![Regulated Power Supply [ppt]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001086228_1-9a7fc8aab7a3192d0e202a8163eee145-300x300.png)
( ) cos60 sin60 , 0. it Be t Be tt = +
... The capacitor has a value of 500μF; the initial value of the current is zero, and the initial voltage on the capacitor is 1V. Find the values of R, L, B1, and B2. ...
... The capacitor has a value of 500μF; the initial value of the current is zero, and the initial voltage on the capacitor is 1V. Find the values of R, L, B1, and B2. ...
Electricity
... Voltages inside a computer do not exceed 12 V, except at the power supply and power switch on older computers, which are at 120 V. Be careful in these areas! ...
... Voltages inside a computer do not exceed 12 V, except at the power supply and power switch on older computers, which are at 120 V. Be careful in these areas! ...
sb6100 industrial shock-block™ technical faq
... where reliable equipment grounding or double insulation is provided. Class D – A GFCI that will interrupt the circuit to the load when the ground-fault current is 20 mA or more and is intended to be used in circuits with one or more conductors over 300 V to ground (i.e. 600 V systems), and with spec ...
... where reliable equipment grounding or double insulation is provided. Class D – A GFCI that will interrupt the circuit to the load when the ground-fault current is 20 mA or more and is intended to be used in circuits with one or more conductors over 300 V to ground (i.e. 600 V systems), and with spec ...
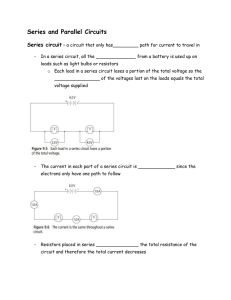
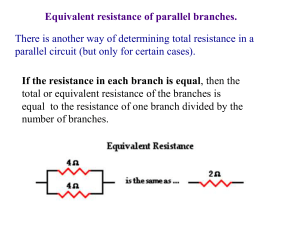
There is another way of determining total resistance in a parallel circuit
... Each time current direction reverses, the direction of the magnetic field reverses. Since current alternates continuously, the magnetic field is never static. Power plants switched to AC circuits because they could carry electricity hundreds of miles with little loss of power. In addition, AC circui ...
... Each time current direction reverses, the direction of the magnetic field reverses. Since current alternates continuously, the magnetic field is never static. Power plants switched to AC circuits because they could carry electricity hundreds of miles with little loss of power. In addition, AC circui ...
Generator and Transformer
... Moving Electricity How does electric energy transmit over large distances? How much power is wasted when 10000W of power is transmitted along a cable with a resistance of 1 at 200V? What would be lost if transmitted at 2000V instead? Much less lost when travels at a higher V and lower I ...
... Moving Electricity How does electric energy transmit over large distances? How much power is wasted when 10000W of power is transmitted along a cable with a resistance of 1 at 200V? What would be lost if transmitted at 2000V instead? Much less lost when travels at a higher V and lower I ...
Snímek 1 - cidel argentina 2010
... • Try to find out the reason of damaged concrete towers in the distribution network • To measure the voltage and currents during the earth fault for fault on unearthed console of concrete tower and for other types of fault • The method of shunting (connecting affected phase to earth system in substa ...
... • Try to find out the reason of damaged concrete towers in the distribution network • To measure the voltage and currents during the earth fault for fault on unearthed console of concrete tower and for other types of fault • The method of shunting (connecting affected phase to earth system in substa ...
Download the Quiz
... What kind of hazard might exist in a power supply when it is turned off and disconnected? A. Static electricity could damage the grounding system B. Circulating currents inside the transformer might cause damage C. The fuse might blow if you remove the cover D. You might receive an electric shock fr ...
... What kind of hazard might exist in a power supply when it is turned off and disconnected? A. Static electricity could damage the grounding system B. Circulating currents inside the transformer might cause damage C. The fuse might blow if you remove the cover D. You might receive an electric shock fr ...
CHAPTER 3 QUIZ – ELECTROMAGNETISM
... An _______________ is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a _________________. _____________ found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a _________________. __________________ is t ...
... An _______________ is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a _________________. _____________ found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a _________________. __________________ is t ...
chapter7-Section6
... automatically disconnect a circuit if the current is large enough to cause excessive ohmic heating. • At extremely low temperatures, many materials become superconductors—they have zero resistance. ...
... automatically disconnect a circuit if the current is large enough to cause excessive ohmic heating. • At extremely low temperatures, many materials become superconductors—they have zero resistance. ...
Science (done) > Mrs Potts > 11A5 Physics
... current flows into the appliance through one conductor and back into the outlet through the other. This completes the circuit and the appliance starts working. • In cases where there is a danger of an electric shock a 3 core cable should be used. The third conductor connects the metal part of the ap ...
... current flows into the appliance through one conductor and back into the outlet through the other. This completes the circuit and the appliance starts working. • In cases where there is a danger of an electric shock a 3 core cable should be used. The third conductor connects the metal part of the ap ...