User Manual/Handbook: Microphone Handbook Volume 1
... to provide sufficient background information for customers to get the best out of these products. It also gives adequate information for customers to be able to make informed and qualified decisions about the microphone products which are most suitable for their measurement requirements. These produ ...
... to provide sufficient background information for customers to get the best out of these products. It also gives adequate information for customers to be able to make informed and qualified decisions about the microphone products which are most suitable for their measurement requirements. These produ ...
Design of Variable Gain Amplifier - Nanyang Technological University
... power consumption and die area, as well as achieving the required bandwidth for the targeted application. In this thesis, a new design approach which is the “cell-based” design method is proposed. The advantage of cell-based VGA design is that the number of unit cells to be cascaded can be chosen ac ...
... power consumption and die area, as well as achieving the required bandwidth for the targeted application. In this thesis, a new design approach which is the “cell-based” design method is proposed. The advantage of cell-based VGA design is that the number of unit cells to be cascaded can be chosen ac ...
Reconfigurable CMOS Mixers for Radio-Frequency Applications Min Wang
... The momentum for lower cost transceivers in the market is enormous, which makes CMOS the most attractive technology due to its low cost and high yield. Since the cost of CMOS transceivers is heavily weighted by the silicon area and packaging, extensive effort has been taken to reduce the chip size a ...
... The momentum for lower cost transceivers in the market is enormous, which makes CMOS the most attractive technology due to its low cost and high yield. Since the cost of CMOS transceivers is heavily weighted by the silicon area and packaging, extensive effort has been taken to reduce the chip size a ...
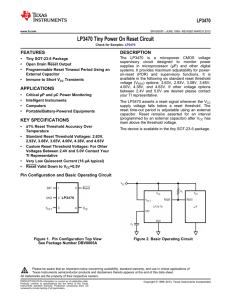
LP3470 Tiny Power On Reset Circuit (Rev. G)
... time period (tRP) programmed by an external capacitor (C1); after this interval Reset goes to logic high. If a brownout condition occurs (monitored voltage falls below the reset threshold minus a small hysteresis), Reset goes low. When VCC returns above the reset threshold, Reset remains low for a t ...
... time period (tRP) programmed by an external capacitor (C1); after this interval Reset goes to logic high. If a brownout condition occurs (monitored voltage falls below the reset threshold minus a small hysteresis), Reset goes low. When VCC returns above the reset threshold, Reset remains low for a t ...
PowerNet MIB Reference Guide
... that might provide an alternative law or forum or to have this agreement written in any language other than English. Any translation of this agreement to a language other than English is provided only for the convenience of the customer and is not the legally binding version of the agreement. The te ...
... that might provide an alternative law or forum or to have this agreement written in any language other than English. Any translation of this agreement to a language other than English is provided only for the convenience of the customer and is not the legally binding version of the agreement. The te ...
A Design Methodology for Switched-Capacitor DC
... Switched-capacitor (SC) DC-DC power converters are a subset of DC-DC power converters that use a network of switches and capacitors to efficiently convert one voltage to another. Unlike traditional inductor-based DC-DC converters, SC converters do not rely on magnetic energy storage. This fact makes ...
... Switched-capacitor (SC) DC-DC power converters are a subset of DC-DC power converters that use a network of switches and capacitors to efficiently convert one voltage to another. Unlike traditional inductor-based DC-DC converters, SC converters do not rely on magnetic energy storage. This fact makes ...
100327DRFSinLCWS.Beijin10
... Concept of DRFS • The Distributed RF System (DRFS) is another possibility for a costeffective solution in support of a single Main Linac tunnel design. • Base line of proposed DRFS one unit of 750kW Modulating Anode (MA) klystron would drive two cavities (in basic configuration scheme –BCS/HCS). ...
... Concept of DRFS • The Distributed RF System (DRFS) is another possibility for a costeffective solution in support of a single Main Linac tunnel design. • Base line of proposed DRFS one unit of 750kW Modulating Anode (MA) klystron would drive two cavities (in basic configuration scheme –BCS/HCS). ...
Alberta Reliability Standard Voltage and Reactive Control VAR-001-AB-
... R1 The ISO must develop and maintain requirements for monitoring and controllingspecify a system voltage levels and reactive power flows within the transmission system, including consulting with each operator of a transmission facility and any transmission operatorrange with an associated tolerance ...
... R1 The ISO must develop and maintain requirements for monitoring and controllingspecify a system voltage levels and reactive power flows within the transmission system, including consulting with each operator of a transmission facility and any transmission operatorrange with an associated tolerance ...