Lecture, Gene Expression
... After DNA Replication, there is enough DNA make 2 new cells… and then again, and again until the organism stops performing cell division (i.e., never, really). Once a new cell is made, it can begin to use the DNA to create phenotypes. We call this next part Gene Expression, or the production of a ph ...
... After DNA Replication, there is enough DNA make 2 new cells… and then again, and again until the organism stops performing cell division (i.e., never, really). Once a new cell is made, it can begin to use the DNA to create phenotypes. We call this next part Gene Expression, or the production of a ph ...
Genetic Information DNA - Barnegat Township School District
... that affect a gene or a gene control region (Note: not all of our DNA is genes, lots of 'filler' DNA) • Mutations can occur spontaneously (very rare) or can be caused by exposure to certain agents (UV rays, radiation, chemicals) • Different types of mutations: insertions, deletions, substitutions. ...
... that affect a gene or a gene control region (Note: not all of our DNA is genes, lots of 'filler' DNA) • Mutations can occur spontaneously (very rare) or can be caused by exposure to certain agents (UV rays, radiation, chemicals) • Different types of mutations: insertions, deletions, substitutions. ...
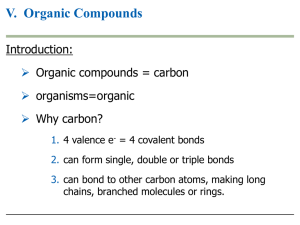
What are organic compounds?
... • Lysis = to split apart (or breakdown) • Hydrolysis = process by which complex molecules are broken down to form simple molecules by adding water. ...
... • Lysis = to split apart (or breakdown) • Hydrolysis = process by which complex molecules are broken down to form simple molecules by adding water. ...
Essential amino acids
... III. The metabolism of α-ketoacid Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids TCA cycle member + amino acid α-keto acid + nonessential ...
... III. The metabolism of α-ketoacid Biosynthesis of nonessential amino acids TCA cycle member + amino acid α-keto acid + nonessential ...
notes for mondays lab
... 1. Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS): a salty solution of constant pH to keep tissues, cells, and proteins intact during maceration 2. Proteinase K: an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution t ...
... 1. Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS): a salty solution of constant pH to keep tissues, cells, and proteins intact during maceration 2. Proteinase K: an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution t ...
Unit Topic: Chemistry of Life
... Broad Concept: All life is built out of four essential molecules: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbon compounds: 1. Organic means made from carbon - CHONPS (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur) 2. Protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids 3. Draw ...
... Broad Concept: All life is built out of four essential molecules: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbon compounds: 1. Organic means made from carbon - CHONPS (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur) 2. Protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids 3. Draw ...
Macromolecules: Proteins
... 2. Proteins also act as __________ in cells to control reactions. 3. Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. _________________________________________________ 4. Cells have ___________________ of enzymes to act as biological ___________________. 5. Enzymes have an attachment site called the ___ ...
... 2. Proteins also act as __________ in cells to control reactions. 3. Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. _________________________________________________ 4. Cells have ___________________ of enzymes to act as biological ___________________. 5. Enzymes have an attachment site called the ___ ...
(key)
... b. What is the main functionality/functional group of the compounds you choose above that gives rise to their ability to harvest light. C6n.J"J~d Aoublt B;;.J; ...
... b. What is the main functionality/functional group of the compounds you choose above that gives rise to their ability to harvest light. C6n.J"J~d Aoublt B;;.J; ...
Chemistry of Proteins Model Making
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...
Fatty oxidation, Amino acid degradation and energy metabolism
... 10. Ammonia toxicity leads to depletion of ATP in brain. Explain How? 11. How many ATP molecules will be produced if Alanine or Serine or Cysteine is completely catabolized? (Calculate 3ATP/NADH and 2ATP/FADH2). 12. Which metabolic pathway is defective in Maple syrup urine disease? Name the enzyme a ...
... 10. Ammonia toxicity leads to depletion of ATP in brain. Explain How? 11. How many ATP molecules will be produced if Alanine or Serine or Cysteine is completely catabolized? (Calculate 3ATP/NADH and 2ATP/FADH2). 12. Which metabolic pathway is defective in Maple syrup urine disease? Name the enzyme a ...
Functional groups - Montgomery County Schools
... 2. Phospholipids -important part of cell membrane 3. Steroids -lipids made of fused ring structures • cholesterol a steroid that plays a significant role in the structure of the cell membrane & sex hormones 4. Waxes – cuticle coating on plants ...
... 2. Phospholipids -important part of cell membrane 3. Steroids -lipids made of fused ring structures • cholesterol a steroid that plays a significant role in the structure of the cell membrane & sex hormones 4. Waxes – cuticle coating on plants ...
Quale Vita? - uniroma1.it
... constant, in some cases they do not make H bonds with solutes, in other cases they attack the organic material (e.g. ammonia) ...
... constant, in some cases they do not make H bonds with solutes, in other cases they attack the organic material (e.g. ammonia) ...
Translation March 32, 2009000 *10-3
... Catalyst Review HW Review Transcription/Central Dogma Review ...
... Catalyst Review HW Review Transcription/Central Dogma Review ...
Notes
... • DNA holds instructions to make a protein • Instructions are copied into mRNA, which will be used to make a protein • Codon - each three-nucleotide sequence of an mRNA molecule • Each codon represents 1 amino acid • There are 64 possible codons, and only 20 amino acids, so most amino acids have mor ...
... • DNA holds instructions to make a protein • Instructions are copied into mRNA, which will be used to make a protein • Codon - each three-nucleotide sequence of an mRNA molecule • Each codon represents 1 amino acid • There are 64 possible codons, and only 20 amino acids, so most amino acids have mor ...
supp-MBS 103-B
... Note: 1. Attempt all questions and return this part of the question paper to the invigilator after 20 Minutes. 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
... Note: 1. Attempt all questions and return this part of the question paper to the invigilator after 20 Minutes. 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
Biomolecules
... the fatty acid chains it forms a carboxyl group between them •They link by the loss of a water molecule. animation ...
... the fatty acid chains it forms a carboxyl group between them •They link by the loss of a water molecule. animation ...
A1984SZ47200001
... homocystine to cystathionine. Since then, to examine the children and was impressed three genetically determined enzyme deby the similarity and unusual nature of their fects are now known in the remethylation symptoms, i.e., mental retardation, fits, ec- pathway from homocystine to methamine. topia ...
... homocystine to cystathionine. Since then, to examine the children and was impressed three genetically determined enzyme deby the similarity and unusual nature of their fects are now known in the remethylation symptoms, i.e., mental retardation, fits, ec- pathway from homocystine to methamine. topia ...
Goal 2.01 Quiz 2
... Which choice best explains why unsaturated fats are considered healthier to eat than saturated fats? A. Unsaturated fats are made of lipids that melt easily and are less likely to deposit as solid fat on blood vessels. B. Saturated fats are made of lipids that melt easily and are less likely to dep ...
... Which choice best explains why unsaturated fats are considered healthier to eat than saturated fats? A. Unsaturated fats are made of lipids that melt easily and are less likely to deposit as solid fat on blood vessels. B. Saturated fats are made of lipids that melt easily and are less likely to dep ...
The Living World
... An organic molecule consists of a carbon-based core with special groups attached These groups have special properties and are referred to as functional groups Organisms are primarily made of four kinds of molecules ...
... An organic molecule consists of a carbon-based core with special groups attached These groups have special properties and are referred to as functional groups Organisms are primarily made of four kinds of molecules ...
Download PDF
... Biochemistry is the study of the variety of chemical structures and chemical reactions that occur in living organisms. In order to truly understand the detailed mechanisms of these diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and ap ...
... Biochemistry is the study of the variety of chemical structures and chemical reactions that occur in living organisms. In order to truly understand the detailed mechanisms of these diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and ap ...
Section 1.3 Name:
... that it contains the sugar ____________________ instead of _____________________. The second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g ...
... that it contains the sugar ____________________ instead of _____________________. The second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g ...
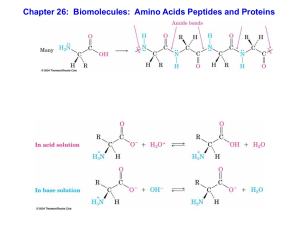
Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids Peptides and Proteins
... Draw Fisher diagrams of L-Alanine (R = CH3) and L-cysteine (R = CH2-SH) and assign stereochemistry as R or S ...
... Draw Fisher diagrams of L-Alanine (R = CH3) and L-cysteine (R = CH2-SH) and assign stereochemistry as R or S ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.