Text S1.
... The endpoint of adaptive evolution as characterized above was compared to optimal behavior predicted by performing FBA on our genome-scale model. During the very first simulations, however, we noticed that very high biomass yields could be obtained, with concomitant production of only CO2 and water ...
... The endpoint of adaptive evolution as characterized above was compared to optimal behavior predicted by performing FBA on our genome-scale model. During the very first simulations, however, we noticed that very high biomass yields could be obtained, with concomitant production of only CO2 and water ...
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
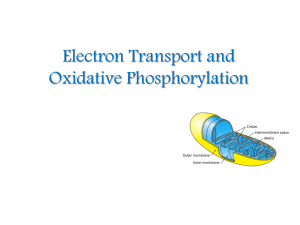
... liberated, which can be used to generate ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation is the process in which ATP is formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 by a series of electron carriers. ...
... liberated, which can be used to generate ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation is the process in which ATP is formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 by a series of electron carriers. ...
04. Introduction to metabolism
... Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled directly to ATP synthesis. ...
... Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled directly to ATP synthesis. ...
Name
... CO2= (1 pyruvate dehydrogenase + 2 TCA) = 3 CO2 Total ATP Produced following electron transport by all of the above mitochondrial reactions:___1+12+2=15ATP 2) Draw a diagram that shows with names or numbers the specific enzymes and pathways that feed electrons from FADH2 into electron transport and ...
... CO2= (1 pyruvate dehydrogenase + 2 TCA) = 3 CO2 Total ATP Produced following electron transport by all of the above mitochondrial reactions:___1+12+2=15ATP 2) Draw a diagram that shows with names or numbers the specific enzymes and pathways that feed electrons from FADH2 into electron transport and ...
Citric Acid Cycle - University of California, Berkeley
... Oxaloacetate + Acetyl-CoA + H2O Citrate + CoA Mechanism. Claisen condensation reaction from organic chemistry, where thioester is combined with ketone. Methyl carbon of acetylCoA attack the electron poor ketone carbon of oxaloacetate. You have to abstract a proton, so you produce a carbanion here. ...
... Oxaloacetate + Acetyl-CoA + H2O Citrate + CoA Mechanism. Claisen condensation reaction from organic chemistry, where thioester is combined with ketone. Methyl carbon of acetylCoA attack the electron poor ketone carbon of oxaloacetate. You have to abstract a proton, so you produce a carbanion here. ...
LECTURE #1 STUDY GUIDE
... Complete the following chemical equation: NADH + H+ + 3ADP + 3 P + 1/2 O2 –––––––> ...
... Complete the following chemical equation: NADH + H+ + 3ADP + 3 P + 1/2 O2 –––––––> ...
Kreb Cycle
... of the intermediate products and the number of carbons in each. Where do these carbons come from/go when they are gained/lost? (15 points) 3. Which steps generate energy? How is ATP formed during these steps? How much total energy is generated by the cycle? (10 points) 4. Which steps generate electr ...
... of the intermediate products and the number of carbons in each. Where do these carbons come from/go when they are gained/lost? (15 points) 3. Which steps generate energy? How is ATP formed during these steps? How much total energy is generated by the cycle? (10 points) 4. Which steps generate electr ...
Exam 3
... Section 3. Problems. 4 questions 10 points each. 31. (10pts) A molecule of glucose stored in glycogen can be catabolized to two molecules of lactate under anaerobic conditions in muscle. Fill in each box with the name or structure of the intermediates along this pathway. Then indicate every step th ...
... Section 3. Problems. 4 questions 10 points each. 31. (10pts) A molecule of glucose stored in glycogen can be catabolized to two molecules of lactate under anaerobic conditions in muscle. Fill in each box with the name or structure of the intermediates along this pathway. Then indicate every step th ...
BIo Exam Trashketball Review Questions
... Milk is converted to yogurt under certain conditions when the microorganisms in the milk produce acid. Which of these processes would you expect to be key in the production of yogurt? a) b) c) d) ...
... Milk is converted to yogurt under certain conditions when the microorganisms in the milk produce acid. Which of these processes would you expect to be key in the production of yogurt? a) b) c) d) ...
Bacterial Metabolism and Growth
... – pyruvate cannot enter directly into the TCA cycle – 1 NADH is produced for every pyruvate – 1 molecule of CO2 is release for every pyruvate ...
... – pyruvate cannot enter directly into the TCA cycle – 1 NADH is produced for every pyruvate – 1 molecule of CO2 is release for every pyruvate ...
Chapter 13 - TCA Cycle
... The citric acid cycle, aka the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), or the Krebs cycle: Series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy. It works by the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into CO2 and G in the form of ATP. The cycle also provi ...
... The citric acid cycle, aka the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), or the Krebs cycle: Series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy. It works by the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into CO2 and G in the form of ATP. The cycle also provi ...
BIS103-002 (Spring 2008) - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... h) Two reactions in glycolysis and one reaction of the TCA cycle generate ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. The way ATP is produced in the TCA cycle by substrate-level phosphorylation is conceptually very similar to one of the two ATP-generating reactions in glycolysis. Briefly describe the co ...
... h) Two reactions in glycolysis and one reaction of the TCA cycle generate ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. The way ATP is produced in the TCA cycle by substrate-level phosphorylation is conceptually very similar to one of the two ATP-generating reactions in glycolysis. Briefly describe the co ...
respiration 4 - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... – It’s a cycle! Regeneration of OAA in mt keeps acetyl CoA incorporation high – The products of the cycle enter gluconeogenesis to generate sucrose in the __________ – Glycerol from triglyceride also enters gluconeogenesis for sucrose biosynthesis – NADH enters oxidative phosphorylation ...
... – It’s a cycle! Regeneration of OAA in mt keeps acetyl CoA incorporation high – The products of the cycle enter gluconeogenesis to generate sucrose in the __________ – Glycerol from triglyceride also enters gluconeogenesis for sucrose biosynthesis – NADH enters oxidative phosphorylation ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... G6P can be converted to glucose by glucose-6phosphatase (transport via bloodstream to the peripheral organs) G6P can be converted to glycogen – when body’s demand for glucose is low G6P can be converted to acetyl-CoA via glycolysis and action of pyruvate dehydrogenase (this glucosederived acetyl-CoA ...
... G6P can be converted to glucose by glucose-6phosphatase (transport via bloodstream to the peripheral organs) G6P can be converted to glycogen – when body’s demand for glucose is low G6P can be converted to acetyl-CoA via glycolysis and action of pyruvate dehydrogenase (this glucosederived acetyl-CoA ...
CHM 365 Name: Exam 3 Do all of the following 21 questions
... e) absolute requirement for ATP hydrolysis, no other energy source will work. ...
... e) absolute requirement for ATP hydrolysis, no other energy source will work. ...
objectives - WordPress.com
... atoms produced during stage 2 are carried by coenzymes to cristae of mitochondria ...
... atoms produced during stage 2 are carried by coenzymes to cristae of mitochondria ...
CLINICAL CASE (UREA CYCLE)
... Oral therapy was started by administering a combination of essential amino acids (including arginine) at a dose of 1.1g/kg/d. By the seventh day, his plasma NH4+ level was 40 uM, and he appeared clinically well. Learning objectives: Explain ...
... Oral therapy was started by administering a combination of essential amino acids (including arginine) at a dose of 1.1g/kg/d. By the seventh day, his plasma NH4+ level was 40 uM, and he appeared clinically well. Learning objectives: Explain ...
26_Test
... A mutase catalyzes a reaction in which a group is transferred from one part of the molecule to another part of the same molecule. ...
... A mutase catalyzes a reaction in which a group is transferred from one part of the molecule to another part of the same molecule. ...
Oxidation of Glucose
... penetrate mitochondria membrane , it can be used to produce energy (4 or , 6ATP) by respiratory chain phosphorylation in the mitochondria. ...
... penetrate mitochondria membrane , it can be used to produce energy (4 or , 6ATP) by respiratory chain phosphorylation in the mitochondria. ...
An outline of glycolysis. Each of the 10 steps shown is catalyzed by
... stage of the breakdown of food molecules. In these cells, pyruvate formed at the end of glycolysis is rapidly transported into the mitochondria, completely oxidized to CO2 and H20. But for many anaerobic organisms, which do not use molecular oxygen and can grow and divide in its absence, glycolysis ...
... stage of the breakdown of food molecules. In these cells, pyruvate formed at the end of glycolysis is rapidly transported into the mitochondria, completely oxidized to CO2 and H20. But for many anaerobic organisms, which do not use molecular oxygen and can grow and divide in its absence, glycolysis ...
I. Background - Berks Catholic
... The 4 c compound is oxidized by FAD to form FADH2 The 4 c compound is oxidized and NADH is formed If more acetyl CO A enters, citric acid is formed Reactants Acetyl CO A ADP NAD FAD Products – why is everything counted twice 2 ATP’s 2 FADH2 6 NADH’s 4 carbon dioxides ...
... The 4 c compound is oxidized by FAD to form FADH2 The 4 c compound is oxidized and NADH is formed If more acetyl CO A enters, citric acid is formed Reactants Acetyl CO A ADP NAD FAD Products – why is everything counted twice 2 ATP’s 2 FADH2 6 NADH’s 4 carbon dioxides ...
Chapter 9
... FORMATION OF ACETYL CO A Before the Krebs Cycle begins When oxygen is present, pyruvic acid is transported to the mitochondrion. Each pyruvic acid (a three-carbon molecule) is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (a two-carbon molecule) and CO2 is released: 2 Pyruvic acid + 2 Coenzyme A + 2 NAD+ --> 2 Ac ...
... FORMATION OF ACETYL CO A Before the Krebs Cycle begins When oxygen is present, pyruvic acid is transported to the mitochondrion. Each pyruvic acid (a three-carbon molecule) is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (a two-carbon molecule) and CO2 is released: 2 Pyruvic acid + 2 Coenzyme A + 2 NAD+ --> 2 Ac ...
Exam I Review - Iowa State University
... water into the matrix through the ATP synthase channel by osmosis, and the energy in this water flow is used to power ATP synthesis. *c. H+ movement down a concentration gradient from the intermembrane space into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase results in ATP synthesis d. All these sta ...
... water into the matrix through the ATP synthase channel by osmosis, and the energy in this water flow is used to power ATP synthesis. *c. H+ movement down a concentration gradient from the intermembrane space into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase results in ATP synthesis d. All these sta ...
AP Biology Midterm Studyguide 2017
... B. Establishment of chemical gradients/ATP production C. During which processes of photosynthesis/respiration is ATP produced? D. Anaerobic vs aerobic respiration E. Terms: G3P, lactate, Acetyl CoA, Citric Acid, NAD+, NADPH, RuBisCo…..(this is a sample) F. Enzymes! 1. be sure to understand the enzym ...
... B. Establishment of chemical gradients/ATP production C. During which processes of photosynthesis/respiration is ATP produced? D. Anaerobic vs aerobic respiration E. Terms: G3P, lactate, Acetyl CoA, Citric Acid, NAD+, NADPH, RuBisCo…..(this is a sample) F. Enzymes! 1. be sure to understand the enzym ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.