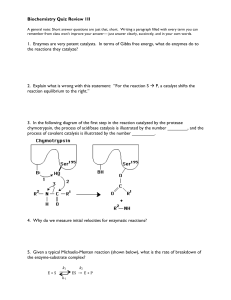
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1II 1. Enzymes are very potent catalysts
... 28. When glucose labeled with a 14C at C-2 passes through glycolysis, the glyceraldehyde 3phosphate that is produced from it still contains the radioactive carbon atom. Draw the structure of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and circle the atom(s) that would be radioactive. ...
... 28. When glucose labeled with a 14C at C-2 passes through glycolysis, the glyceraldehyde 3phosphate that is produced from it still contains the radioactive carbon atom. Draw the structure of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and circle the atom(s) that would be radioactive. ...
File - Grange Academy
... State that green plants make their own food which may be stored as starch Green plants are able to make their own food. They make the food in the form of sugar. The sugar may be used by the plant straight away or converted to starch and stored. Plants use the process of photosynthesis to make ...
... State that green plants make their own food which may be stored as starch Green plants are able to make their own food. They make the food in the form of sugar. The sugar may be used by the plant straight away or converted to starch and stored. Plants use the process of photosynthesis to make ...
Friday Calvin Cycle How you will always remember… Rubisco
... then it would have developed a more specific binding site for CO2 to avoid compe55on with O2 ...
... then it would have developed a more specific binding site for CO2 to avoid compe55on with O2 ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF ALL PLANTS
... promotespollination. Angiosperm pollen will be observed during the flower dissection. ...
... promotespollination. Angiosperm pollen will be observed during the flower dissection. ...
Plants Study Guide
... 11. Define sepals: small leaf-like part of the flower that protects the developing petals ...
... 11. Define sepals: small leaf-like part of the flower that protects the developing petals ...
Where can water be found?
... create glucose (C6H12O6) We then eat plants and break down that glucose for energy (ATP) in a process called cellular respiration. The carbon molecules we take from the glucose are then exhaled as carbon dioxide that plants can use. Plants also give off the oxygen we need to perform cellular res ...
... create glucose (C6H12O6) We then eat plants and break down that glucose for energy (ATP) in a process called cellular respiration. The carbon molecules we take from the glucose are then exhaled as carbon dioxide that plants can use. Plants also give off the oxygen we need to perform cellular res ...
BreBrewton
... roots, stems, and leafs. The reproductive organs are variables. Photosynthesis and respiration are both apart of the metabolism of a flower, The flowers respiration version of the human action respiration is photosynthesis. There's only four parts to a flower: calyx, corolla, stamens, and gynoecium. ...
... roots, stems, and leafs. The reproductive organs are variables. Photosynthesis and respiration are both apart of the metabolism of a flower, The flowers respiration version of the human action respiration is photosynthesis. There's only four parts to a flower: calyx, corolla, stamens, and gynoecium. ...
Genomic foundations of carbon fixation in bacteria living in hot springs
... Mentor - Brian Hedlund Photosynthesis does not occur above 73°C, so organisms living above this temperature must obtain useable carbon by some other mechanism. It is generally assumed that carbon is fixed by thermophiles through the process of chemolithoautotrophy; however, primary production has ne ...
... Mentor - Brian Hedlund Photosynthesis does not occur above 73°C, so organisms living above this temperature must obtain useable carbon by some other mechanism. It is generally assumed that carbon is fixed by thermophiles through the process of chemolithoautotrophy; however, primary production has ne ...
2-A Chemical Compounds of Life Organic Compounds
... a) Provide structure, transport substances, act as chemical messengers, control chemical reactions, and control cell growth b) Built from amino acids • Each has a carboxyl group (COOH) & amino group (NH2) • variable group makes one a.a. different from another c) Polypeptide: made from many a.a. ...
... a) Provide structure, transport substances, act as chemical messengers, control chemical reactions, and control cell growth b) Built from amino acids • Each has a carboxyl group (COOH) & amino group (NH2) • variable group makes one a.a. different from another c) Polypeptide: made from many a.a. ...
Chapter 9 - Mrs. O`Hare Barrows` Classroom Web
... made by producers, or by eating other consumers. Examples of producers are flowers, corn and grass. Examples of consumers are flies, humans and lions. ...
... made by producers, or by eating other consumers. Examples of producers are flowers, corn and grass. Examples of consumers are flies, humans and lions. ...
You Light Up My Life
... Regions of Deforestation • Rates of forest loss are greatest in Brazil, Indonesia, Mexico, and Columbia • Highly mechanized logging is proceeding in temperate forests of the United States and Canada ...
... Regions of Deforestation • Rates of forest loss are greatest in Brazil, Indonesia, Mexico, and Columbia • Highly mechanized logging is proceeding in temperate forests of the United States and Canada ...
Chapter 13 - missdannocksyear11biologyclass
... One extreme condition faced by many plants in Australia is fire. Trees like Eucalypts have adaptations which help them to survive and regenerate after fire. These include: - Having thick bark which protects the inner cambium layer which is the tissue which produces new growth of bark and stem tissue ...
... One extreme condition faced by many plants in Australia is fire. Trees like Eucalypts have adaptations which help them to survive and regenerate after fire. These include: - Having thick bark which protects the inner cambium layer which is the tissue which produces new growth of bark and stem tissue ...
final biology review powerpoint
... All animal life on Earth (including humans) depends on the oxygen produced by photosynthesis! ...
... All animal life on Earth (including humans) depends on the oxygen produced by photosynthesis! ...
Biology Objective 3
... land run-off, dumping of wastes and excess heat directly into lakes, oceans and rivers. ...
... land run-off, dumping of wastes and excess heat directly into lakes, oceans and rivers. ...
final biology review powerpoint
... All animal life on Earth (including humans) depends on the oxygen produced by photosynthesis! ...
... All animal life on Earth (including humans) depends on the oxygen produced by photosynthesis! ...
Paracoccus denitrificans
... Bacteriorhodopsin-Based Phototrophy • Some archaea use a type of phototrophy that involves bacteriorhodopsin, a membrane protein which functions as a light-driven proton pump • a proton motive force is generated • an electron transport chain is not involved ...
... Bacteriorhodopsin-Based Phototrophy • Some archaea use a type of phototrophy that involves bacteriorhodopsin, a membrane protein which functions as a light-driven proton pump • a proton motive force is generated • an electron transport chain is not involved ...
Document
... • Photosynthesis – conversion of carbon dioxide into sugars by plants using the sun as a source of energy • Respiration – conversion of sugars into carbon dioxide to release energy used by organisms ...
... • Photosynthesis – conversion of carbon dioxide into sugars by plants using the sun as a source of energy • Respiration – conversion of sugars into carbon dioxide to release energy used by organisms ...
Slide 1
... A. Sunlight—plants have adaptations to gather sunlight for photosynthesis B. Water and minerals—all cells require a constant supply of water. Minerals are absorbed along with water. C. Gas exchange—plants must exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) to perform photosynthesis D. Movement of water ...
... A. Sunlight—plants have adaptations to gather sunlight for photosynthesis B. Water and minerals—all cells require a constant supply of water. Minerals are absorbed along with water. C. Gas exchange—plants must exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) to perform photosynthesis D. Movement of water ...
Chemical Reaction
... The smallest units of matter; combines with other atoms to form molecules. Both living and nonliving things are made from atoms. ...
... The smallest units of matter; combines with other atoms to form molecules. Both living and nonliving things are made from atoms. ...
Microbial Metabolism Overview
... Fermentation If a cell runs out of electron acceptor (O2 or N or S), respiration can only proceed through glycolysis. Prokaryotes – some only go this far to make energy, they only do fermentation and do not have the capability to do respiration. 6C molecule (glucose) → two 3 carbon molecules (pyruva ...
... Fermentation If a cell runs out of electron acceptor (O2 or N or S), respiration can only proceed through glycolysis. Prokaryotes – some only go this far to make energy, they only do fermentation and do not have the capability to do respiration. 6C molecule (glucose) → two 3 carbon molecules (pyruva ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.