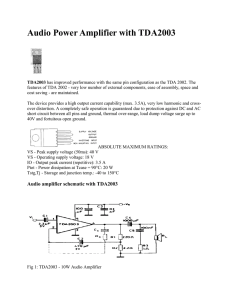
Circuit Notes
... 3. Higher Current = ____________________________________________ 4. Electric circuits control the movement of ________________________________________ __________________________. The path of an electric circuit is a ____________________. 5. An electric circuit allows electrons to ___________________ ...
... 3. Higher Current = ____________________________________________ 4. Electric circuits control the movement of ________________________________________ __________________________. The path of an electric circuit is a ____________________. 5. An electric circuit allows electrons to ___________________ ...
1) Draw a circuit to show how the resistance of a circuit can be
... c) copy the diagram and mark on the direction of conventional current flow d) Which way does the current ACTUALLY flow? 4) A bulb is marked 240V 60W. a) What does this mean? b) Calculate the current flowing through the light bulb c) What is the resistance of the light bulb? A person has a number of ...
... c) copy the diagram and mark on the direction of conventional current flow d) Which way does the current ACTUALLY flow? 4) A bulb is marked 240V 60W. a) What does this mean? b) Calculate the current flowing through the light bulb c) What is the resistance of the light bulb? A person has a number of ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... *AC Generator uses slip rings attached to the ends of the armature *DC Generator uses a commutator instead of slip rings. A DC generator is the same as an Electric Motor. 7. The electric company uses giant generators to produce Electrical energy –instead of a crank and armature it uses Turbines ...
... *AC Generator uses slip rings attached to the ends of the armature *DC Generator uses a commutator instead of slip rings. A DC generator is the same as an Electric Motor. 7. The electric company uses giant generators to produce Electrical energy –instead of a crank and armature it uses Turbines ...
F1 Notes.cwk
... Series circuit - has only one path for the current to follow Parallel circuit - more than one path for current to follow Magnet -attracts objects made of iron or steel Magnetic pole - where a magnet’s pull is the strongest Magnetic field - space all around a magnet where the force of the magnet can ...
... Series circuit - has only one path for the current to follow Parallel circuit - more than one path for current to follow Magnet -attracts objects made of iron or steel Magnetic pole - where a magnet’s pull is the strongest Magnetic field - space all around a magnet where the force of the magnet can ...
Wire free Door Guard
... contacts remain closed so that the reset pin of IC HEF 4060 will be high. This inhibits its oscillation and it remains standby. When an intruder opens the door, magnet and reed switch move away taking the reset pin of IC to ground potential. IC starts oscillating using the components C1 and R3.Blink ...
... contacts remain closed so that the reset pin of IC HEF 4060 will be high. This inhibits its oscillation and it remains standby. When an intruder opens the door, magnet and reed switch move away taking the reset pin of IC to ground potential. IC starts oscillating using the components C1 and R3.Blink ...
DN-26 UC3842A Low-Cost Start-up and Fault Protection Circuit PDF
... initiates a clock cycle and the PWM output at pin 6 goes high. This is fed to transistor Q1 which pulls the Rt/Ct input at pin 4 low, thus "freezing" the oscillator, while keeping the PWM output high. Once a valid fault (greater than 1 volt) is received at the current sense input (pin 3), the output ...
... initiates a clock cycle and the PWM output at pin 6 goes high. This is fed to transistor Q1 which pulls the Rt/Ct input at pin 4 low, thus "freezing" the oscillator, while keeping the PWM output high. Once a valid fault (greater than 1 volt) is received at the current sense input (pin 3), the output ...
Day and Night Review
... on its , an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. It takes the Earth or one day to make one complete turn. We do not feel the Earth moving because it moves so quickly and so smoothly. The Earth’s movement causes day and night. The sun seems to move across the sky during the ...
... on its , an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. It takes the Earth or one day to make one complete turn. We do not feel the Earth moving because it moves so quickly and so smoothly. The Earth’s movement causes day and night. The sun seems to move across the sky during the ...
Guide to preventing shocks from entertai nment systems
... All modern mains-powered electrical equipment has filter components reducing mains and airborne electrical interference. In Class I products, these components are connected between L+ E and N + E and cause some current leakage to Earth. As Class II products have no protective earth, the ...
... All modern mains-powered electrical equipment has filter components reducing mains and airborne electrical interference. In Class I products, these components are connected between L+ E and N + E and cause some current leakage to Earth. As Class II products have no protective earth, the ...
Positive Negative
... The following is a Lucas reply to a similar question regarding positive and negative earth put in 1966. “Electrical equipment will only function with current flow which requires a return path for the current that has passed through the component. Originally most vehicle manufacturers utilised either ...
... The following is a Lucas reply to a similar question regarding positive and negative earth put in 1966. “Electrical equipment will only function with current flow which requires a return path for the current that has passed through the component. Originally most vehicle manufacturers utilised either ...
Electric Circuits
... • Current in a circuit increases as the voltage increases • Current in a circuit decreases as the resistance increases ...
... • Current in a circuit increases as the voltage increases • Current in a circuit decreases as the resistance increases ...
COPPER WIRE APPLIANCE CLASSES Index
... Japan). A fault in the appliance which causes a live conductor to contact the casing will cause a current to flow in the earth conductor. This current should trip either an overcurrent dev ...
... Japan). A fault in the appliance which causes a live conductor to contact the casing will cause a current to flow in the earth conductor. This current should trip either an overcurrent dev ...
Download PGN-3000 Datasheet
... The PGN Pulsing High-Resistance-Grounding Systems are used to ground power systems by inserting a resistor between system neutral and ground to lower the ground-fault current to a predetermined value. Properly sized Resistance Grounding Systems solve two problems of ungrounded systems—transient over ...
... The PGN Pulsing High-Resistance-Grounding Systems are used to ground power systems by inserting a resistor between system neutral and ground to lower the ground-fault current to a predetermined value. Properly sized Resistance Grounding Systems solve two problems of ungrounded systems—transient over ...
Technical Reference - Ericson Manufacturing Company
... CSA - Canadian Standards Association.This is a nonprofit, independent organization that operates a listing service for electronic materials and equipment.The Canadian counterpart of the Underwriters Laboratories. Current Carrying Capacity - The maximum current an insulated conductor can safely carry ...
... CSA - Canadian Standards Association.This is a nonprofit, independent organization that operates a listing service for electronic materials and equipment.The Canadian counterpart of the Underwriters Laboratories. Current Carrying Capacity - The maximum current an insulated conductor can safely carry ...
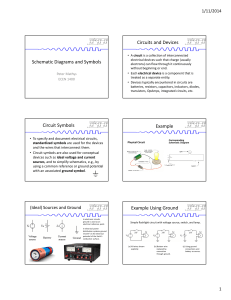
Schematic Diagrams and Symbols Circuits and Devices Circuit
... standardized symbols are used for the devices and the wires that interconnect them. • Circuit symbols are also used for conceptual devices such as ideal voltage and current sources, and to simplify schematics, e.g., by using a common reference or ground potential with an associated ground symbol. ...
... standardized symbols are used for the devices and the wires that interconnect them. • Circuit symbols are also used for conceptual devices such as ideal voltage and current sources, and to simplify schematics, e.g., by using a common reference or ground potential with an associated ground symbol. ...