12.1 Electricity at Home (Pages 485
... • Fuses must be replaced after they are set off, breakers can be reset ...
... • Fuses must be replaced after they are set off, breakers can be reset ...
Major I
... 2. Three single-phase, 20/2.4-KV, ideal transformers are connected to form a three-phase, 10MVA, 34.5/2.4-KV transformer bank. The transformer bank supplies a load of 6 MW at 2.4 KV and 0.85 power factor lagging. (Draw the schematic diagram of the required transformer) a. Determine the line and phas ...
... 2. Three single-phase, 20/2.4-KV, ideal transformers are connected to form a three-phase, 10MVA, 34.5/2.4-KV transformer bank. The transformer bank supplies a load of 6 MW at 2.4 KV and 0.85 power factor lagging. (Draw the schematic diagram of the required transformer) a. Determine the line and phas ...
Series & Parallel Circuits
... • A circuit that has only one path for the current to flow • Remember that charge cannot be created or destroyed and current is amount charge moving per second • The potential difference is shared by each device in the circuit. • Also call voltage drop because as the current passes through each devi ...
... • A circuit that has only one path for the current to flow • Remember that charge cannot be created or destroyed and current is amount charge moving per second • The potential difference is shared by each device in the circuit. • Also call voltage drop because as the current passes through each devi ...
Wiring Matters cover
... connect together all extraneousconductive-parts (which could include metal handrails, pipes, exposed steelwork, etc) and the protective conductor of all exposed-conductiveparts, irrespective of whether the conductive parts are simultaneouslyaccessible. If a metallic grid is installed, it must be con ...
... connect together all extraneousconductive-parts (which could include metal handrails, pipes, exposed steelwork, etc) and the protective conductor of all exposed-conductiveparts, irrespective of whether the conductive parts are simultaneouslyaccessible. If a metallic grid is installed, it must be con ...
APPENDIX A – ELECTRICAL SAFETY GLOSSARY 1
... and/or other serious safety hazards (e.g., electrical hazard). 5. Disconnecting Means/Switch. A device designed to close and/or open an electric circuit. 6. Electrically Safe Work Condition. A state in which an electrical conductor or circuit part has been disconnected from energized parts, locked/t ...
... and/or other serious safety hazards (e.g., electrical hazard). 5. Disconnecting Means/Switch. A device designed to close and/or open an electric circuit. 6. Electrically Safe Work Condition. A state in which an electrical conductor or circuit part has been disconnected from energized parts, locked/t ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #2
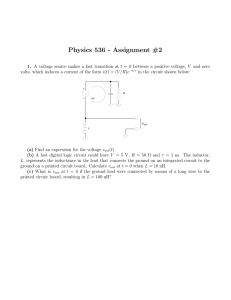
... (b) A fast digital logic circuit could have V = 5 V, R = 50 Ω and τ = 1 ns. The inductor, L, represents the inductance in the lead that connects the ground on an integrated circuit to the ground on a printed circuit board. Calculate vout at t = 0 when L = 10 nH. (c) What is vout at t = 0 if the grou ...
... (b) A fast digital logic circuit could have V = 5 V, R = 50 Ω and τ = 1 ns. The inductor, L, represents the inductance in the lead that connects the ground on an integrated circuit to the ground on a printed circuit board. Calculate vout at t = 0 when L = 10 nH. (c) What is vout at t = 0 if the grou ...
Unit 7: Electrical Circuits and Systems Review KEY
... If resistance is decreased in a circuit, what happens to the current? What law is this? ...
... If resistance is decreased in a circuit, what happens to the current? What law is this? ...
ELECTRICAL SAFETY DEVICES
... protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold. The terms surge protection device (SPD), or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVS ...
... protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold. The terms surge protection device (SPD), or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVS ...
Workshop Materials
... •Ungrounded windings greatly affect relay performance during grounded faults •If primary winding is delta and a phaseto-ground fault occurs on the grid, the current relays of the DG will not be as sensitive to it. DG voltage relays on the primary side must see rise in voltage. ...
... •Ungrounded windings greatly affect relay performance during grounded faults •If primary winding is delta and a phaseto-ground fault occurs on the grid, the current relays of the DG will not be as sensitive to it. DG voltage relays on the primary side must see rise in voltage. ...
Theories In Electronics Vocabulary Teacher`s Guide
... Conductor – A material that has a loose grip on its electrons so the electrical current can pass through it. Insulator – A material that maintains a tight grip on its electrons so that an electrical current cannot flow through it. Fuse – A circuit protection device consisting of a thin strip of meta ...
... Conductor – A material that has a loose grip on its electrons so the electrical current can pass through it. Insulator – A material that maintains a tight grip on its electrons so that an electrical current cannot flow through it. Fuse – A circuit protection device consisting of a thin strip of meta ...
G / E-Series Motor Protection Relay Product Features Specifications
... Apply appropriate personal protective equipment(PPE) and follow safety work practices Only qualified electrical workers should install this equipment. Such work should be performed only after reading this entire set of instructions. If the equipment is not used in the manner specified by the manufac ...
... Apply appropriate personal protective equipment(PPE) and follow safety work practices Only qualified electrical workers should install this equipment. Such work should be performed only after reading this entire set of instructions. If the equipment is not used in the manner specified by the manufac ...