PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
... acid with methenamine. MANDELAMINE (Methenamine Mandelate Tablets U.S.P.) is available for oral use as film-coated tablets. Methenamine mandelate is readily absorbed but remains essentially inactive until it is excreted by the kidney and concentrated in the urine. An acid urine is essential for anti ...
... acid with methenamine. MANDELAMINE (Methenamine Mandelate Tablets U.S.P.) is available for oral use as film-coated tablets. Methenamine mandelate is readily absorbed but remains essentially inactive until it is excreted by the kidney and concentrated in the urine. An acid urine is essential for anti ...
University of Groningen Molecular basis of two novel
... strain CBS-3 is a homotrimer, of which each subunit folds into two domains. The Nterminal domain contains a 10-stranded β-sheet, forming two nearly perpendicular layers, which are flanked by α-helices (Figure 3A). The C-terminal domain is composed of three amphiphilic α-helices, and is primarily inv ...
... strain CBS-3 is a homotrimer, of which each subunit folds into two domains. The Nterminal domain contains a 10-stranded β-sheet, forming two nearly perpendicular layers, which are flanked by α-helices (Figure 3A). The C-terminal domain is composed of three amphiphilic α-helices, and is primarily inv ...
Genetic code as a harmonic system
... Figure 1 (left). The distribution of amino acids according to Gauss’ algorithm; (a) the distribution of amino acids has been derived from Table 1.1, by presenting two pairs here in one row as the “pair of pairs”. In the beginning of each row obtained in this way one “contact” amino acid has been as ...
... Figure 1 (left). The distribution of amino acids according to Gauss’ algorithm; (a) the distribution of amino acids has been derived from Table 1.1, by presenting two pairs here in one row as the “pair of pairs”. In the beginning of each row obtained in this way one “contact” amino acid has been as ...
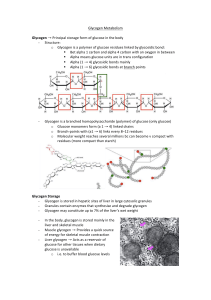
Glycogen!Metabolism! ! Glycogen$→!Principal!storage!form!of
... Fates$of$GlucoseI6IPhosphate$$ - In!skeletal!muscle!G6P!may!enter!glycolysis!and!serve!as!an!energy!source!! - In!liver!G6P!may!be!dephosphorylated!(to!glucose)!for!release!into!the!blood!to!be! transported! o Reaction!catalysed!by!Glucose=6=phosphatase! - Glucose=6=Phosphatase!catalyses!the!followi ...
... Fates$of$GlucoseI6IPhosphate$$ - In!skeletal!muscle!G6P!may!enter!glycolysis!and!serve!as!an!energy!source!! - In!liver!G6P!may!be!dephosphorylated!(to!glucose)!for!release!into!the!blood!to!be! transported! o Reaction!catalysed!by!Glucose=6=phosphatase! - Glucose=6=Phosphatase!catalyses!the!followi ...
Advantages of compound-specific stable isotope
... the root followed by the transport of released [15NH4]þ to the shoot would also lead to a relative enrichment of 13C in the root and therefore overestimate intact amino acid uptake in the root material (Fig. 1(C)). For glycine, there is yet a third mechanism through microbial metabolism via the glyc ...
... the root followed by the transport of released [15NH4]þ to the shoot would also lead to a relative enrichment of 13C in the root and therefore overestimate intact amino acid uptake in the root material (Fig. 1(C)). For glycine, there is yet a third mechanism through microbial metabolism via the glyc ...
Mitochondrial cytopathy in adults: What we know so far
... of a mitochondrial disease was in 1962, when Luft and colleagues reported a case of a 35-year-old euthyroid woman with myopathy, excessive perspiration, heat intolerance, polydipsia with polyuria, and a basal metabolic rate 180% of normal. 1 Study of her muscle cells revealed an increase in the numb ...
... of a mitochondrial disease was in 1962, when Luft and colleagues reported a case of a 35-year-old euthyroid woman with myopathy, excessive perspiration, heat intolerance, polydipsia with polyuria, and a basal metabolic rate 180% of normal. 1 Study of her muscle cells revealed an increase in the numb ...
falciparum - Griffith Research Online
... amino acids. We obtained a detailed substrate fingerprint for recombinant forms of the enzymes revealing that PfM1AAP exhibits a very broad substrate tolerance, capable of efficiently hydrolyzing neutral and basic amino acids, while PfM17LAP has narrower substrate specificity and preferentially clea ...
... amino acids. We obtained a detailed substrate fingerprint for recombinant forms of the enzymes revealing that PfM1AAP exhibits a very broad substrate tolerance, capable of efficiently hydrolyzing neutral and basic amino acids, while PfM17LAP has narrower substrate specificity and preferentially clea ...
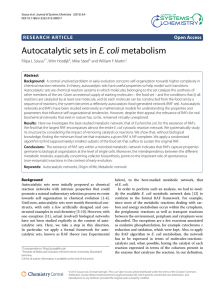
Autocatalytic sets in E. coli metabolism
... coli metabolic network, the following transformations of the metabolic network were performed: i) Transport reactions and reactions localized within the E. coli periplasm (except those involved in oxidative phosphorylation) are removed from the network, and the affected molecules are included in the ...
... coli metabolic network, the following transformations of the metabolic network were performed: i) Transport reactions and reactions localized within the E. coli periplasm (except those involved in oxidative phosphorylation) are removed from the network, and the affected molecules are included in the ...
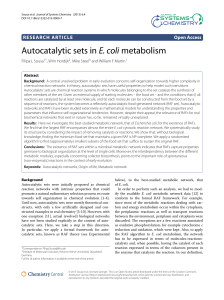
Autocatalytic sets in E. coli metabolism
... coli metabolic network, the following transformations of the metabolic network were performed: i) Transport reactions and reactions localized within the E. coli periplasm (except those involved in oxidative phosphorylation) are removed from the network, and the affected molecules are included in the ...
... coli metabolic network, the following transformations of the metabolic network were performed: i) Transport reactions and reactions localized within the E. coli periplasm (except those involved in oxidative phosphorylation) are removed from the network, and the affected molecules are included in the ...
aminoacids
... It is often found in the active site of enzymes Imidazole ring can act as electron acceptor/donor in an enzyme catalyzed reactions Aminoacids ...
... It is often found in the active site of enzymes Imidazole ring can act as electron acceptor/donor in an enzyme catalyzed reactions Aminoacids ...
Interactions of TCA cycle enzymes and of the CcpA
... activity of Icd in the presence of Mdh leads to an overproduction of α-ketoglutarate, since the activity of Mdh does not change. This might be a response to signal high anabolic demands triggered by high availability of ...
... activity of Icd in the presence of Mdh leads to an overproduction of α-ketoglutarate, since the activity of Mdh does not change. This might be a response to signal high anabolic demands triggered by high availability of ...
Chemistry 100 Second Homework
... molecules? (Be careful! Think about the shape of the molecule.) c. The C-F bond in polytetrafluoroethylene has a bond energy of about 504 kJ/mole. (As a comparison, the C-C single bond has a bond energy of 376 kJ/mole.) Would you expect polytetrafluoroethylene to be very reactive? Briefly explain yo ...
... molecules? (Be careful! Think about the shape of the molecule.) c. The C-F bond in polytetrafluoroethylene has a bond energy of about 504 kJ/mole. (As a comparison, the C-C single bond has a bond energy of 376 kJ/mole.) Would you expect polytetrafluoroethylene to be very reactive? Briefly explain yo ...
Functional Anatomy of the Liver
... Glycogenolysis in muscle produces lactic acid as major product In Fed State: Liver serves as a reserve for glucose (Insulin Glucagon ) Used to synthesize glycogen Liver captures glucose from portal blood broken down to pyruvate Oxidized to H20 and CO2 (TCA Cycle) aerobic phase ...
... Glycogenolysis in muscle produces lactic acid as major product In Fed State: Liver serves as a reserve for glucose (Insulin Glucagon ) Used to synthesize glycogen Liver captures glucose from portal blood broken down to pyruvate Oxidized to H20 and CO2 (TCA Cycle) aerobic phase ...
A Mechanistic Analysis of Enzymatic Degradation - J
... enzymes. 2-Haloacrylate reductase catalyzed the asymmetric reduction of 2-haloacrylate to produce L-2haloalkanoic acid in an NADPH-dependent manner. 2-Haloacrylate hydratase catalyzed the hydration of 2-haloacrylate to produce pyruvate. The enzyme is unique in that it catalyzes the non-redox reactio ...
... enzymes. 2-Haloacrylate reductase catalyzed the asymmetric reduction of 2-haloacrylate to produce L-2haloalkanoic acid in an NADPH-dependent manner. 2-Haloacrylate hydratase catalyzed the hydration of 2-haloacrylate to produce pyruvate. The enzyme is unique in that it catalyzes the non-redox reactio ...
Defective intestinal amino acid absorption in Ace2 null mice
... thought to result from defective intestinal absorption of its precursor L-tryptophan. Since Ace2 is necessary for intestinal B0AT1 expression, we tested the impact of intestinal B0AT1 absence in ace2 null mice. Their weight gain following weaning was decreased, and Na⫹-dependent uptake of B0AT1 subs ...
... thought to result from defective intestinal absorption of its precursor L-tryptophan. Since Ace2 is necessary for intestinal B0AT1 expression, we tested the impact of intestinal B0AT1 absence in ace2 null mice. Their weight gain following weaning was decreased, and Na⫹-dependent uptake of B0AT1 subs ...
mammalian hibernation: biochemical adaptation
... their colony (surrounding the queen) at 34 to 358C throughout the winter by varying the rate and number of shivering bees and the density of packing of the cluster. The high rate of ATP production needed to support their shivering is supplied by aerobic sugar oxidation in muscle using the massive st ...
... their colony (surrounding the queen) at 34 to 358C throughout the winter by varying the rate and number of shivering bees and the density of packing of the cluster. The high rate of ATP production needed to support their shivering is supplied by aerobic sugar oxidation in muscle using the massive st ...
Exogenous glutamine increases lipid accumulation in
... responds to variation in carbon and nitrogen availability from the maternal assimilate supply (Severino and Auld, 2013). Protein, carbohydrates and oil accumulation depend on both the capacity for assimilate uptake, metabolism and storage within the seed (zygotic control), and the assimilate supply ...
... responds to variation in carbon and nitrogen availability from the maternal assimilate supply (Severino and Auld, 2013). Protein, carbohydrates and oil accumulation depend on both the capacity for assimilate uptake, metabolism and storage within the seed (zygotic control), and the assimilate supply ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
Document
... Transfer electrons (hydride ions or H a play a major role in energy metabolism. e.g., the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to many different acceptors. ...
... Transfer electrons (hydride ions or H a play a major role in energy metabolism. e.g., the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to many different acceptors. ...
Evolution - Amino Acid wksht
... can examine the amino acid sequence of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequences of amino acids in their proteins and be closely related through evol ...
... can examine the amino acid sequence of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequences of amino acids in their proteins and be closely related through evol ...
Consensus temporal order of amino acids and evolution
... Forty different single-factor criteria and multi-factor hypotheses about chronological order of appearance of amino acids in the early evolution are summarized in consensus ranking. All available knowledge and thoughts about origin and evolution of the genetic code are thus combined in a single list ...
... Forty different single-factor criteria and multi-factor hypotheses about chronological order of appearance of amino acids in the early evolution are summarized in consensus ranking. All available knowledge and thoughts about origin and evolution of the genetic code are thus combined in a single list ...
Origins and Evolution of Pathways of Anaerobic Metabolism in the
... situations, or tissues, where relatively higher rates of energy production are required. Where the two pathways occur together, the aspartate-succinate pathway functions during the early stages of environmental anaerobiosis, whereas the glucose-succinate pathway does not become operative until later ...
... situations, or tissues, where relatively higher rates of energy production are required. Where the two pathways occur together, the aspartate-succinate pathway functions during the early stages of environmental anaerobiosis, whereas the glucose-succinate pathway does not become operative until later ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.