Processes of Life
... Cells contain hereditary information that is passed on to new cells Cells have the same chemical composition within a species ...
... Cells contain hereditary information that is passed on to new cells Cells have the same chemical composition within a species ...
Ecology
... Energetic Hypothesis—food chain can’t be long because there is an insufficient transfer of energy (10% Rule) ...
... Energetic Hypothesis—food chain can’t be long because there is an insufficient transfer of energy (10% Rule) ...
cellular respiration
... Oxygen is not the only possible electron acceptor in the oxidation of glucose in a cell. obligate anaerobes – micro-organisms that use NO2, SO4, CO2 as final electron acceptors (cannot live in the presence of oxygen) obligate aerobes – most animals, plants, fungi and bacteria require oxygen as the f ...
... Oxygen is not the only possible electron acceptor in the oxidation of glucose in a cell. obligate anaerobes – micro-organisms that use NO2, SO4, CO2 as final electron acceptors (cannot live in the presence of oxygen) obligate aerobes – most animals, plants, fungi and bacteria require oxygen as the f ...
Krebs Cycle
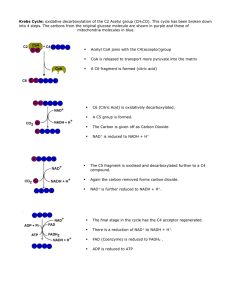
... Krebs Cycle: oxidative decarboxylation of the C2 Acetyl group (CH3CO). This cycle has been broken down into 4 steps. The carbons from the original glucose molecule are shown in purple and those of mitochondria molecules in blue. ...
... Krebs Cycle: oxidative decarboxylation of the C2 Acetyl group (CH3CO). This cycle has been broken down into 4 steps. The carbons from the original glucose molecule are shown in purple and those of mitochondria molecules in blue. ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint Notes
... 1. Volcanoes, respiration, fossil fuels, and decomposition add CO2 to atmosphere. 2. Plants take CO2 and make carbohydrates 3. Plants are eaten by animals and carbohydrates are passed through the food chain. 4. As the animal breathes and eventually dies and decomposes CO2 is return to atmosphere. ...
... 1. Volcanoes, respiration, fossil fuels, and decomposition add CO2 to atmosphere. 2. Plants take CO2 and make carbohydrates 3. Plants are eaten by animals and carbohydrates are passed through the food chain. 4. As the animal breathes and eventually dies and decomposes CO2 is return to atmosphere. ...
Photosynthesis
... Photorespiration consumes O2 and organic fuel and releases CO2 without producing ATP or sugar ...
... Photorespiration consumes O2 and organic fuel and releases CO2 without producing ATP or sugar ...
Principles of Ecology BL / ENVS 402 Exam I 9-22-2008
... a. a net input; warmer than b. a net input; colder than c. a net output; warmer than d. a net output; colder than e. a zero net change; the same as 18. In the summer, leaves of E. farinosa show _______ pubescence than in the winter. The change in pubescence is an example of _______. a. greater; adap ...
... a. a net input; warmer than b. a net input; colder than c. a net output; warmer than d. a net output; colder than e. a zero net change; the same as 18. In the summer, leaves of E. farinosa show _______ pubescence than in the winter. The change in pubescence is an example of _______. a. greater; adap ...
Exam Review 2 10/2/16
... 8. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? A. 3 B. 6 C. 9 D. 12 E. It can’t be done 9. During what stage of photosynthesis are ATP and NADPH converted to ADP + Pi and NADP+? A. The light dependent reactions B. The light independent reactions C. Both of the above D. None of the above ...
... 8. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? A. 3 B. 6 C. 9 D. 12 E. It can’t be done 9. During what stage of photosynthesis are ATP and NADPH converted to ADP + Pi and NADP+? A. The light dependent reactions B. The light independent reactions C. Both of the above D. None of the above ...
An ULTIMATE Study Guide for Semester 1
... Mitochondria: An organelle in the cytoplasm of cells that functions in energy (ATP) production ...
... Mitochondria: An organelle in the cytoplasm of cells that functions in energy (ATP) production ...
Name__________________________________________
... ATP to light Light to chemical Heat to electrical Chemical to chemical ...
... ATP to light Light to chemical Heat to electrical Chemical to chemical ...
Study-Guide-Bio-9-Sem1
... 46. During photosynthesis, the energy from the sun splits the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. What happens to the oxygen during the process of photosynthesis? (117) 47. Plants produce large amounts of oxygen during photosynthesis because…(Hint: See #14). (pg. 117) 48. An acorn weighs appro ...
... 46. During photosynthesis, the energy from the sun splits the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. What happens to the oxygen during the process of photosynthesis? (117) 47. Plants produce large amounts of oxygen during photosynthesis because…(Hint: See #14). (pg. 117) 48. An acorn weighs appro ...
science - WordPress.com
... Give one example each of a rhizome, a corm, a stem tuber, a bulb and a sucker. State two reasons why a rhizome, a corm and a stem tuber are considered as stems. ...
... Give one example each of a rhizome, a corm, a stem tuber, a bulb and a sucker. State two reasons why a rhizome, a corm and a stem tuber are considered as stems. ...
Cell Energyrespiration
... • Cells require a constant source of energy for life processes but keep only a small amount of ATP on hand. • Cells can regenerate ATP as needed by using the energy stored in foods like glucose. • The energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is released by cellular respiration and repackaged into ...
... • Cells require a constant source of energy for life processes but keep only a small amount of ATP on hand. • Cells can regenerate ATP as needed by using the energy stored in foods like glucose. • The energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is released by cellular respiration and repackaged into ...
Chapter 7 How are Plants Classified
... down what you come up with! You will have approximately 15 minutes to do this (and do it WELL!) You will be sharing your thoughts! ...
... down what you come up with! You will have approximately 15 minutes to do this (and do it WELL!) You will be sharing your thoughts! ...
Mattie Knebel Kyler Salazar Jared Hansen Biology 1610 Sperry
... After this, ADP is added and takes the phosphate group, leaving only the two separate 3 Carbon molecules called Pyruvate. This cycle takes place in the cytosol, located just outside of the mitochondria. This process has a net gain of 2 ATP which is then carried on to the next cycle. Diagram A, whic ...
... After this, ADP is added and takes the phosphate group, leaving only the two separate 3 Carbon molecules called Pyruvate. This cycle takes place in the cytosol, located just outside of the mitochondria. This process has a net gain of 2 ATP which is then carried on to the next cycle. Diagram A, whic ...
Study Guide : Life Science
... petal : decorative leaf like part phloem : tubing of vascular system responsible for distributing food through plant pistil : female part of flower sepal : specialized leaf to protect bud and support flower xylem : vascular tubing in center of stem responsible for bringing up water to rest ...
... petal : decorative leaf like part phloem : tubing of vascular system responsible for distributing food through plant pistil : female part of flower sepal : specialized leaf to protect bud and support flower xylem : vascular tubing in center of stem responsible for bringing up water to rest ...
Decomposers and Autotrophs - Penn State York Home Page
... – Anamorphs (asexual forms) of Ascomycota and some Basidiomycota are most abundant on detritus (leaves, wood). – Along with bacteria, they increase the nutritional quality of detritus. – Some are very adapted for this role in aquatic environments (see example of amphibious fungi below ...
... – Anamorphs (asexual forms) of Ascomycota and some Basidiomycota are most abundant on detritus (leaves, wood). – Along with bacteria, they increase the nutritional quality of detritus. – Some are very adapted for this role in aquatic environments (see example of amphibious fungi below ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Duplin County Schools
... • Enzymes regulate many chemical reactions such as: – Photosynthesis – Cellular respiration – Digestion ...
... • Enzymes regulate many chemical reactions such as: – Photosynthesis – Cellular respiration – Digestion ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... Some organisms, such as yeast and some bacteria, do not require oxygen and can survive on a less efficient way of getting energy Other organisms that generally require oxygen sometimes don’t have enough for all their cells to do aerobic respiration so they can use a less effiecent way of breaking do ...
... Some organisms, such as yeast and some bacteria, do not require oxygen and can survive on a less efficient way of getting energy Other organisms that generally require oxygen sometimes don’t have enough for all their cells to do aerobic respiration so they can use a less effiecent way of breaking do ...
一、專有名詞(簡潔回答以下專有名詞)
... A.Nitrogen fixation is done solely by bacteria. B.When plants and animals die, their nitrogen is recycled. C.It requires different types of bacteria. D.Plants can take in and utilize atmospheric nitrogen using their leaves. E.Nitrogen needs to be cycled through living organisms. 10.Which of the foll ...
... A.Nitrogen fixation is done solely by bacteria. B.When plants and animals die, their nitrogen is recycled. C.It requires different types of bacteria. D.Plants can take in and utilize atmospheric nitrogen using their leaves. E.Nitrogen needs to be cycled through living organisms. 10.Which of the foll ...
Gas Exchange in Plants
... dioxide and give off oxygen. But plants also respire constantly, absorbing oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide. During the day, both photosynthesis and respiration occur simultaneously in the leaf. Both photosynthesis and respiration require the leaf to exchange gases with its environment. At the s ...
... dioxide and give off oxygen. But plants also respire constantly, absorbing oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide. During the day, both photosynthesis and respiration occur simultaneously in the leaf. Both photosynthesis and respiration require the leaf to exchange gases with its environment. At the s ...
Carbon
... Overview of the carbon reactions • The Calvin cycle: • Stage 2: – Each of the two 3-phosphycerate molecules are altered. – First phosphorylated through the use of the 3 ATPs generated during the light reaction. – Then reduced through the use of the 2 NADPHs generated during the light reaction. – Fo ...
... Overview of the carbon reactions • The Calvin cycle: • Stage 2: – Each of the two 3-phosphycerate molecules are altered. – First phosphorylated through the use of the 3 ATPs generated during the light reaction. – Then reduced through the use of the 2 NADPHs generated during the light reaction. – Fo ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.