Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... Describe the major steps involved in DNA Replication & the function of the enzymes we discussed in class (DNA polymerase I, III, Helicase, Primase, LIgase). Form of the free nucleiotides? Be sure to thoroughly compare and contrast continuous DNA replication & discontinuous DNA replication? (remember ...
... Describe the major steps involved in DNA Replication & the function of the enzymes we discussed in class (DNA polymerase I, III, Helicase, Primase, LIgase). Form of the free nucleiotides? Be sure to thoroughly compare and contrast continuous DNA replication & discontinuous DNA replication? (remember ...
EOC Macromolecules
... One category of organic compounds contains molecules composed of long hydrocarbon chains. The hydrocarbon chains may be saturated or unsaturated. ...
... One category of organic compounds contains molecules composed of long hydrocarbon chains. The hydrocarbon chains may be saturated or unsaturated. ...
DNA and Mutations Power Point
... doesn't change due to the DNA mutation missense mutations cause an amino acid substitution (sicklecell anemia), these mutations may reduce or disable protein function codon has a point or shift change that causes the translation process to be terminated too early frame-shift is when a single-base is ...
... doesn't change due to the DNA mutation missense mutations cause an amino acid substitution (sicklecell anemia), these mutations may reduce or disable protein function codon has a point or shift change that causes the translation process to be terminated too early frame-shift is when a single-base is ...
Translation - clemson.edu
... 7. The ribosome reads the mRNA… how many nucleotides at a time? 3 8. What is a codon? Each group of 3 nucleotides 9. What is the start codon that the ribosome looks for? AUG 10. What brings the amino acids to the mRNA strand and ribosome? A tRNA 11. What is the significance of the start codon? It te ...
... 7. The ribosome reads the mRNA… how many nucleotides at a time? 3 8. What is a codon? Each group of 3 nucleotides 9. What is the start codon that the ribosome looks for? AUG 10. What brings the amino acids to the mRNA strand and ribosome? A tRNA 11. What is the significance of the start codon? It te ...
Free Form Amino Acids
... natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body must first break these molecular (pepetide) bonds for amino acid absorption to take place. Solgar's free form amino acids are already in their simplest form (no peptide bonds) and can be r ...
... natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body must first break these molecular (pepetide) bonds for amino acid absorption to take place. Solgar's free form amino acids are already in their simplest form (no peptide bonds) and can be r ...
Examination questions
... 53. Catabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine; metabolic disorders of their catabolism (phenylketonuria, tyrosinemia, alkaptonuria). 54. Hydroxylation of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan (coenzyme, phenylketonuria, DOPA, serotonin). 55. Significance and the basic features of the branched-chain ...
... 53. Catabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine; metabolic disorders of their catabolism (phenylketonuria, tyrosinemia, alkaptonuria). 54. Hydroxylation of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan (coenzyme, phenylketonuria, DOPA, serotonin). 55. Significance and the basic features of the branched-chain ...
BIOCHEMISTRY I Spring 2013 (General medicine, Dental
... 53. Catabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine; metabolic disorders of their catabolism (phenylketonuria, tyrosinemia, alkaptonuria). 54. Hydroxylation of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan (coenzyme, phenylketonuria, DOPA, serotonin). 55. Significance and the basic features of the branched-chain ...
... 53. Catabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine; metabolic disorders of their catabolism (phenylketonuria, tyrosinemia, alkaptonuria). 54. Hydroxylation of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan (coenzyme, phenylketonuria, DOPA, serotonin). 55. Significance and the basic features of the branched-chain ...
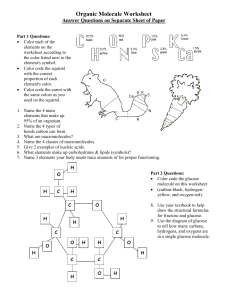
Organic Molecule Worksheet
... and box the carboxyl groups on the drawing to the right. 19. What subunits make up proteins? 20. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ___ in a process called ___. 21. ___ bonds form when water is removed to hold ___ ___ together. ...
... and box the carboxyl groups on the drawing to the right. 19. What subunits make up proteins? 20. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ___ in a process called ___. 21. ___ bonds form when water is removed to hold ___ ___ together. ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... nucleus so that the cell can make a protein out of the information obtained from the DNA in the gene Every 3 nitrogen bases in the DNA that makes up a gene is called a codon, and codes for a specific amino acid DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) i ...
... nucleus so that the cell can make a protein out of the information obtained from the DNA in the gene Every 3 nitrogen bases in the DNA that makes up a gene is called a codon, and codes for a specific amino acid DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) i ...
Proteins - RMC Science Home
... Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. There are 20 different amino acids. 2 types Essential Amino Acids Non-essential Amino Acids Essential amino acids are the acids that you must consume in your diet 8 amino acids Non-essential amino acids are the ones your body can produce 12 amino acids ...
... Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. There are 20 different amino acids. 2 types Essential Amino Acids Non-essential Amino Acids Essential amino acids are the acids that you must consume in your diet 8 amino acids Non-essential amino acids are the ones your body can produce 12 amino acids ...
protein synthesis
... codes for a single protein) B. The promoter site on the DNA contains a sequence called a TATA box - recognized by RNA polymerase - can be up to 25 bases away from point of transcription ...
... codes for a single protein) B. The promoter site on the DNA contains a sequence called a TATA box - recognized by RNA polymerase - can be up to 25 bases away from point of transcription ...
DNA Structure, Replication and Protein Synthesis
... Cooling the mixture after exactly 15 minutes ________________________________________ ...
... Cooling the mixture after exactly 15 minutes ________________________________________ ...
Photosynthesis “Carbon Fixation” λ Energy H20 O2 water oxidized
... reactions that are energetically favorable reactions to those that are energetically unfavorable ...
... reactions that are energetically favorable reactions to those that are energetically unfavorable ...
Is DNA the Genetic Material?
... Hypothetically, which of the following molecules could work as a replacement for tRNA? 1) A protein that can bind to the major groove of DNA and a specific amino acid. 2) A carbohydrate that can recognize a short RNA sequence and bind to a particular amino acid. 3) A lipid that can basepair with ...
... Hypothetically, which of the following molecules could work as a replacement for tRNA? 1) A protein that can bind to the major groove of DNA and a specific amino acid. 2) A carbohydrate that can recognize a short RNA sequence and bind to a particular amino acid. 3) A lipid that can basepair with ...
Document
... 20 different amino acids exist in nature Amino acids bind together to form a protein polymer by forming peptide bonds Form muscles, bones, hair, transport materials in and out of the cell, regulate the speed of chemical reactions (enzymes) Ending: “-ine” (for amino acids: monomer for protein ...
... 20 different amino acids exist in nature Amino acids bind together to form a protein polymer by forming peptide bonds Form muscles, bones, hair, transport materials in and out of the cell, regulate the speed of chemical reactions (enzymes) Ending: “-ine” (for amino acids: monomer for protein ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 3. Write the components that are involved in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A. 4. What would be the decarboxylated product of pyruvate in glycolysis? Mention the structure. 5. Define glycosuria. 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for pa ...
... 3. Write the components that are involved in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A. 4. What would be the decarboxylated product of pyruvate in glycolysis? Mention the structure. 5. Define glycosuria. 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for pa ...
General pathways of amino acids transformation
... L-Glutamate dehydrogenase plays a central role in amino acid deamination In most organisms glutamate is the only amino acid that has active dehydrogenase Present in both the cytosol and mitochondria of the liver ...
... L-Glutamate dehydrogenase plays a central role in amino acid deamination In most organisms glutamate is the only amino acid that has active dehydrogenase Present in both the cytosol and mitochondria of the liver ...
TECHNICAL NOTES Aurich, H .
... Investigotians of free amino clcids in Neurospora have been mode by one- or two-dimensional paper chromatography and by microbiological assays. In our I&ra+ory we used a commercial automatic recording apparatus for the determination of amino acids by ion exchange chromatography (Bender and H&in, Mun ...
... Investigotians of free amino clcids in Neurospora have been mode by one- or two-dimensional paper chromatography and by microbiological assays. In our I&ra+ory we used a commercial automatic recording apparatus for the determination of amino acids by ion exchange chromatography (Bender and H&in, Mun ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.