* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry - Brookwood High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
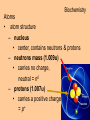
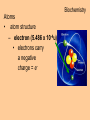
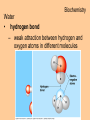
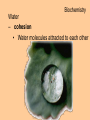
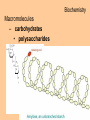
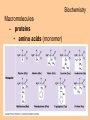
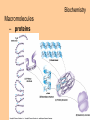
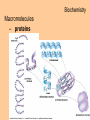
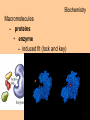
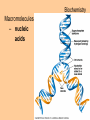
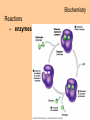
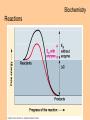
Biochemistry Biochemistry Essential Question What is it that makes up an atom? 10.8.2007 Biochemistry Matter • Properties – physical property • description of shape, mass, volume • melting point, boiling point – chemical property • structure of molecules which make up substance • how substance reacts with another Biochemistry Matter • Elements – element • a substance that can not be broken down into a simpler substance – 25 elements are essential to life • CHNOPS – 6 greatest Biochemistry Matter • atom – smallest particle of an element that has the characteristics of that element Biochemistry Atoms • atom structure – nucleus • center, contains neutrons & protons – neutrons mass (1.009u) • carries no charge, neutral = n0 – protons (1.007u) • carries a positive charge = p+ Biochemistry Atoms • atom structure – electron (5.486 x 10-4u) • electrons carry a negative charge = e- Biochemistry Atoms • atom structure – electron • electrons orbit nucleus in separate energy levels or clouds Biochemistry Atoms Biochemistry Atoms • periodic table – atomic number • number of protons – atomic mass • total mass of protons, neutrons, & electrons – atomic symbol • 1or 2 letter symbol symbol for element Biochemistry Essential Question How are covalent and ionic bonds different? What is an example of each? 10.9.2007 Biochemistry chemical bonds • chemical bond – two or more atoms chemically bonded together ex: oxygen gas, water, glucose • molecular formula – uses atomic symbols to represent atoms bound together in a compound ex: O2, H2O, C6H12O6 Biochemistry chemical bonds • covalent bond – atoms share electrons ex: water, sugars, proteins • ionic bond – attractive force between ions of opposite charge Biochemistry chemical bonds covalent bond ionic bond Biochemistry Essential Question What ions are released by an acid in water? By a base? 10.10.2007 Biochemistry Mixtures and solutions • mixture – combination of substances in which individuals retain individual properties ex: mixed sugar and sand, oil and water • solution – mixture of one or more solutes are evenly distributed in a solvent ex: salt in water Biochemistry Mixtures and solutions • solution – solute • substance which dissolves ex: sugar – solvent • holds dissolved substance ex: water – the greater the solute = greater the concentration Biochemistry Acids and bases • pH – • measure of how acidic or basic a solution is acid – – • forms hydrogen ions (H+) in water pH below 7 base – – forms hydroxide ions (OH-) in water pH above 7 Biochemistry Acids and bases Biochemistry Water • polar molecule – molecule with uneven distribution of charge – water is polar, O atom pulls e-’s from H atoms Biochemistry Water • hydrogen bond – weak attraction between hydrogen and oxygen atoms in different molecules Biochemistry Water • properties of water – water resists temperature change – water expands when it freezes – cohesion • water molecules attracted to each other – adhesion • water molecules attracted to sides of container Biochemistry Water • properties of water – water resists temperature change Biochemistry Water • properties of water – water expands when it freezes Biochemistry Water – cohesion • Water molecules attracted to each other Biochemistry Water – adhesion • Water molecules attracted to sides of container Biochemistry More compounds – isomer • compounds with same number elements but different structure Biochemistry More compounds – monomer • Small molecule that can be bound to other monomers to form polymers – polymer • larger molecule formed from smaller subunits Biochemistry More compounds – monomer • Small molecule that can be bound to other monomers to form polymers – polymer • larger molecule formed from smaller subunits Biochemistry More compounds – polymer • larger molecule formed from smaller subunits Biochemistry More compounds – polymer Biochemistry Macromolecules – carbohydrates • used by cells to store and release energy • 1:2:1 C:H:O ex: glucose C6H12O6 Biochemistry Macromolecules – carbohydrates • monomer → polymer monosaccharide glucose, fructose disaccharide polysaccharide sucrose cellulose, glycogen Biochemistry Macromolecules – carbohydrates • monomer → polymer monosaccharide glucose, fructose disaccharide polysaccharide monomer sucrose cellulose, glycogen polymer Biochemistry Macromolecules – carbohydrates • monosaccharides Biochemistry Macromolecules – carbohydrates • disaccharides Biochemistry Macromolecules – carbohydrates • polysaccharides verbascose Biochemistry Essential Question What are the components of a lipid and of a protein? 10.17.2007 Biochemistry Macromolecules – lipids • used for energy storage, insulation, protection ex fats, waxes and oils • nonpolar, does not dissolve in water • contains CHO Biochemistry Macromolecules – lipids • glycerol head • 3 fatty acid tails Biochemistry Macromolecules – lipids • glycerol head • 3 fatty acid tails Biochemistry Macromolecules – lipids • large proportion of C–H bonds – saturated fats » C atoms in tail all have single (C–C) bonds – unsaturated fats » C at least 1 double bond (C=C) in tail Biochemistry Macromolecules – lipids Biochemistry Macromolecules – Proteins • used for growth, maintenance, and repair • used as structure for tissues and organs • contain CHON Biochemistry Macromolecules – proteins • polymer of amino acids – formed using peptide bonds (covalent bond) Biochemistry Macromolecules – proteins • amino acids (monomer) Biochemistry Macromolecules – proteins • peptide bonds – bond between amino acids Biochemistry Macromolecules – proteins Biochemistry Macromolecules – proteins Biochemistry Macromolecules – proteins • enzyme – increase rate of metabolic reactions – induced fit (lock and key) mechanism Biochemistry Macromolecules – proteins • enzyme – induced fit (lock and key) Biochemistry Macromolecules – nucleic acids • stores cellular information • polymer of nucleotides • contains CHONP Biochemistry Macromolecules – nucleic acids • DNA – genetic information for whole cell • RNA – copies DNA to form protein Biochemistry Macromolecules – nucleic acids • polymer of nucleotides Biochemistry Macromolecules – nucleic acids Biochemistry Reactions – chemical equations • 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O Biochemistry Reactions – chemical equations • 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O products reactantants Biochemistry Reactions – chemical equations • 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O • # of atoms on each side of reaction must be balanced • coefficients must be balanced __ C6H12O6 → C12H22O11 + H2O Biochemistry Reactions – chemical equations • dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction) – two subunits make polymer – water is released 2C6H12O6 → C12H22O11 + H2O Biochemistry Reactions – chemical equations • dehydration synthesis Biochemistry Reactions – chemical equations • hydrolysis – H2O splits bond – two subunits created – C12H22O11 + H2O → 2C6H12O6 Biochemistry Reactions – chemical equations • hydrolysis Biochemistry Reactions – enzymes • lowers activation energy • acts as catalysts, speeds up rate of reaction • induced fit model (lock and key) Biochemistry Reactions – enzymes • substrate – changed after released by enzyme • enzyme – active site » where substrate binds to enzyme » can be used over and over Biochemistry Reactions – enzymes Biochemistry Reactions – enzymes