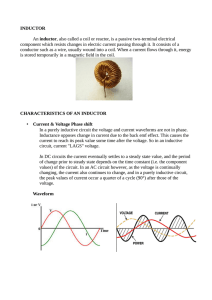
2005-2 Second Exercise: The circuit breaker in a kitchen ( 6.5 points
... The electrical installation in a kitchen is fed by a sinusoidal alternating voltage of effective value U = 220 V. This installation includes the following electrical appliances: A refrigerator; A washing machine; An electric water heater (which can be considered as a resistor) of power P = 154 ...
... The electrical installation in a kitchen is fed by a sinusoidal alternating voltage of effective value U = 220 V. This installation includes the following electrical appliances: A refrigerator; A washing machine; An electric water heater (which can be considered as a resistor) of power P = 154 ...
HW2 Solutions
... has 0 degree phase angle). The transformers both have leakage reactance of 0.12 pu. Both generators have subtransient reactance of 0.1 pu. a. For the pre-fault conditions, compute the pu real power consumed by each load, the pu real power delivered by each generator, the power angle δ, and the pu re ...
... has 0 degree phase angle). The transformers both have leakage reactance of 0.12 pu. Both generators have subtransient reactance of 0.1 pu. a. For the pre-fault conditions, compute the pu real power consumed by each load, the pu real power delivered by each generator, the power angle δ, and the pu re ...
Electricity
... Series circuit quiz on Thursday, 2/6 Week of 2/10 ‘Kindness Week’ Quiz on Wednesday, 2/12 Electricity test on Wednesday, 2/19 ...
... Series circuit quiz on Thursday, 2/6 Week of 2/10 ‘Kindness Week’ Quiz on Wednesday, 2/12 Electricity test on Wednesday, 2/19 ...
Electric Circuits
... converted to another form of energy. Electrical power is calculated by multiplying voltage by current. P (watts) = I (amps) x V (volts) ...
... converted to another form of energy. Electrical power is calculated by multiplying voltage by current. P (watts) = I (amps) x V (volts) ...
File
... Is the power supply switched on and is the polarity of the power supply correct. Inspect the circuit for obvious concerns, like:- Broken wires - missing components - fuses blown Is their power at each part of the circuit? (use multimeter) Check each component to see if current is travelling through ...
... Is the power supply switched on and is the polarity of the power supply correct. Inspect the circuit for obvious concerns, like:- Broken wires - missing components - fuses blown Is their power at each part of the circuit? (use multimeter) Check each component to see if current is travelling through ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 2) Find any parallel loads. Calculate their equivalent resistance with 1 1 1 1 RT R1 R2 R3 Draw a new schematic with one resistor with the new value. 3) Find any resistor in series. Calculate their equivalent resistance by adding. Draw a new schematic with a new resistor with that valu ...
... 2) Find any parallel loads. Calculate their equivalent resistance with 1 1 1 1 RT R1 R2 R3 Draw a new schematic with one resistor with the new value. 3) Find any resistor in series. Calculate their equivalent resistance by adding. Draw a new schematic with a new resistor with that valu ...
14.3 Electrical Power, AC, and DC Electricity
... hot wire carries 120 volts AC. The neutral wire stays at zero volts. The ground wire is for safety and is connected to the ground (0 V) near your house ...
... hot wire carries 120 volts AC. The neutral wire stays at zero volts. The ground wire is for safety and is connected to the ground (0 V) near your house ...
Berechnung von Netztransienten
... • Single phase faults in stator windings are in most cases intermittent faults. • The corresponding transient fault currents are by a factor of 60 higher than the small steady state fault current and hence responsible for damages in stator iron and winding. • High resistance grounding (most usual) o ...
... • Single phase faults in stator windings are in most cases intermittent faults. • The corresponding transient fault currents are by a factor of 60 higher than the small steady state fault current and hence responsible for damages in stator iron and winding. • High resistance grounding (most usual) o ...
Slide 1
... Short-circuit current rise with the increase of power supply; causing power supply disruptions, equipment damage and major outages ...
... Short-circuit current rise with the increase of power supply; causing power supply disruptions, equipment damage and major outages ...
Use this Jeopardy game to study for the Electricity
... is designed to protect your home by opening a switch when a circuit is overloaded or has a short circuit ...
... is designed to protect your home by opening a switch when a circuit is overloaded or has a short circuit ...
Gravity Near Earth
... The height of the surface varies – so the radius does, too The material under the surface is not uniform The earth is spinning The tides affect the earth as well as the oceans ...
... The height of the surface varies – so the radius does, too The material under the surface is not uniform The earth is spinning The tides affect the earth as well as the oceans ...
Hazards in the home from mains electricity Hazards can include: 1
... and fuse (or circuit breaker) are just for safety and work together like this: If a fault develops in which the live somehow touches the metal case, then because the case is earthed, a big current flows in through the live, through the case and out down the earth wire. This surge in current blows t ...
... and fuse (or circuit breaker) are just for safety and work together like this: If a fault develops in which the live somehow touches the metal case, then because the case is earthed, a big current flows in through the live, through the case and out down the earth wire. This surge in current blows t ...
the mechanical universe - Binghamton City School District
... What famous royal figure attended a formal lecture given by Michael Faraday in the lat 1700’s at the Royal Institute? ...
... What famous royal figure attended a formal lecture given by Michael Faraday in the lat 1700’s at the Royal Institute? ...
MTL MA15 Surge Protectors Manual PDF
... “UNPROTECTED” side of the MA15 device, as indicated on the product labeling. This will install the SPD in parallel with the supply and it will not be subjected to any load current. Install 15A overcurrent protection (fuse or circuit breaker) in the LINE wire. The Live wire must be connected to the “ ...
... “UNPROTECTED” side of the MA15 device, as indicated on the product labeling. This will install the SPD in parallel with the supply and it will not be subjected to any load current. Install 15A overcurrent protection (fuse or circuit breaker) in the LINE wire. The Live wire must be connected to the “ ...