Document
... Glucose is broken down with or without oxygen in the cytoplasm into pyruvate One Glucose is cleaved into two pyruvate Produces little energy Two ATP and Two NADH produced ...
... Glucose is broken down with or without oxygen in the cytoplasm into pyruvate One Glucose is cleaved into two pyruvate Produces little energy Two ATP and Two NADH produced ...
Cellular Respiration PowerPoint
... In this case study, students learn about the function of cellular respiration and the electron transport chain and what happens when that function is impaired. Students play the role of medical examiner as they analyze the autopsy results to determine the cause of the mysterious deaths of these seve ...
... In this case study, students learn about the function of cellular respiration and the electron transport chain and what happens when that function is impaired. Students play the role of medical examiner as they analyze the autopsy results to determine the cause of the mysterious deaths of these seve ...
Cellular Respiration
... In this case study, students learn about the function of cellular respiration and the electron transport chain and what happens when that function is impaired. Students play the role of medical examiner as they analyze the autopsy results to determine the cause of the mysterious deaths of these seve ...
... In this case study, students learn about the function of cellular respiration and the electron transport chain and what happens when that function is impaired. Students play the role of medical examiner as they analyze the autopsy results to determine the cause of the mysterious deaths of these seve ...
Cellular Respiration
... In this case study, students learn about the function of cellular respiration and the electron transport chain and what happens when that function is impaired. Students play the role of medical examiner as they analyze the autopsy results to determine the cause of the mysterious deaths of these seve ...
... In this case study, students learn about the function of cellular respiration and the electron transport chain and what happens when that function is impaired. Students play the role of medical examiner as they analyze the autopsy results to determine the cause of the mysterious deaths of these seve ...
Chapter 7 Notes
... 1.) Glycolysis: sugar splitting phase (glucose is the sugar) 2.) Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Extracts the energy from glucose 3.) Electron Transport Chain/ATP Synthase: Turns the energy into ATP for the body to use *In total makes from 34 to 38 ATP** ...
... 1.) Glycolysis: sugar splitting phase (glucose is the sugar) 2.) Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Extracts the energy from glucose 3.) Electron Transport Chain/ATP Synthase: Turns the energy into ATP for the body to use *In total makes from 34 to 38 ATP** ...
Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism
... Respiration Maximum potential yield for aerobic glucose metabolism: 30-32 ATP synthesized from ADP H2O is a byproduct ...
... Respiration Maximum potential yield for aerobic glucose metabolism: 30-32 ATP synthesized from ADP H2O is a byproduct ...
Mock Exam 2 BY 123 – Dr. Biga Supplemental Instruction 1. Which
... A) Substrate level phosphorylation involves the transfer of a phosphate group directly from an organic molecule to ADP using an enzyme and oxidative phosphorylation uses chemiosmosis and ATP synthase B) Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in cellular respiration and substrate level phosphorylation ...
... A) Substrate level phosphorylation involves the transfer of a phosphate group directly from an organic molecule to ADP using an enzyme and oxidative phosphorylation uses chemiosmosis and ATP synthase B) Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in cellular respiration and substrate level phosphorylation ...
18 Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA to Krebs Cycle A/P
... b.) this is when the ATP is used as a substrate c.) this is when inorganic phosphate is added to ADP through ATP synthetase d.) this is when there is no phosphate available and the enzymes make some e.) none of the above are correct _____ 12.) In the Citric Acid Cycle- how many turns does it take to ...
... b.) this is when the ATP is used as a substrate c.) this is when inorganic phosphate is added to ADP through ATP synthetase d.) this is when there is no phosphate available and the enzymes make some e.) none of the above are correct _____ 12.) In the Citric Acid Cycle- how many turns does it take to ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide
... Carbohydrates, such as glucose, are energy-rich because when catabolized they can yield a large number of electrons per molecule. Glycolysis is a pathway that degrades glucose to pyruvic acid without requiring oxygen. Pyruvic acid is processed in aerobic respiration via the Krebs cycle and its assoc ...
... Carbohydrates, such as glucose, are energy-rich because when catabolized they can yield a large number of electrons per molecule. Glycolysis is a pathway that degrades glucose to pyruvic acid without requiring oxygen. Pyruvic acid is processed in aerobic respiration via the Krebs cycle and its assoc ...
1 Which of the following are the smallest cells? A) human ovum B
... phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP ...
... phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 6, Part 2 Notes – Aerobic Cellular
... membrane into the intermembrane space. 4. The last molecule to receive the electrons is oxygen gas (O 2). Oxygen gas combines with the electrons and H+ to form H2O, one of the products of aerobic cellular respiration. 5. H+ builds up in the intermembrane space and wants to flow back down its concent ...
... membrane into the intermembrane space. 4. The last molecule to receive the electrons is oxygen gas (O 2). Oxygen gas combines with the electrons and H+ to form H2O, one of the products of aerobic cellular respiration. 5. H+ builds up in the intermembrane space and wants to flow back down its concent ...
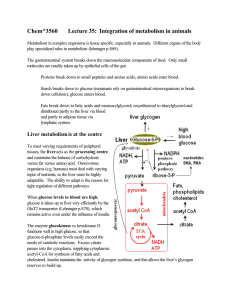
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... Repair enlarges and generates stronger muscles, and is the basis of body building. Because this involves very active protein degradation and resynthesis, qamino acids can be withdrawn from the muscle when other nutrients are in short supply. Brain and nervous system: use primarily aerobic glucose me ...
... Repair enlarges and generates stronger muscles, and is the basis of body building. Because this involves very active protein degradation and resynthesis, qamino acids can be withdrawn from the muscle when other nutrients are in short supply. Brain and nervous system: use primarily aerobic glucose me ...
APBioReview
... Non-germinating seeds are alive but dormant. To take CO2 out of the equation a CO2 absorbent was used (KOH) ...
... Non-germinating seeds are alive but dormant. To take CO2 out of the equation a CO2 absorbent was used (KOH) ...
Respiration
... • Less than 38 ATP (~30 in humans) • Most cells transfer electrons from cytosolic NADH to FADH2 in the mitochondrial matrix – Lose 2 ATP ...
... • Less than 38 ATP (~30 in humans) • Most cells transfer electrons from cytosolic NADH to FADH2 in the mitochondrial matrix – Lose 2 ATP ...
Chapter 7: Where it Starts – Photosynthesis
... - This type of photosystem uses ___________ photophosphorylation - ________ is split by _______ energy, and an e- enters the chlorophyll _____ - The chlorophyll’s original ____ is used to form ___________ - _______ is also formed; this is a much more __________ use of the energy (cyclic, light, wate ...
... - This type of photosystem uses ___________ photophosphorylation - ________ is split by _______ energy, and an e- enters the chlorophyll _____ - The chlorophyll’s original ____ is used to form ___________ - _______ is also formed; this is a much more __________ use of the energy (cyclic, light, wate ...
Metabolism Aerobic Respiration Other Ways of Generating ATP
... – Low energy yield – Acid production affects cell/body pH ...
... – Low energy yield – Acid production affects cell/body pH ...
energy2
... Usable energy is released as reactions break down carbon compounds, such as glucose. ...
... Usable energy is released as reactions break down carbon compounds, such as glucose. ...
Introduction to metabolism. Specific and general pathways of
... Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled directly to ATP synthesis. ...
... Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled directly to ATP synthesis. ...
Glucose Metabolism: Generating Energy in Life and Disease
... PFK1 (phosphofructokinase): activated by AMP (low energy state) ...
... PFK1 (phosphofructokinase): activated by AMP (low energy state) ...
Biochemistry Study Guide – Exam 1
... Peptide formation, peptide bond structure Protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quartenary ...
... Peptide formation, peptide bond structure Protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quartenary ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The electron transport "chain" is a series of electron carrying proteins in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. • These proteins transfer electrons from one to another, down the chain. • These electrons are added, along with some of the H+ protons, to oxygen, which is the final electron accept ...
... • The electron transport "chain" is a series of electron carrying proteins in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. • These proteins transfer electrons from one to another, down the chain. • These electrons are added, along with some of the H+ protons, to oxygen, which is the final electron accept ...
Aerobic Respiration
... energy whilst many are required for the release of energy from glucose. It releases energy in small amounts unlike ...
... energy whilst many are required for the release of energy from glucose. It releases energy in small amounts unlike ...
Major Metabolic Pathway
... produces ethanol when grown under anaerobic conditions. However, the major product is yeast cells when growth conditions are aerobic. More over, even under aerobic conditions at high glucose concentrations, some ethanol production is observed. Which indicates metabolic regulation not only by oxygen ...
... produces ethanol when grown under anaerobic conditions. However, the major product is yeast cells when growth conditions are aerobic. More over, even under aerobic conditions at high glucose concentrations, some ethanol production is observed. Which indicates metabolic regulation not only by oxygen ...
Unit7CellRespirationTargetPractice
... concentration of protons is _________________ in the intermembrane space than in the matrix of the mitochondria. The protons cannot freely _____________ across the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Protons move across the inner membrane via a large protein called _________________; the energy rele ...
... concentration of protons is _________________ in the intermembrane space than in the matrix of the mitochondria. The protons cannot freely _____________ across the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Protons move across the inner membrane via a large protein called _________________; the energy rele ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.