Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
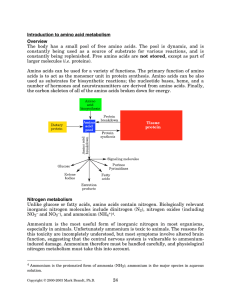
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... to a-ketoglutarate, glutamate, and glycine. All other amino acids receive their nitrogen by transfer of organic nitrogen from one amino acid to another. In amino acid metabolism, the most common nitrogen donor is glutamate, and the most common acceptor is a-ketoglutarate. This is logical, since glut ...
... to a-ketoglutarate, glutamate, and glycine. All other amino acids receive their nitrogen by transfer of organic nitrogen from one amino acid to another. In amino acid metabolism, the most common nitrogen donor is glutamate, and the most common acceptor is a-ketoglutarate. This is logical, since glut ...
Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
... Myoglobin facilitates oxygen diffusion. Oxygen storage is also a function because Myoglobin concentrations are 10-fold greater in whales and seals than in land mammals ...
... Myoglobin facilitates oxygen diffusion. Oxygen storage is also a function because Myoglobin concentrations are 10-fold greater in whales and seals than in land mammals ...
Pyruvate Oxidation and the Krebs Cycle
... ● step 3:Isocitrate (6-C) is converted to -ketoglutarate (5C) by losing a CO2 and two hydrogen atoms that reduce NAD+to NADH. ● step 4:-ketoglutarate (5-C) is converted to succinyl-CoA (4-C). A CO2 is removed, coenzyme A is added, and two hydrogen atoms reduce NAD+ to NADH. ...
... ● step 3:Isocitrate (6-C) is converted to -ketoglutarate (5C) by losing a CO2 and two hydrogen atoms that reduce NAD+to NADH. ● step 4:-ketoglutarate (5-C) is converted to succinyl-CoA (4-C). A CO2 is removed, coenzyme A is added, and two hydrogen atoms reduce NAD+ to NADH. ...
13-Krebs cycle
... Overview of Krebs cycle: The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle– is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxi ...
... Overview of Krebs cycle: The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle– is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxi ...
9/5/08 Transcript I
... (and now, the quote of the day) “Mother nature is usually very thrifty.” If you’ve got a 3 carbon intermediate in glycolysis and you need a 3 carbon amino acid, it is going to use that because it doesn’t want to waste time and energy using other things. Page 13 of “Overview of Amino Acid Metaboli ...
... (and now, the quote of the day) “Mother nature is usually very thrifty.” If you’ve got a 3 carbon intermediate in glycolysis and you need a 3 carbon amino acid, it is going to use that because it doesn’t want to waste time and energy using other things. Page 13 of “Overview of Amino Acid Metaboli ...
Plant Phenomics Teacher Resource
... The Food and Agriculture Organization (www.fao.org) predicts that the world will need to produce 70 per cent more food for the 9.1 billion people that will populate the planet by 2050. Since the late 1960s, researchers and plant breeders have been able to increase crop yields – that is, the amount o ...
... The Food and Agriculture Organization (www.fao.org) predicts that the world will need to produce 70 per cent more food for the 9.1 billion people that will populate the planet by 2050. Since the late 1960s, researchers and plant breeders have been able to increase crop yields – that is, the amount o ...
13-Krebs cycle
... The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle– is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in ...
... The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle– is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in ...
MCAS Review Booklet
... Vocabulary thylakoid photosystem stroma NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) light-dependent reactions ATP synthase Calvin cycle ...
... Vocabulary thylakoid photosystem stroma NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) light-dependent reactions ATP synthase Calvin cycle ...
Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation
... ergy. Living cells carry out three major types of work, and all are essential to life processes. Chemical work involves the synthesis of complex biological molecules required by cells from much simpler precursors; energy is needed to increase the molecular complexity of a cell. Molecules and ions of ...
... ergy. Living cells carry out three major types of work, and all are essential to life processes. Chemical work involves the synthesis of complex biological molecules required by cells from much simpler precursors; energy is needed to increase the molecular complexity of a cell. Molecules and ions of ...
Ecosystems and Human Interference
... Precipitation on land enters the ground, surface waters, or aquifers. Water eventually returns to the oceans. ...
... Precipitation on land enters the ground, surface waters, or aquifers. Water eventually returns to the oceans. ...
Alice and Lewis Carroll
... Alone in his study, the aged Dr. Faust despairs that his lifelong search for a solution to the riddle of life has been in vain. Twice he raises a goblet of poison to his lips but falters when the songs of young men and women outside his window re-awaken the unfulfilled passions and desires of his y ...
... Alone in his study, the aged Dr. Faust despairs that his lifelong search for a solution to the riddle of life has been in vain. Twice he raises a goblet of poison to his lips but falters when the songs of young men and women outside his window re-awaken the unfulfilled passions and desires of his y ...
Effects of light availability on Streptanthus bracteatus, a rare annual
... Menges 2006). Zippin’s study on the population biology of this plant identified a few possible factors contributing to its rarity (1997). First, plants found in areas with thinned or removed overstory were larger compared to those under more dense canopy. Because woody cover and canopy density in th ...
... Menges 2006). Zippin’s study on the population biology of this plant identified a few possible factors contributing to its rarity (1997). First, plants found in areas with thinned or removed overstory were larger compared to those under more dense canopy. Because woody cover and canopy density in th ...
The physiology of Curcuma alismatifolia Gagnep. as a
... roots stored only 1–2% N and were the major organ for carbohydrate storage. Arginine is the predominant free amino acid in the rhizome, and glutamic acid is the major free amino acid in the storage roots (Ruamrungsri et al., 2001). During the growing period, nitrogen uptake [from Na15NO3 and (15NH4) ...
... roots stored only 1–2% N and were the major organ for carbohydrate storage. Arginine is the predominant free amino acid in the rhizome, and glutamic acid is the major free amino acid in the storage roots (Ruamrungsri et al., 2001). During the growing period, nitrogen uptake [from Na15NO3 and (15NH4) ...
Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle Krebs Cycle Oxidative
... no ATP produced; makes NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue Part of the Cori Cycle at right ...
... no ATP produced; makes NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue Part of the Cori Cycle at right ...
Plant Structure and Function
... Surrounded by ground tissue, the system of vascular tissue transports water, mineral nutrients, and organic compounds to all parts of the plant. Plants can transport necessary fluids and nutrients throughout their systems. A plant’s vascular system is made up of two networks of hollow tubes somewhat ...
... Surrounded by ground tissue, the system of vascular tissue transports water, mineral nutrients, and organic compounds to all parts of the plant. Plants can transport necessary fluids and nutrients throughout their systems. A plant’s vascular system is made up of two networks of hollow tubes somewhat ...
2.01 structure of cells.
... that uses only one lens for magnification, and is the original light microscope.It includes a magnifying glass which is limited to a magnifying power of about ten times. Extremely small things thus can not be observed with a magnifying glass. 1.02 COMPOUND MICROSCOPE It is the one that consists of a ...
... that uses only one lens for magnification, and is the original light microscope.It includes a magnifying glass which is limited to a magnifying power of about ten times. Extremely small things thus can not be observed with a magnifying glass. 1.02 COMPOUND MICROSCOPE It is the one that consists of a ...
29
... into the blood, in muscle the cause of acidosis is different. All the glycolytic intermediates of glycolysis are weak organic acids and dissociate protons, while the degradation of ATP also results in H+ formation. This means that lactate accumulation is associated with acidosis for more than one re ...
... into the blood, in muscle the cause of acidosis is different. All the glycolytic intermediates of glycolysis are weak organic acids and dissociate protons, while the degradation of ATP also results in H+ formation. This means that lactate accumulation is associated with acidosis for more than one re ...
Vascular Seedless Plants
... The trees tower in the sky, while the mosses carpet the forest floor. Mosses, like the first plants, are restricted to life near the ground because they lack vascular system. Only with a vascular system can these trees transport sugars, nutrients, and water up and down their tall trunks. The evoluti ...
... The trees tower in the sky, while the mosses carpet the forest floor. Mosses, like the first plants, are restricted to life near the ground because they lack vascular system. Only with a vascular system can these trees transport sugars, nutrients, and water up and down their tall trunks. The evoluti ...
aipmt-2006
... A uniform rod of length l and mass m is free to rotate in a vertical plane about A. The rod initially in horizontal position is released. The initial angular acceleration of the rod is : (Moment of inertia of rod about A is (ml2/3)) ...
... A uniform rod of length l and mass m is free to rotate in a vertical plane about A. The rod initially in horizontal position is released. The initial angular acceleration of the rod is : (Moment of inertia of rod about A is (ml2/3)) ...
ATP - RCSD
... • Stage 3: Oxidative phosphorylation • As the electron transport chain passes electrons down the energy hill, it also pumps hydrogen ions (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane, into the narrow intermembrane space, and produces a concentration gradient of H+ across the membrane. • In chemiosmo ...
... • Stage 3: Oxidative phosphorylation • As the electron transport chain passes electrons down the energy hill, it also pumps hydrogen ions (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane, into the narrow intermembrane space, and produces a concentration gradient of H+ across the membrane. • In chemiosmo ...
05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and
... • In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... • In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Chapter 2 - Water - Technicalsymposium
... 1) globular - spherical; water-soluble molecules with a hydrophobic interior and hydrophobic surface; have mostly functional roles in the cell, e.g. enzymes 2) fibrous - made into threads or cables with repeating units; water-insoluble molecules that provide mechanical or structural support, e.g. ...
... 1) globular - spherical; water-soluble molecules with a hydrophobic interior and hydrophobic surface; have mostly functional roles in the cell, e.g. enzymes 2) fibrous - made into threads or cables with repeating units; water-insoluble molecules that provide mechanical or structural support, e.g. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.