chapter 6: earthing system tn systems
... • The total lack of earth in some cases, or the introduction of current limiting into the earth path, means that the usual methods of protection will not be effective. • For this reason, IT systems are not allowed in the public supply system. • An exception is in medical situations such as hospitals ...
... • The total lack of earth in some cases, or the introduction of current limiting into the earth path, means that the usual methods of protection will not be effective. • For this reason, IT systems are not allowed in the public supply system. • An exception is in medical situations such as hospitals ...
air courier services - Service Link
... One method of protection against injury caused by an electrical fault is the use of an equipment grounding conductor commonly known as the 3rd, or green, wire. This equipment grounding conductor grounds the exposed, non current carrying metal parts of tools or equipment and carries off the leakage a ...
... One method of protection against injury caused by an electrical fault is the use of an equipment grounding conductor commonly known as the 3rd, or green, wire. This equipment grounding conductor grounds the exposed, non current carrying metal parts of tools or equipment and carries off the leakage a ...
Electrical Injury
... - Class 1: third pin of plug (direct earthing) + metal casing -> this circuit should be low resistance and if live wire comes in contact with an accessible part should be linked to a fuse that breaks the circuit - Class 2: double or reinforced insulation (non-conductive plastic), earthing wire not n ...
... - Class 1: third pin of plug (direct earthing) + metal casing -> this circuit should be low resistance and if live wire comes in contact with an accessible part should be linked to a fuse that breaks the circuit - Class 2: double or reinforced insulation (non-conductive plastic), earthing wire not n ...
Telecommunications Earthing Training
... of lightning rod selection and placement. Some of these developments have already began to have an impact on practices around the world. This training discuses some new developments a) Discussion on lightning formation and the key criteria for lightning to attach to a target. b) Discussions of vario ...
... of lightning rod selection and placement. Some of these developments have already began to have an impact on practices around the world. This training discuses some new developments a) Discussion on lightning formation and the key criteria for lightning to attach to a target. b) Discussions of vario ...
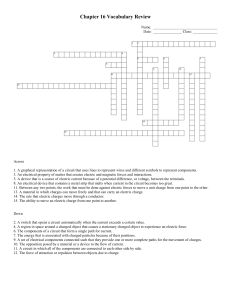
Chapter 16 Vocabulary Review Name: Date: Class: ______ Across
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
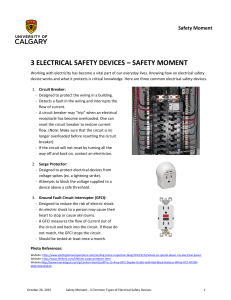
3 ELECTRICAL SAFETY DEVICES – SAFETY MOMENT
... receptacle has become overloaded. One can reset the circuit breaker to restore current flow. (Note: Make sure that the circuit is no longer overloaded before resetting the circuit breaker). - If the circuit will not reset by turning all the way off and back on, contact an electrician. 2. Surge Prote ...
... receptacle has become overloaded. One can reset the circuit breaker to restore current flow. (Note: Make sure that the circuit is no longer overloaded before resetting the circuit breaker). - If the circuit will not reset by turning all the way off and back on, contact an electrician. 2. Surge Prote ...
Brad`s Lecture on Electricity and Power Supplies
... PARTS OF THE TRANSFORMER CONSIST OF ONLY ONE DEVICE! THE TRANSFORMER ITSELF! IT CONSIST OF 2 COILS WHICH “STEP DOWN” OR REDUCE THE VOLTAGE DOWN TO 5 AND 12 VOLTS ...
... PARTS OF THE TRANSFORMER CONSIST OF ONLY ONE DEVICE! THE TRANSFORMER ITSELF! IT CONSIST OF 2 COILS WHICH “STEP DOWN” OR REDUCE THE VOLTAGE DOWN TO 5 AND 12 VOLTS ...
Electical Safety Presentation
... set a number of rules and regulations for working with electricity. These rules are in the 29 CFR 1910. ...
... set a number of rules and regulations for working with electricity. These rules are in the 29 CFR 1910. ...
Mains electricity - Thomas Tallis Science Department
... • Plastic is used as it is a good insulator, as well as being tough and flexible • The whole cable is encased in another layer of plastic ...
... • Plastic is used as it is a good insulator, as well as being tough and flexible • The whole cable is encased in another layer of plastic ...