I. Student misconceptions
... In discussing vertebrate immune systems, emphasize the adaptive value of the incredible diversity of lymphocytes. Make sure students understand how gene rearrangement generates this diversity. Ask probing questions to encourage students to understand why such a complex mechanism has arisen. Why don’ ...
... In discussing vertebrate immune systems, emphasize the adaptive value of the incredible diversity of lymphocytes. Make sure students understand how gene rearrangement generates this diversity. Ask probing questions to encourage students to understand why such a complex mechanism has arisen. Why don’ ...
Unit 4: Infectious disease
... • A virus consisting of viral genes that are similar to a human, a bird (avian) and 2 types of pig viruses • First identified in Mexico in April, 2009 • June 11, 2009 the WHO declared it a level 6 ...
... • A virus consisting of viral genes that are similar to a human, a bird (avian) and 2 types of pig viruses • First identified in Mexico in April, 2009 • June 11, 2009 the WHO declared it a level 6 ...
How Immunity Evolved
... antigen recognized is derived from, or belongs to, a pathogen. •Activation of lymphocytes specific for self antigens, or innocuous persistent environmental antigens, is deleterious. ...
... antigen recognized is derived from, or belongs to, a pathogen. •Activation of lymphocytes specific for self antigens, or innocuous persistent environmental antigens, is deleterious. ...
Boosting the immune system by giving T cells a push By
... Scientists have discovered a way to potentially create stronger, more robust vaccines by hijacking a newly discovered signaling protein that helps certain immune cells grow. Many vaccines work by getting the body’s antibodies to respond, and immune cells called Tfh, or T follicular helper cells, ...
... Scientists have discovered a way to potentially create stronger, more robust vaccines by hijacking a newly discovered signaling protein that helps certain immune cells grow. Many vaccines work by getting the body’s antibodies to respond, and immune cells called Tfh, or T follicular helper cells, ...
Immunology – Immune System Overview
... effect because we are unable to readily have transplantation of organs from one individual to another. Although immunosuppressive drugs are widely used nowadays when transplantation is necessary. What comprises the immune system? The immune system can be systematically broken down to different arms. ...
... effect because we are unable to readily have transplantation of organs from one individual to another. Although immunosuppressive drugs are widely used nowadays when transplantation is necessary. What comprises the immune system? The immune system can be systematically broken down to different arms. ...
No Slide Title
... decrease in precursor cells decreased differentiation into T- and B-cells increased suppressor T-cells ...
... decrease in precursor cells decreased differentiation into T- and B-cells increased suppressor T-cells ...
Blood System
... with gray blue cytoplasm • In tissues become macrophages • Increase in % possible chronic infections i.e. TB & certain viruses & intracellular parasites • Activate lymphocytic immune response • Lifespan: several months ...
... with gray blue cytoplasm • In tissues become macrophages • Increase in % possible chronic infections i.e. TB & certain viruses & intracellular parasites • Activate lymphocytic immune response • Lifespan: several months ...
IN RESPONSE TO DAMAGE Innate, or nonspecific, immunity
... Non-specific responses - the second line of defense Non-specific responses are generalized responses to pathogen infection or to damage of the tissues - they do not target a specific cell type , The non-specific response consist of some WBC's and plasma proteins. This type of defense is directed aga ...
... Non-specific responses - the second line of defense Non-specific responses are generalized responses to pathogen infection or to damage of the tissues - they do not target a specific cell type , The non-specific response consist of some WBC's and plasma proteins. This type of defense is directed aga ...
Immune System Information
... Disorders of the Immune System Allergy- is an overreaction or hypersensitive reaction to a foreign substance. The foreign substance can be called an allergen, i.e. a harmless substance in the environment that the body overreacts to like pollen, dust or mold. Repeated exposure to allergens can result ...
... Disorders of the Immune System Allergy- is an overreaction or hypersensitive reaction to a foreign substance. The foreign substance can be called an allergen, i.e. a harmless substance in the environment that the body overreacts to like pollen, dust or mold. Repeated exposure to allergens can result ...
Specific Defense and Immunology 1. Define: Adaptive or Acquired
... that is developed as a result of previous exposure to a pathogen or foreign agent. It involves WBCs called lymphocytes (B-cells and T-cells), and the production of antibodies and cytokines. The functions of adaptive or acquired immunity are to recognize “self” VS “nonself”, eliminate specific pathog ...
... that is developed as a result of previous exposure to a pathogen or foreign agent. It involves WBCs called lymphocytes (B-cells and T-cells), and the production of antibodies and cytokines. The functions of adaptive or acquired immunity are to recognize “self” VS “nonself”, eliminate specific pathog ...
Document
... This system is activated when pathogens get past the general defence system Organs of the immune system that store WBC’s called lymphocytes and monocytes include the lymphatic vessels, tonsils, spleen lymph nodes ...
... This system is activated when pathogens get past the general defence system Organs of the immune system that store WBC’s called lymphocytes and monocytes include the lymphatic vessels, tonsils, spleen lymph nodes ...
IMMUNITY MEDIATED BY B LYMPHOCYTES AND ANTIBODIES
... * First line of defense against pathogens * Components ...
... * First line of defense against pathogens * Components ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM NON-SPECIFIC DEFENSE
... 1. Injured cells release a chemical signal called histamine to increase blood flow to area 2. platelets cause clotting trapping pathogens 3. Area swells, becomes warm, and macrophages/phagocyte (wbc) move in and engulf bacteria ...
... 1. Injured cells release a chemical signal called histamine to increase blood flow to area 2. platelets cause clotting trapping pathogens 3. Area swells, becomes warm, and macrophages/phagocyte (wbc) move in and engulf bacteria ...
Genetics and Innate and Adaptive Immunity in IBD
... has yet to be identified. The strong family history in many patients, especially those with Crohn’s disease suggests a genetic predisposition. It has been hypothesized that the abnormal inflammatory response is due in part to genetically determined alterations in the normal homeostatic processes in ...
... has yet to be identified. The strong family history in many patients, especially those with Crohn’s disease suggests a genetic predisposition. It has been hypothesized that the abnormal inflammatory response is due in part to genetically determined alterations in the normal homeostatic processes in ...
Immunosenescence and Its Aplications to Artificial Immune
... Bulatti, M., Pellican, M., Vasto, S., Colonna-Romano, G.: Understanding ageing:Biomedical and bioengineering approaches, the immunologic view. Immunity & Ageing 5 (2008) Franceschi, C., Bonaf, M., Valensin, S.: Human immonosenescence: the prevailing of innate immunity, the failing of clonotypic immu ...
... Bulatti, M., Pellican, M., Vasto, S., Colonna-Romano, G.: Understanding ageing:Biomedical and bioengineering approaches, the immunologic view. Immunity & Ageing 5 (2008) Franceschi, C., Bonaf, M., Valensin, S.: Human immonosenescence: the prevailing of innate immunity, the failing of clonotypic immu ...
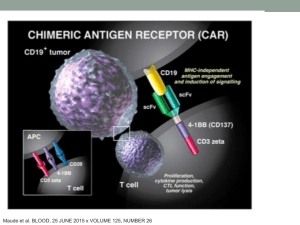
CAR T cell lecture 11.25
... • Best of both worlds of the immune system • B cell specificity • T cell cytotoxicity without presentation • Form of Adoptive T cell therapy ...
... • Best of both worlds of the immune system • B cell specificity • T cell cytotoxicity without presentation • Form of Adoptive T cell therapy ...
Project name: Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in
... They are one of the first effector cells to arrive at the site of infection and play critical roles in pathogen clearance, recruitment, as well as in activation of other immune cells. To combat microbes, neutrophils employ three major strategies: the well-known (1) phagocytosis and (2) degranulation ...
... They are one of the first effector cells to arrive at the site of infection and play critical roles in pathogen clearance, recruitment, as well as in activation of other immune cells. To combat microbes, neutrophils employ three major strategies: the well-known (1) phagocytosis and (2) degranulation ...
Acquired Immune Response
... • Highly specific attack on a specific pathogen or antigen. An antigen is a non-living particle or substance that body cannot recognize. ...
... • Highly specific attack on a specific pathogen or antigen. An antigen is a non-living particle or substance that body cannot recognize. ...
Chapter 24: The Immune System
... Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) • Note foreign protein on their surfaces • Macrophages, dendritic cells, lymphocytes ...
... Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) • Note foreign protein on their surfaces • Macrophages, dendritic cells, lymphocytes ...
Cells of inflammation and Immunity
... Detect and respond to antigens Protects against pathogenic microorganisms Also elicits response against noninfectious foreign organisms Used in inflammatory response and tissue repair ...
... Detect and respond to antigens Protects against pathogenic microorganisms Also elicits response against noninfectious foreign organisms Used in inflammatory response and tissue repair ...
546-547 Research Highlights WF SA.indd
... Fruitflies recruit distinct neural circuits when undergoing different forms of arousal — either waking from sleep, or being disturbed by puffs of air. David Anderson at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena and his colleagues found that flies with lossof-function mutations in the dopami ...
... Fruitflies recruit distinct neural circuits when undergoing different forms of arousal — either waking from sleep, or being disturbed by puffs of air. David Anderson at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena and his colleagues found that flies with lossof-function mutations in the dopami ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑