Ecological Pyramids pp
... Ecological Pyramids 1. energy pyramid – shows energy flow through a food chain 2. biomass pyramid- shows the mass in grams of organisms at each trophic level 3. numbers pyramid- shows the number of organisms at each trophic level ...
... Ecological Pyramids 1. energy pyramid – shows energy flow through a food chain 2. biomass pyramid- shows the mass in grams of organisms at each trophic level 3. numbers pyramid- shows the number of organisms at each trophic level ...
1) Which of the following is not true of
... 10. The kidneys use energy to move molecules and ions in order to keep the blood chemically balanced. This process is an example of cells using energy for what purpose? A B C D ...
... 10. The kidneys use energy to move molecules and ions in order to keep the blood chemically balanced. This process is an example of cells using energy for what purpose? A B C D ...
Semester Review
... What are the 4 parts of cell theory? a. All living things are made of cells b. All cells come from existing cells c. Cells are the basic unit of life d. Cells in multicellular organisms have specific jobs List the functions that are performed by every cell. a. Receive nutrients b. Exchange carbon d ...
... What are the 4 parts of cell theory? a. All living things are made of cells b. All cells come from existing cells c. Cells are the basic unit of life d. Cells in multicellular organisms have specific jobs List the functions that are performed by every cell. a. Receive nutrients b. Exchange carbon d ...
Chapter 2 - Jenksps.org
... the organism by itself populations, communities, and ecosystems. 7. Organism: An ___________________living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds, grows, and develops. 8. Population: a group of organisms, all of the__________________________, which interbreed and live in the ...
... the organism by itself populations, communities, and ecosystems. 7. Organism: An ___________________living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds, grows, and develops. 8. Population: a group of organisms, all of the__________________________, which interbreed and live in the ...
Document
... not directly from acetyl-CoA. The carbons donated by acetyl-CoA become part of the oxaloacetate carbon backbone after the first turn of the citric acid cycle. Loss of the acetyl-CoA-donated carbons as CO2 requires several turns of the citric acid cycle. However, because of the role of the citric aci ...
... not directly from acetyl-CoA. The carbons donated by acetyl-CoA become part of the oxaloacetate carbon backbone after the first turn of the citric acid cycle. Loss of the acetyl-CoA-donated carbons as CO2 requires several turns of the citric acid cycle. However, because of the role of the citric aci ...
Cellular Respiration
... eukaryotic cells it is in the mitochondria. It does not refer to ‘breathing’ although it requires oxygen. ...
... eukaryotic cells it is in the mitochondria. It does not refer to ‘breathing’ although it requires oxygen. ...
L9 PS Variations Fa08
... • Stomata need to be open for gas exchange – No incoming CO2, then low input for Calvin cycle • Stomata need to be closed to prevent excessive water loss – If water in the soil is limited, and – The day is hot or dry ...
... • Stomata need to be open for gas exchange – No incoming CO2, then low input for Calvin cycle • Stomata need to be closed to prevent excessive water loss – If water in the soil is limited, and – The day is hot or dry ...
biology 103 final exam review sheet
... 31. Types of chemical reactions based on energy flow 32. Specific types of chemical reactions 33. Enzymes a. Characteristics b. Define substrate, active site c. Factors that influence enzyme activity 34. ATP-what is this? a. ATP/ADP cycle 35. Equation for photosynthesis 36. Types of plant pigments 3 ...
... 31. Types of chemical reactions based on energy flow 32. Specific types of chemical reactions 33. Enzymes a. Characteristics b. Define substrate, active site c. Factors that influence enzyme activity 34. ATP-what is this? a. ATP/ADP cycle 35. Equation for photosynthesis 36. Types of plant pigments 3 ...
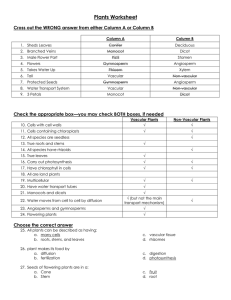
Plants Worksheet_answer key - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... Check the appropriate box—you may check BOTH boxes, if needed 10. Cells with cell walls 11. Cells containing chloroplasts ...
... Check the appropriate box—you may check BOTH boxes, if needed 10. Cells with cell walls 11. Cells containing chloroplasts ...
Properties of Water
... Chemical Bonds: Ionic • Electrons transferred from one atom to another • Ex: NaCl (salt) • Importance to biology: many salts are made this way (homeostatic balance) ...
... Chemical Bonds: Ionic • Electrons transferred from one atom to another • Ex: NaCl (salt) • Importance to biology: many salts are made this way (homeostatic balance) ...
Section 7.1 Describing Reactions
... of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. 4. Circle the letter of the correct answer. According to the equation C ⫹ O2 h CO2, how many carbon atoms react with 14 molecules of oxygen to form 14 molecules of carbon dioxide? a. 1 ...
... of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. 4. Circle the letter of the correct answer. According to the equation C ⫹ O2 h CO2, how many carbon atoms react with 14 molecules of oxygen to form 14 molecules of carbon dioxide? a. 1 ...
Date ______ Mid-Term Review Name _______________ Chapter 1
... 5. Why are theories different from hypotheses? Hypotheses refer to specific single questions that are then united by theories. Theories are supported by wide bodies of evidence and many hypotheses that have been accepted. Theories are accepted as true, but are not facts. 6. Science is a way of __kno ...
... 5. Why are theories different from hypotheses? Hypotheses refer to specific single questions that are then united by theories. Theories are supported by wide bodies of evidence and many hypotheses that have been accepted. Theories are accepted as true, but are not facts. 6. Science is a way of __kno ...
1. Emissions can be controlled by using devices that capture
... acids fall as acid rain, slowly deteriorating building surfaces. Smoke and soot also coat buildings. 4. It was the first scientific and governmental recognition of the problem of air pollution. The law increased public awareness of the problem. (6/3) 5.Answers include conservation of energy and redu ...
... acids fall as acid rain, slowly deteriorating building surfaces. Smoke and soot also coat buildings. 4. It was the first scientific and governmental recognition of the problem of air pollution. The law increased public awareness of the problem. (6/3) 5.Answers include conservation of energy and redu ...
Molecules to metabolism
... terms of the chemical substances involved - Carbon atoms can form four bonds allowing a diversity of compounds to exist - Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids - Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism ...
... terms of the chemical substances involved - Carbon atoms can form four bonds allowing a diversity of compounds to exist - Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids - Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism ...
AS-biology answers
... Proteins are made from amino acids (1). The amino acids are joined together in a long (polypeptide) chain (1). The sequence of amino acids is the proteins primary structure (1). The amino acid chain / polypeptide coils in a certain way (1). The way its coiled is the proteins secondary structure (1). ...
... Proteins are made from amino acids (1). The amino acids are joined together in a long (polypeptide) chain (1). The sequence of amino acids is the proteins primary structure (1). The amino acid chain / polypeptide coils in a certain way (1). The way its coiled is the proteins secondary structure (1). ...
flowers - mitchelltechblitz2010
... The small shoot then begins to develop leaves that contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll contains pigments that take in energy from the sun and convert it to carbon dioxide and water into sugars—the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis allows the plant to feed itself and continue to grow. The plant ...
... The small shoot then begins to develop leaves that contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll contains pigments that take in energy from the sun and convert it to carbon dioxide and water into sugars—the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis allows the plant to feed itself and continue to grow. The plant ...
Chapter_7 - South Johnston High School
... Biochemistry of Seaweeds • Photosynthetic pigments – Due to wavelengths of light not absorbed by seaweed pigments – Chlorophyll absorbs blue and red wavelengths of light • Pass green light ...
... Biochemistry of Seaweeds • Photosynthetic pigments – Due to wavelengths of light not absorbed by seaweed pigments – Chlorophyll absorbs blue and red wavelengths of light • Pass green light ...
Biology First Semester Study Questions
... 11. DNA, RNA 12. DNA= heredity codes; RNA= protein synthesis 13. both 14. animal structures, enzymes, stores nutrients, defend against disease 15. both 16. speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy 17. Denaturation means an enzyme changes shape, making it useless. Two causes are heat ...
... 11. DNA, RNA 12. DNA= heredity codes; RNA= protein synthesis 13. both 14. animal structures, enzymes, stores nutrients, defend against disease 15. both 16. speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy 17. Denaturation means an enzyme changes shape, making it useless. Two causes are heat ...
biolablecturefinalal..
... Seaweed. 50-100 meters long. Fucoxanthan masks chlorophyll. Algin is the base material for pectin Rhodophyta (red algae) Phycoerythin masks green. 200 meters. They absorb blue and violet light. Red algae makes agar. Carrogeenan is an ingredient in chocolate milk. Bacilliarophyta (diatoms chrysop ...
... Seaweed. 50-100 meters long. Fucoxanthan masks chlorophyll. Algin is the base material for pectin Rhodophyta (red algae) Phycoerythin masks green. 200 meters. They absorb blue and violet light. Red algae makes agar. Carrogeenan is an ingredient in chocolate milk. Bacilliarophyta (diatoms chrysop ...
Document
... that allow them to attain stable arrangements of electrons. In the stratosphere free radicals can combine with oxygen molecules to form ozone. A third molecule, typically nitrogen gas or atmospheric oxygen (represented by M in the equation), carries away excess energy from the reaction but remains u ...
... that allow them to attain stable arrangements of electrons. In the stratosphere free radicals can combine with oxygen molecules to form ozone. A third molecule, typically nitrogen gas or atmospheric oxygen (represented by M in the equation), carries away excess energy from the reaction but remains u ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.