heterogeneous chiral catalyst derived from hydrolyzed
... and c, a chiral (asymmetric) centre is produced in (C abcd). In other words, it is a compound or group that has two enantiotopic atoms, faces or groups. For example, CH2XY has two enantiotopic H atoms. Asymmetric synthesis is only possible when the starting materials or conditions are optically acti ...
... and c, a chiral (asymmetric) centre is produced in (C abcd). In other words, it is a compound or group that has two enantiotopic atoms, faces or groups. For example, CH2XY has two enantiotopic H atoms. Asymmetric synthesis is only possible when the starting materials or conditions are optically acti ...
genetic code: a new understanding of codon
... two classes, 10+10, in correspondence to two classes of enzymes aminoacyltRNA synthetases. The simpler and/or smaller AAs (within AAs pairs) are handled by less complex enzymes of class II, whereas larger (more complex) AAs molecules are handled by more complex enzymes of class I (bold underlined) t ...
... two classes, 10+10, in correspondence to two classes of enzymes aminoacyltRNA synthetases. The simpler and/or smaller AAs (within AAs pairs) are handled by less complex enzymes of class II, whereas larger (more complex) AAs molecules are handled by more complex enzymes of class I (bold underlined) t ...
Sustained nonoxidative glucose utilization and depletion of
... mCi/mmol) followed by constant intravenous infusion at a rate of 25 &i/h. After an equilibration period of 25 min (16), arterial and venous samples were withdrawn as outlined to determine concentrations and specific activities of lactate and glucose, as well as 14C02 content. Chemical analysis. Weig ...
... mCi/mmol) followed by constant intravenous infusion at a rate of 25 &i/h. After an equilibration period of 25 min (16), arterial and venous samples were withdrawn as outlined to determine concentrations and specific activities of lactate and glucose, as well as 14C02 content. Chemical analysis. Weig ...
No Slide Title
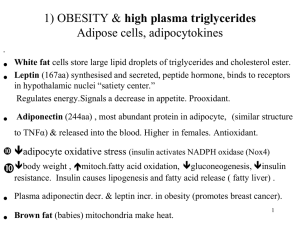
... i) The STATINS inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis to decrease plasma LDL cholesterol and cut the risk of heart attacks and strokes by at least 33% even in people with normal cholesterol. Several million Canadians are taking statins. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors but can induce rhabdomyolysis (test for ...
... i) The STATINS inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis to decrease plasma LDL cholesterol and cut the risk of heart attacks and strokes by at least 33% even in people with normal cholesterol. Several million Canadians are taking statins. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors but can induce rhabdomyolysis (test for ...
Untitled - Heart and Metabolism
... into mechanical energy, and because of its high energy requirement and relatively low content of high energy compounds (ATP and creatine phosphate [PCr]) ATP must be continuously generated at a high rate. Thus, the heart must adjust energy production to energy utilization, and at the same time secur ...
... into mechanical energy, and because of its high energy requirement and relatively low content of high energy compounds (ATP and creatine phosphate [PCr]) ATP must be continuously generated at a high rate. Thus, the heart must adjust energy production to energy utilization, and at the same time secur ...
to the PDF file. - CURVE
... Resistance to, metronidazole and tinidazole, the drugs currently prescribed for the treatment of trichomoniasis, an infection of the genito-urinary tract of humans by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis, has created a need for the development of therapeutics with a different mode of action. Trifluor ...
... Resistance to, metronidazole and tinidazole, the drugs currently prescribed for the treatment of trichomoniasis, an infection of the genito-urinary tract of humans by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis, has created a need for the development of therapeutics with a different mode of action. Trifluor ...
Lesson Overview
... • NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) is a carrier molecule. • NADP+ accepts and holds two high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+). In this way, it is converted into NADPH. ...
... • NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) is a carrier molecule. • NADP+ accepts and holds two high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+). In this way, it is converted into NADPH. ...
Amino acid composition of kolomikta actinidia
... Higher levels of leucine in a diet may induce pellagra, and the leucine/lysine ratio is used as an indicator of the pellagragenic character of a food protein (Mbitki-Mwikya et al., 2000). In all of the investigated kolomikta actinidia fruits Leu/Ile ratio ranged between 1.26–1.32 and it was three an ...
... Higher levels of leucine in a diet may induce pellagra, and the leucine/lysine ratio is used as an indicator of the pellagragenic character of a food protein (Mbitki-Mwikya et al., 2000). In all of the investigated kolomikta actinidia fruits Leu/Ile ratio ranged between 1.26–1.32 and it was three an ...
Fructokinase (Fraction III)of Pea Seeds
... The properties of hexokinase (ATP:D-hexose 6-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.1) from yeast and mammalian tissues have been the hexose kinases fractionated on a DEAE-cellulose column as studied extensively (2, 15). Bakers' yeast contains two native described previously (20). The fractions containing the ...
... The properties of hexokinase (ATP:D-hexose 6-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.1) from yeast and mammalian tissues have been the hexose kinases fractionated on a DEAE-cellulose column as studied extensively (2, 15). Bakers' yeast contains two native described previously (20). The fractions containing the ...
New Insights into the Interaction of Carbohydrate and Fat
... ON N1G 2W1, Canada e-mail: [email protected] ...
... ON N1G 2W1, Canada e-mail: [email protected] ...
Unit 8 Acids and Bases Notes (answers)
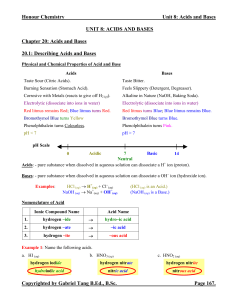
... Polyprotic Acids: - acids that can donate more than one protons. - this includes all diprotic and triprotic acids (acids that can donate three protons). - polyprotic acids dissociate one proton at a time. Each successive proton donation has its own Ka, which gets smaller until the last proton is don ...
... Polyprotic Acids: - acids that can donate more than one protons. - this includes all diprotic and triprotic acids (acids that can donate three protons). - polyprotic acids dissociate one proton at a time. Each successive proton donation has its own Ka, which gets smaller until the last proton is don ...
CHEMISTRY OF p-ELEMENTS - Львівський національний
... including proteins, nucleic acids, hydrocarbons, enzymes, vitamins. The study of life is known as biological chemistry or biochemistry. Oxygen atoms are present in water (H2O) and water is essential to all life. Oxygen is present in many organic compounds. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration. ...
... including proteins, nucleic acids, hydrocarbons, enzymes, vitamins. The study of life is known as biological chemistry or biochemistry. Oxygen atoms are present in water (H2O) and water is essential to all life. Oxygen is present in many organic compounds. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration. ...
linolenic acid prevent insulin resistance but have divergent impacts
... which was analogous to that observed in ATP synthase protein content (Fig. 4). Similar adaptations were seen in obese ALA rats compared with their lean counterparts, including a significant increase in pyruvate-supported state 4 respiration (Fig. 5A). In contrast, respiration of SS mitochondria from ...
... which was analogous to that observed in ATP synthase protein content (Fig. 4). Similar adaptations were seen in obese ALA rats compared with their lean counterparts, including a significant increase in pyruvate-supported state 4 respiration (Fig. 5A). In contrast, respiration of SS mitochondria from ...
H. Heldt
... deliberately omitted dealing with elements such as the structure and function of amino acids, carbohydrates, and nucleotides; the function of nucleic acids as carriers of genetic information; and the structure and function of proteins and the basis of enzyme catalysis. I have dealt with topics of ge ...
... deliberately omitted dealing with elements such as the structure and function of amino acids, carbohydrates, and nucleotides; the function of nucleic acids as carriers of genetic information; and the structure and function of proteins and the basis of enzyme catalysis. I have dealt with topics of ge ...
Plant Biochemistry
... deliberately omitted dealing with elements such as the structure and function of amino acids, carbohydrates, and nucleotides; the function of nucleic acids as carriers of genetic information; and the structure and function of proteins and the basis of enzyme catalysis. I have dealt with topics of ge ...
... deliberately omitted dealing with elements such as the structure and function of amino acids, carbohydrates, and nucleotides; the function of nucleic acids as carriers of genetic information; and the structure and function of proteins and the basis of enzyme catalysis. I have dealt with topics of ge ...
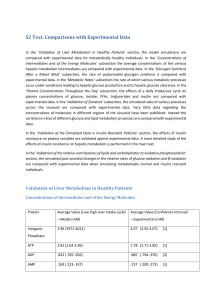
The model was provided with glucose and FFA inputs to
... than the experimental data, whilst the simulated increase in FFA concentration is delayed relative to the experimental data. However, in both cases the simulated data remain within one standard deviation of the experimental data, and the shape of the simulated curves remains consistent with the expe ...
... than the experimental data, whilst the simulated increase in FFA concentration is delayed relative to the experimental data. However, in both cases the simulated data remain within one standard deviation of the experimental data, and the shape of the simulated curves remains consistent with the expe ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... motifs TENEP and ITENG, which contain the two glutamic acids (Glu-191 and Glu-406) involved in the general acid/base catalysis and the respective family 1 b-glucosidases nucleophiles (San-Aparicio et al. 1998). A part slot-like active site (Davies and Henrissat 1995) was formed by these residues nec ...
... motifs TENEP and ITENG, which contain the two glutamic acids (Glu-191 and Glu-406) involved in the general acid/base catalysis and the respective family 1 b-glucosidases nucleophiles (San-Aparicio et al. 1998). A part slot-like active site (Davies and Henrissat 1995) was formed by these residues nec ...
Aalborg Universitet metabolic engineering approach
... types of biorefinery systems; the most described type is probably the enzymatic and microbial conversion of lignocellulose to different products, e.g. bioethanol. However, for this type of biorefinery to be economical competitive on the open market, emphasis on high value products like certain chemi ...
... types of biorefinery systems; the most described type is probably the enzymatic and microbial conversion of lignocellulose to different products, e.g. bioethanol. However, for this type of biorefinery to be economical competitive on the open market, emphasis on high value products like certain chemi ...
Carbohydrates & Lipids - mvhs
... Monomers and Polymers • Monomer = single unit – Examples: amino acids, monosaccharides ...
... Monomers and Polymers • Monomer = single unit – Examples: amino acids, monosaccharides ...
Making protein (translation)
... Part II: Translation • Using the length of messenger RNA to assemble amino acids into proteins. • Takes place in a ribosome. ...
... Part II: Translation • Using the length of messenger RNA to assemble amino acids into proteins. • Takes place in a ribosome. ...
Differences in the amino acid composition of muscles from pheasant
... Historically, game represented the major portion of meat consumed by man before the development of agriculture (STEINHAUSER, 2000). Recently, there have been some trends to revive and develop intensive pheasant farming. Pheasant farms and nurseries have to ensure that game receives adequate nutritio ...
... Historically, game represented the major portion of meat consumed by man before the development of agriculture (STEINHAUSER, 2000). Recently, there have been some trends to revive and develop intensive pheasant farming. Pheasant farms and nurseries have to ensure that game receives adequate nutritio ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.