Blank Jeopardy
... Your immune system recognizes the bacteria, virus, and cancerous cells below as not belonging to your body. What is a name given something your body recognizes as an ...
... Your immune system recognizes the bacteria, virus, and cancerous cells below as not belonging to your body. What is a name given something your body recognizes as an ...
immune system - Solon City Schools
... Neutrophil- 60% WBC, patrol tissue, large numbers when infected short lives (die after digesting bacteria) ...
... Neutrophil- 60% WBC, patrol tissue, large numbers when infected short lives (die after digesting bacteria) ...
Immune System
... Immunization= process that increases an organism’s rxn to antigen & therefore improves its ability to resist or overcome infection ...
... Immunization= process that increases an organism’s rxn to antigen & therefore improves its ability to resist or overcome infection ...
REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 26
... When the body loses tolerance for its own antigens and attacks them, autoimmune disease results. Autoimmune disease results in cellular damage of the body by its own immune system; it is treated with immunosuppressive drugs. ...
... When the body loses tolerance for its own antigens and attacks them, autoimmune disease results. Autoimmune disease results in cellular damage of the body by its own immune system; it is treated with immunosuppressive drugs. ...
Commensalism • Benefits both the host and the commensal
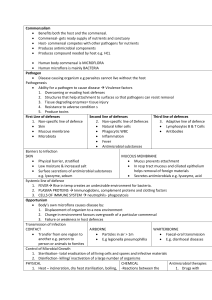
... Skin Natural killer cells Lymphocytes B & T Cells Mucous membrane Phagocytic WBC Antibodies Microbiota Inflammation Fever Antimicrobial substances Barriers to Infection SKIN MUCOUS MEMBRANE Physical barrier, stratified Mucus prevents attachment Low moisture & increased salt ...
... Skin Natural killer cells Lymphocytes B & T Cells Mucous membrane Phagocytic WBC Antibodies Microbiota Inflammation Fever Antimicrobial substances Barriers to Infection SKIN MUCOUS MEMBRANE Physical barrier, stratified Mucus prevents attachment Low moisture & increased salt ...
Ch. 24 Presentation
... – immune cells capable of phagocytosis, cellular ingestion and digestion of foreign substances. ...
... – immune cells capable of phagocytosis, cellular ingestion and digestion of foreign substances. ...
Immunology 3
... of phagocytes. Essentially the idea of phagocytosis involves what is known as ‘celleating’. The specialized phagocytic cells engulfs the invading pathogen by short cytoplasmic processes known as pseudopodia or literally false feet. They engulf the pathogen, the membrane forms a small ring around it, ...
... of phagocytes. Essentially the idea of phagocytosis involves what is known as ‘celleating’. The specialized phagocytic cells engulfs the invading pathogen by short cytoplasmic processes known as pseudopodia or literally false feet. They engulf the pathogen, the membrane forms a small ring around it, ...
PowerPoint **
... For years we’ve just said ‘HIV infects the cells and kills them,’ but it’s clearly more complicated than that. Productively infected by HIV, meaning that the virus has integrated with hostcell genome and can make copies of itself (death occurs through apoptosis mediated by an enzyme called caspase-3 ...
... For years we’ve just said ‘HIV infects the cells and kills them,’ but it’s clearly more complicated than that. Productively infected by HIV, meaning that the virus has integrated with hostcell genome and can make copies of itself (death occurs through apoptosis mediated by an enzyme called caspase-3 ...
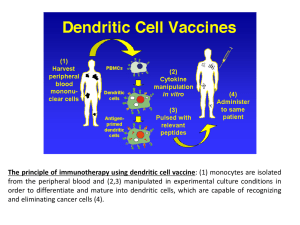
The principle of immunotherapy using dendritic
... The principle of immunotherapy using dendritic cell vaccine: (1) monocytes are isolated from the peripheral blood and (2,3) manipulated in experimental culture conditions in order to differentiate and mature into dendritic cells, which are capable of recognizing and eliminating cancer cells (4). ...
... The principle of immunotherapy using dendritic cell vaccine: (1) monocytes are isolated from the peripheral blood and (2,3) manipulated in experimental culture conditions in order to differentiate and mature into dendritic cells, which are capable of recognizing and eliminating cancer cells (4). ...
Immune system
... MALT (mucous associated lymphoid tissue) diffuse lymphatic tissue, the main role is capture of antigens passing through the mucosal epithelium ...
... MALT (mucous associated lymphoid tissue) diffuse lymphatic tissue, the main role is capture of antigens passing through the mucosal epithelium ...
MCQs: What cell types can be made tolerant? T
... 11. All the following sentences are true regarding genetic defects of the immune system except: (a) Fas deficiency in human causes lymphadenopathy and thrombocytopenia (b) C1q deficiency is associated with systemic endocrine erythematosus (c) Mutations of the AIRE gene are associated with endocrine ...
... 11. All the following sentences are true regarding genetic defects of the immune system except: (a) Fas deficiency in human causes lymphadenopathy and thrombocytopenia (b) C1q deficiency is associated with systemic endocrine erythematosus (c) Mutations of the AIRE gene are associated with endocrine ...
The Immune System
... • White blood cells have specialized receptors on their surface that enable them to determine what is "self" and "non-self” • When "non-self" proteins are encountered, an immune response is mounted to destroy the foreign (non-self) substance. ...
... • White blood cells have specialized receptors on their surface that enable them to determine what is "self" and "non-self” • When "non-self" proteins are encountered, an immune response is mounted to destroy the foreign (non-self) substance. ...
Suggested Answers to Discussion topics
... infections. Macrophages in particular that are located in the lung and liver (two organs that are affected with Daniel’s alpha-1 antitrypsin history) are primarily responsible for their phagocytic ability. The fact that activated macrophages impact on the self-nonself response and adaptive immunity ...
... infections. Macrophages in particular that are located in the lung and liver (two organs that are affected with Daniel’s alpha-1 antitrypsin history) are primarily responsible for their phagocytic ability. The fact that activated macrophages impact on the self-nonself response and adaptive immunity ...
MICROBIO320 Short Answers – These should be typically 1
... They are clonally distributed transmembrane molecules. They have extensive cytoplasmic domains that interact with intracellular molecules. They consist of polypeptides with variable and constant regions. They are associated with signal transduction molecules at the cell surface. They can interact wi ...
... They are clonally distributed transmembrane molecules. They have extensive cytoplasmic domains that interact with intracellular molecules. They consist of polypeptides with variable and constant regions. They are associated with signal transduction molecules at the cell surface. They can interact wi ...
**** 1 - School of Life Sciences
... Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a widely used clinical diagnostic tool because it is non-invasive, provides contrast among soft tissues at high spatial resolution. Conventional MRI focuses almost exclusively on visualizing anatomy and has no specificity for any particular cell type. The 'probe' ...
... Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a widely used clinical diagnostic tool because it is non-invasive, provides contrast among soft tissues at high spatial resolution. Conventional MRI focuses almost exclusively on visualizing anatomy and has no specificity for any particular cell type. The 'probe' ...
Edward Jenner, 1796 - University of California, Los Angeles
... • Allows a vast number of receptors to be generated from a small amount of genes • Maximizes diversity by introducing sequence variation at sites of recombination • Regulates the development of individual lymphocytes – Signal expansion and development of only cells with ...
... • Allows a vast number of receptors to be generated from a small amount of genes • Maximizes diversity by introducing sequence variation at sites of recombination • Regulates the development of individual lymphocytes – Signal expansion and development of only cells with ...
introduction and overview
... responses Diversification: converting one response into multiple types Turning responses off so that they don’t get out of control Memory The ability to respond to a changing environment by inventing new Ag receptors ...
... responses Diversification: converting one response into multiple types Turning responses off so that they don’t get out of control Memory The ability to respond to a changing environment by inventing new Ag receptors ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑