Mechanisms underlying the essential role of mitochondrial
... 2.2. The Nematode C. elegans. The extent of longevity extension by various genetic interventions in C. elegans has been shown to correlate with the following coordinated changes in the concentrations/activities of enzymes involved in fatty acid elongation and desaturation: (1) decreased concentratio ...
... 2.2. The Nematode C. elegans. The extent of longevity extension by various genetic interventions in C. elegans has been shown to correlate with the following coordinated changes in the concentrations/activities of enzymes involved in fatty acid elongation and desaturation: (1) decreased concentratio ...
Chapter 19 Slides
... – If O2 is available, NADH is re-oxidized in the electron transport pathway, making ATP in oxidative phosphorylation – In anaerobic conditions, NADH is reoxidized by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), providing additional NAD+ for more glycolysis Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
... – If O2 is available, NADH is re-oxidized in the electron transport pathway, making ATP in oxidative phosphorylation – In anaerobic conditions, NADH is reoxidized by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), providing additional NAD+ for more glycolysis Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... – If O2 is available, NADH is re-oxidized in the electron transport pathway, making ATP in oxidative phosphorylation – In anaerobic conditions, NADH is reoxidized by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), providing additional NAD+ for more glycolysis Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
... – If O2 is available, NADH is re-oxidized in the electron transport pathway, making ATP in oxidative phosphorylation – In anaerobic conditions, NADH is reoxidized by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), providing additional NAD+ for more glycolysis Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
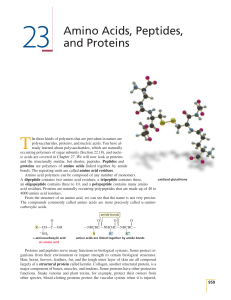
23 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Two amino acid side chains—serine and threonine—contain alcohol groups. Serine is an HO-substituted alanine and threonine has a branched ethanol substituent. There are also two sulfur-containing amino acids: Cysteine is an HS-substituted alanine and methionine has a 2-methylthioethyl substituent. Th ...
... Two amino acid side chains—serine and threonine—contain alcohol groups. Serine is an HO-substituted alanine and threonine has a branched ethanol substituent. There are also two sulfur-containing amino acids: Cysteine is an HS-substituted alanine and methionine has a 2-methylthioethyl substituent. Th ...
Ileal endogenous amino acid flow response to nitrogen
... variability in formulation of NFD may influence the estimation of the basal endogenous AA losses (Adedokun et al., 2011) and consequently the estimation of AA digestibility. The results obtained from current 4-d study showed that the variation in proportion of corn starch and dextrose in the experim ...
... variability in formulation of NFD may influence the estimation of the basal endogenous AA losses (Adedokun et al., 2011) and consequently the estimation of AA digestibility. The results obtained from current 4-d study showed that the variation in proportion of corn starch and dextrose in the experim ...
The tyrosine regulated DAHP synthase and the biosynthetic
... ARO4, that can be feedback-inhibited by phenylalanine and tyrosine, respectively. Crystal structures of the phenylalanine regulated DAHP synthase of Escherichia coli and of the tyrosine inhibitable isoenzyme of S. cerevisiae are available. With the help of amino acid substitutions at the catalytic c ...
... ARO4, that can be feedback-inhibited by phenylalanine and tyrosine, respectively. Crystal structures of the phenylalanine regulated DAHP synthase of Escherichia coli and of the tyrosine inhibitable isoenzyme of S. cerevisiae are available. With the help of amino acid substitutions at the catalytic c ...
Metabolic profiling during nutrient limited growth in bakers` yeast
... nucleotides, which are also products of glutamine, were not similarly decreased. Examination of the growth-rate slope across all amino acids revealed that the concentration of every amino acid dropped with increasingly severe ammonium limitation, with the strongest response for glutamine, histidine ...
... nucleotides, which are also products of glutamine, were not similarly decreased. Examination of the growth-rate slope across all amino acids revealed that the concentration of every amino acid dropped with increasingly severe ammonium limitation, with the strongest response for glutamine, histidine ...
Biochemical and genetic analysis of leucine-, isoleucine
... each of the constituents of the cell is synthesized by a series of biosynthetlc reactions and that each enzyme in the series is under the control of a single gene. If this were true, they reasoned, it should be possible to induce mutations, any one of which result in the failure of production of cer ...
... each of the constituents of the cell is synthesized by a series of biosynthetlc reactions and that each enzyme in the series is under the control of a single gene. If this were true, they reasoned, it should be possible to induce mutations, any one of which result in the failure of production of cer ...
3 Citrate metabolism and aroma compound production in lactic acid
... the conversion of citrate into lactate, since it was observed that in these microorganisms high amounts of diacetyl are formed (reviewed in [2]). The metabolic biosynthetic pathway from citrate to diacetyl was revealed in L. diacetylactis by use of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques [4, 5]. ...
... the conversion of citrate into lactate, since it was observed that in these microorganisms high amounts of diacetyl are formed (reviewed in [2]). The metabolic biosynthetic pathway from citrate to diacetyl was revealed in L. diacetylactis by use of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques [4, 5]. ...
Alcohols - La Salle University
... • In men, ethanol lowers levels of testosterone (and sperm count) due to lack of enzymes needed for the steroid biosynthesis. • The enzyme CYP2E1, which is responsible for converting acetaminophen into liver toxins, is activated by ethanol. • Ethanol has a caloric value of 7.1Cal/g (fat has a value ...
... • In men, ethanol lowers levels of testosterone (and sperm count) due to lack of enzymes needed for the steroid biosynthesis. • The enzyme CYP2E1, which is responsible for converting acetaminophen into liver toxins, is activated by ethanol. • Ethanol has a caloric value of 7.1Cal/g (fat has a value ...
aq - Haverford Alchemy
... Why might these be important? Give examples. • Aqueous reactions cannot take place without water. What do you already know about water that will help us understand aqueous reactions? Aqueous Reactions ...
... Why might these be important? Give examples. • Aqueous reactions cannot take place without water. What do you already know about water that will help us understand aqueous reactions? Aqueous Reactions ...
Acid-Base Equilibria - Riverside Local Schools
... The conjugate base of a BrenstedLowry acid is what remains after the acid has donated a proton. Similarly, the conjugate acid of a Br0nstedLowry base is the species that results when the base accepts a proton. Two such species that differ from each other only by the presence or absence of a proton t ...
... The conjugate base of a BrenstedLowry acid is what remains after the acid has donated a proton. Similarly, the conjugate acid of a Br0nstedLowry base is the species that results when the base accepts a proton. Two such species that differ from each other only by the presence or absence of a proton t ...
PDF format - JOP. Journal of the Pancreas
... Plasma Amino Acid Levels In all, 17 amino acids were detected and identified. The distribution pattern of these amino acids is given in Table 2. As compared to the healthy controls, the chronic pancreatitis patients had lower concentrations of aspartate, serine, histidine, arginine, threonine, tyros ...
... Plasma Amino Acid Levels In all, 17 amino acids were detected and identified. The distribution pattern of these amino acids is given in Table 2. As compared to the healthy controls, the chronic pancreatitis patients had lower concentrations of aspartate, serine, histidine, arginine, threonine, tyros ...
Properties of a newly characterized protein of the bovine - K-REx
... noted above, catalyze inactivation and activation of the complex, ...
... noted above, catalyze inactivation and activation of the complex, ...
Temperature-dependent effects of cadmium and purine nucleotides
... Inhibition of invertebrate mitochondrial aconitase (Roesijadi, 1996) (A. S. Cherkasov, S. Grewal and I. M. Sokolova, manuscript submitted for publication). Thus, a combination of temperature and Cd stress is an environmentally relevant situation for populations of intertidal poikilotherms (includin ...
... Inhibition of invertebrate mitochondrial aconitase (Roesijadi, 1996) (A. S. Cherkasov, S. Grewal and I. M. Sokolova, manuscript submitted for publication). Thus, a combination of temperature and Cd stress is an environmentally relevant situation for populations of intertidal poikilotherms (includin ...
Acid-Base
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
幻灯片 1 - 湖北师范学院生命科学学院
... 2.3.2 Only the L-amino acids have been found in proteins (Disomers have been found only in small peptides of bacteria cell walls and in some peptide antibiotics). 2.3.3 The correlation of structure (or configuration) with optical rotation is very complex and has not been successful to date! (i.e., t ...
... 2.3.2 Only the L-amino acids have been found in proteins (Disomers have been found only in small peptides of bacteria cell walls and in some peptide antibiotics). 2.3.3 The correlation of structure (or configuration) with optical rotation is very complex and has not been successful to date! (i.e., t ...
Ammonia, urea production and pH regulation
... Short-term regulation of urea synthesis primarily takes place at the level of ammonia and bicarbonate provision for mitochondrial CPS I, which presumably is the rate-controlling enzyme for the cycle at physiological substrate concentrations [11,12,21]. The Km (NH +4 ) of CPS I is 1–2 mmol/L, that is ...
... Short-term regulation of urea synthesis primarily takes place at the level of ammonia and bicarbonate provision for mitochondrial CPS I, which presumably is the rate-controlling enzyme for the cycle at physiological substrate concentrations [11,12,21]. The Km (NH +4 ) of CPS I is 1–2 mmol/L, that is ...
COMPARATIVE ASSESSMENT OF PHYTOCHEMICALS AND ANTIOXIDANT POTENTIAL OF CLERODENDRUM COLEBROOKIANUM
... The use of traditional medicine is widespread and plants provide a large source of natural antioxidants that might serve as leads for the development of novel drugs[1]. Normally formed as resultant byproducts of a plethora of metabolic processes, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrog ...
... The use of traditional medicine is widespread and plants provide a large source of natural antioxidants that might serve as leads for the development of novel drugs[1]. Normally formed as resultant byproducts of a plethora of metabolic processes, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrog ...
Quality of Lipids in Fish Fed Vegetable Oils
... 2000). Pacu has semi-lean meat and, like carp, stores most of its fat as adipose tissue in the abdominal wall (Mráz & Pickova, 2009). These fish have also evolved different strategies for metabolic response to xenobiotic compounds (van der Oost et al., 2003) It is well known that n-3 fatty acids, pa ...
... 2000). Pacu has semi-lean meat and, like carp, stores most of its fat as adipose tissue in the abdominal wall (Mráz & Pickova, 2009). These fish have also evolved different strategies for metabolic response to xenobiotic compounds (van der Oost et al., 2003) It is well known that n-3 fatty acids, pa ...
GLUCOKINASE ACTIVATORS: A GLUCOSE SENSOR ROLE IN PANCREATIC ISLETS AND HEPATOCYTE
... several chemical react that are involved in chemical reactions. A kinase is also known as a phosphotransferase. This is a type of enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP to specific substrates. The process is referred to as phosphorylation. Kinases bind s ...
... several chemical react that are involved in chemical reactions. A kinase is also known as a phosphotransferase. This is a type of enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP to specific substrates. The process is referred to as phosphorylation. Kinases bind s ...
Multiomics of tomato glandular trichomes reveals
... Glandular trichomes (GTs) are specialized secretory cells that protrude from the epidermis of approximately 30% of all vascular plants (Fahn, 2000). The morphology of GTs is very diverse across plant species as exemplified by the peltate trichomes of the Lamiaceae, the biseriate trichomes of th ...
... Glandular trichomes (GTs) are specialized secretory cells that protrude from the epidermis of approximately 30% of all vascular plants (Fahn, 2000). The morphology of GTs is very diverse across plant species as exemplified by the peltate trichomes of the Lamiaceae, the biseriate trichomes of th ...
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Acid–Base
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
The reaction pathways of hydrogen peroxide in
... enthalpy, entropy and free energy of the transition states of the formation and breakdown of the intermediate have been calculated. The metal-catalyzed pathway of hydrogen peroxide is dealing with the effect of hydroxyl radicals created by the Fenton reaction and their potential to oxidize the disul ...
... enthalpy, entropy and free energy of the transition states of the formation and breakdown of the intermediate have been calculated. The metal-catalyzed pathway of hydrogen peroxide is dealing with the effect of hydroxyl radicals created by the Fenton reaction and their potential to oxidize the disul ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.