metabolism during adventitious root primordium initiation
... becomes degraded either by the aerobic EMP pathway, leading to the production of pyruvate; or part or all of the G-6-P may enter the PP pathway, which also functions under anaerobic conditions, and may yield pyruvate. Pyruvate, of course, enters the TCA cycle after decarboxylation. Enhanced primordi ...
... becomes degraded either by the aerobic EMP pathway, leading to the production of pyruvate; or part or all of the G-6-P may enter the PP pathway, which also functions under anaerobic conditions, and may yield pyruvate. Pyruvate, of course, enters the TCA cycle after decarboxylation. Enhanced primordi ...
The Nitrogen Cycle: Processes, Players, and Human Impact | Learn
... nitrogen-fixers that are also photosynthetic since they actually produce oxygen. Over time, nitrogen-fixers have evolved different ways to protect their nitrogenase from oxygen. For example, some cyanobacteria have structures called heterocysts that provide a low-oxygen environment for the enzyme an ...
... nitrogen-fixers that are also photosynthetic since they actually produce oxygen. Over time, nitrogen-fixers have evolved different ways to protect their nitrogenase from oxygen. For example, some cyanobacteria have structures called heterocysts that provide a low-oxygen environment for the enzyme an ...
initial rates for many enzymatic reactions exhibit bell
... under standard conditions to determine that it remains constant -if an E is unstable and steadily loses activity with time, it may be possible to correct all the values obtained to those that existed at the start of the studies if a series of standard assays have been carried out at different times ...
... under standard conditions to determine that it remains constant -if an E is unstable and steadily loses activity with time, it may be possible to correct all the values obtained to those that existed at the start of the studies if a series of standard assays have been carried out at different times ...
9th Grade Physical Science Course Syllabus
... Describe the role of enzymes in glycolysis. Write out the intermediate reactions between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. Write the reactions that occur in anaerobic respiration. Explain why lactate is produced in overworked muscle cells. Explain the function of acetyl COA in the transfer of energy i ...
... Describe the role of enzymes in glycolysis. Write out the intermediate reactions between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. Write the reactions that occur in anaerobic respiration. Explain why lactate is produced in overworked muscle cells. Explain the function of acetyl COA in the transfer of energy i ...
Characterization of the regulatory function of the 46
... Arabidopsis Rubisco activase was recently shown to be regulated by redox changes in the larger (46-kDa) isoform specifically mediated by thioredoxin-f [Zhang and Portis (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 9438–9443]. Reduction greatly increases the activity of the 46-kDa isoform and the native protein ...
... Arabidopsis Rubisco activase was recently shown to be regulated by redox changes in the larger (46-kDa) isoform specifically mediated by thioredoxin-f [Zhang and Portis (1999) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 9438–9443]. Reduction greatly increases the activity of the 46-kDa isoform and the native protein ...
Gluconeogenesis differs in developing chick embryos derived from
... isotopes present in the original molecule and that contributed by the derivative using the matrix approach (Fernandez et al., 1996). Natural isotopomer distributions in unlabelled glucose and AA were quantified from blood samples taken from embryos that had not received [13C6]glucose. Enrichments ar ...
... isotopes present in the original molecule and that contributed by the derivative using the matrix approach (Fernandez et al., 1996). Natural isotopomer distributions in unlabelled glucose and AA were quantified from blood samples taken from embryos that had not received [13C6]glucose. Enrichments ar ...
Malonyl CoenzymeA Decarboxylase Regulates Lipid and
... In lipogenic tissues such as liver and adipose tissue, malonyl-CoA is the first intermediate regulator in the synthesis of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs). Malonyl-CoA allosterically binds to carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 (CPT-1), thereby inhibiting the enzyme and the transfer of LCFA into the mi ...
... In lipogenic tissues such as liver and adipose tissue, malonyl-CoA is the first intermediate regulator in the synthesis of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs). Malonyl-CoA allosterically binds to carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 (CPT-1), thereby inhibiting the enzyme and the transfer of LCFA into the mi ...
Intermediary metabolism
... to be found in free-living bacterivorous nematodes such as C. elegans, which live under mostly temperate conditions. During the 1960s and -70s there was much interest in comparative biochemistry and a great deal of work was done on the metabolism of nematodes, albeit predominantly focusing on parasi ...
... to be found in free-living bacterivorous nematodes such as C. elegans, which live under mostly temperate conditions. During the 1960s and -70s there was much interest in comparative biochemistry and a great deal of work was done on the metabolism of nematodes, albeit predominantly focusing on parasi ...
Characteristics of Phenylacrylic Acid Decarboxylase
... conferring cinnamic acid resistance to S. cerevisiae21. PAD1 was cloned into a cinnamic acid-sensitive mutant strain of yeast, restoring cinnamic acid resistance and phenylacrylic acid decarboxylation. However, the product of the pad1 ...
... conferring cinnamic acid resistance to S. cerevisiae21. PAD1 was cloned into a cinnamic acid-sensitive mutant strain of yeast, restoring cinnamic acid resistance and phenylacrylic acid decarboxylation. However, the product of the pad1 ...
Lewis 1..13 - Gerszten Lab
... Exercise provides numerous salutary effects, but our understanding of how these occur is limited. To gain a clearer picture of exercise-induced metabolic responses, we have developed comprehensive plasma metabolite signatures by using mass spectrometry to measure >200 metabolites before and after ex ...
... Exercise provides numerous salutary effects, but our understanding of how these occur is limited. To gain a clearer picture of exercise-induced metabolic responses, we have developed comprehensive plasma metabolite signatures by using mass spectrometry to measure >200 metabolites before and after ex ...
Purification and Characterization of
... 214 6 12.6 kD, suggesting a tetrameric structure for this catalyst. Because H. carterae PRK activity was insensitive to NADH but was stimulated by dithiothreitol, it appears that the enzyme may require a thioredoxin/ferredoxin rather than a metabolite mode of regulation. Kinetic analysis of this enz ...
... 214 6 12.6 kD, suggesting a tetrameric structure for this catalyst. Because H. carterae PRK activity was insensitive to NADH but was stimulated by dithiothreitol, it appears that the enzyme may require a thioredoxin/ferredoxin rather than a metabolite mode of regulation. Kinetic analysis of this enz ...
Malonyl-CoA Signaling, Lipid Partitioning, and
... fuel for the brain and glucose homeostasis. Thus the two defects and/or adaptive processes initially walk hand in hand in the progression toward overt diabetes. Nonetheless, what has recently emerged is that insulin resistance alone (in the non--cell target tissues of the hormone) cannot cause diab ...
... fuel for the brain and glucose homeostasis. Thus the two defects and/or adaptive processes initially walk hand in hand in the progression toward overt diabetes. Nonetheless, what has recently emerged is that insulin resistance alone (in the non--cell target tissues of the hormone) cannot cause diab ...
Metabolism of lactic acid bacteria
... prolonged division l ags , e specially in the absence of Mg . Addition of trace amounts of EDTA de crea se d the death rate by removing toxic cation impurities , while the buffer salt concentration had l ittle e ffe ct on survival within wide l imits . The optimum pH value for survival was ne ar 7 . ...
... prolonged division l ags , e specially in the absence of Mg . Addition of trace amounts of EDTA de crea se d the death rate by removing toxic cation impurities , while the buffer salt concentration had l ittle e ffe ct on survival within wide l imits . The optimum pH value for survival was ne ar 7 . ...
Lesson 8. Enzymes
... enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life processes in essentially all life-forms from viruses to man. Most of the enzymes retain their catalytic potential even after extraction from the living organism. The above catalytic power of enzyme leads to commercial usage of enzymes. In ancient ...
... enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life processes in essentially all life-forms from viruses to man. Most of the enzymes retain their catalytic potential even after extraction from the living organism. The above catalytic power of enzyme leads to commercial usage of enzymes. In ancient ...
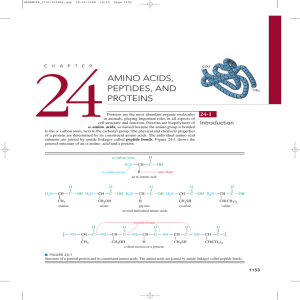
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Proteins that provide all the essential amino acids in about the right proportions for human nutrition are called complete proteins. Examples of complete proteins are those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely ...
... Proteins that provide all the essential amino acids in about the right proportions for human nutrition are called complete proteins. Examples of complete proteins are those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely ...
melatonin and succinate reduce rat liver mitochondrial dysfunction
... reduced glutathione decreased in red blood cells (by 25%, p<0.05) (Table 2). The liver mitochondrial protein thiol group content and mitochondrial total thiol group content did not change as a result of diabetes (Table 2). The level of PSSG increased in mitochondria of diabetic rats (by 50%, p<0.05) ...
... reduced glutathione decreased in red blood cells (by 25%, p<0.05) (Table 2). The liver mitochondrial protein thiol group content and mitochondrial total thiol group content did not change as a result of diabetes (Table 2). The level of PSSG increased in mitochondria of diabetic rats (by 50%, p<0.05) ...
Unit 6 Vitamins Defining a vitamin Essential
... Dissolve in water and Readily excreted In the diet Consumed in _______________________ form, cleaved during digestion, absorbed as free vitamins 50 – 90% B vitamins in diet are absorbed Once absorbed, Vitamin C Ascorbic acid (reduced form), dehydroascorbic acid (oxidized form) Synthesized by most an ...
... Dissolve in water and Readily excreted In the diet Consumed in _______________________ form, cleaved during digestion, absorbed as free vitamins 50 – 90% B vitamins in diet are absorbed Once absorbed, Vitamin C Ascorbic acid (reduced form), dehydroascorbic acid (oxidized form) Synthesized by most an ...
What is Biology? Biology and Biologists: Overview What is Biology
... An Introduction to the Animals: Summary From Invertebrates to Vertebrates: Overview More Protostomes Deuterostomes and Early Vertebrates Vertebrate Diversity From Invertebrates to Vertebrates: Summary ...
... An Introduction to the Animals: Summary From Invertebrates to Vertebrates: Overview More Protostomes Deuterostomes and Early Vertebrates Vertebrate Diversity From Invertebrates to Vertebrates: Summary ...
NITROGEN METABOLISM
... As pointed out in the previous section, nitrogen fixation is confined to selected microbes and plants. But all plants require nitrogen because it has a role to play in the general metabolism. Therefore, plants which do not fix nitrogen, use other combined nitrogen sources such as nitrate and ammonia ...
... As pointed out in the previous section, nitrogen fixation is confined to selected microbes and plants. But all plants require nitrogen because it has a role to play in the general metabolism. Therefore, plants which do not fix nitrogen, use other combined nitrogen sources such as nitrate and ammonia ...
Glycogen Metabolism USP
... Promotes glucagon release > increase blood glucose interacts directly with both muscle and liver cells to promote glycogen degradation High blood sugar > release insulin (B-cells) >>>>> > glycogen synthesis ...
... Promotes glucagon release > increase blood glucose interacts directly with both muscle and liver cells to promote glycogen degradation High blood sugar > release insulin (B-cells) >>>>> > glycogen synthesis ...
De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or
... et al., 2000; Bolwell et al., 1988), which means that efficient conversion of trans-cinnamic acid into p-coumaric acid is required to avoid the accumulation of toxic intermediate. The hydroxylation of transcinnamic acid into p-coumaric acid is catalyzed by cinnamic acid hydroxylase (C4H), a P450 enzy ...
... et al., 2000; Bolwell et al., 1988), which means that efficient conversion of trans-cinnamic acid into p-coumaric acid is required to avoid the accumulation of toxic intermediate. The hydroxylation of transcinnamic acid into p-coumaric acid is catalyzed by cinnamic acid hydroxylase (C4H), a P450 enzy ...
PDF
... N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis The sequence of the first 44 amino acids of T. maritima ferredoxin was determined and this is aligned in Fig. 3 with the corresponding sequences of the two 4Fe-ferredoxins from hyperthermophilic archaea ( P. furiosus and Ts. litoralis; [9]), together with repr ...
... N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis The sequence of the first 44 amino acids of T. maritima ferredoxin was determined and this is aligned in Fig. 3 with the corresponding sequences of the two 4Fe-ferredoxins from hyperthermophilic archaea ( P. furiosus and Ts. litoralis; [9]), together with repr ...
Acid-Base Equilibria and Activity
... which is a very common type of analysis. An assumption in a titration is that the neutralization reaction goes to completion, and in practice we use strong acids or strong bases as titrants so that this result is true. For understanding the chemistry of aqueous systems, it is more common that we are ...
... which is a very common type of analysis. An assumption in a titration is that the neutralization reaction goes to completion, and in practice we use strong acids or strong bases as titrants so that this result is true. For understanding the chemistry of aqueous systems, it is more common that we are ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.