* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 536 - Assignment #2
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
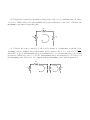
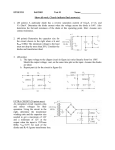
Physics 536 - Assignment #2 1. A voltage source makes a fast transition at t = 0 between a positive voltage, V and zero volts, which induces a current of the form i(t) = (V /R)e−t/τ in the circuit shown below: R i(t) Vout L (a) Find an expression for the voltage vout (t). (b) A fast digital logic circuit could have V = 5 V, R = 50 Ω and τ = 1 ns. The inductor, L, represents the inductance in the lead that connects the ground on an integrated circuit to the ground on a printed circuit board. Calculate vout at t = 0 when L = 10 nH. (c) What is vout at t = 0 if the ground lead were connected by means of a long wire to the printed circuit board, resulting in L = 100 nH? 2. Consider the circuit below in which a voltage source v(t) = V eiωt , with impedance Rs drives a load RL . What value of RL will maximize the power transferred to the load? Calculate the maximum power when RL has this value. Rs v(t) RL i(t) 3. Consider the source connected to the load by means of a transformer as shown√below. Assuming perfect coupling between the primary and secondary coils, ie. k = 1 in M = k L1 L2 , what ratio of L1 /L2 will maximize the power transferred to a load with impedance RL at high frequencies. What turns ratio, n = N1 /N2 , will maximize the power transfered to RL ? How does the maximum power delivered to RL compare with the maximum power found in question 2? Rs v(t) L1 i1 (t) L2 i2 (t) RL