounds are oxidised with the release of energy in the absence of any external electron accepto ...
... Metabolism can be defined as the sum total of all chemical transformations that occur in cells (Stanier, Adelberg & Ingraham 1980). Fermentation is a metabolic process in which carbohydrates and related compounds are oxidised with the release of energy in the absence of any external electron accepto ...
Respiratio
... Ans: 1. Fermentation is a chemical change brought about in an organic substrate due to enzyme activity of microorganisms. ...
... Ans: 1. Fermentation is a chemical change brought about in an organic substrate due to enzyme activity of microorganisms. ...
Phosphorylation - Biology Junction
... RESPIRATION = making ATP (& some heat) by burning fuels in many small steps ATP ...
... RESPIRATION = making ATP (& some heat) by burning fuels in many small steps ATP ...
A Metabolic Node in Action: Chorismate
... and is retro-inhibited by Tyr (45% for the CM and 95% for the dehydrogenase activity).44,45 It is now evident that the mutase and the dehydrogenase active sites are distinct, but display some similar chemical properties.46-50 Kinetic studies have shown that Tyr binds twice at distinct allosteric sit ...
... and is retro-inhibited by Tyr (45% for the CM and 95% for the dehydrogenase activity).44,45 It is now evident that the mutase and the dehydrogenase active sites are distinct, but display some similar chemical properties.46-50 Kinetic studies have shown that Tyr binds twice at distinct allosteric sit ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.