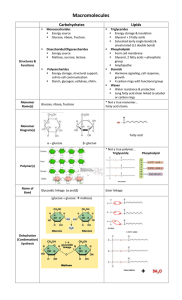
Biomolecules - Fall River Public Schools
... Ex= animal products, coconut • Unsaturated=liquid at room temperature, Raise “good” (HDL) cholesterol Ex= olive oil, avocado, almonds ...
... Ex= animal products, coconut • Unsaturated=liquid at room temperature, Raise “good” (HDL) cholesterol Ex= olive oil, avocado, almonds ...
Test 2 - HCC Learning Web
... 5. Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water? 6. Humans can digest starch but not cellulose because. Explain? 7. How does RNA differ from DNA? 8. Explain how ATP functions as the primary energy transfer molecule in living cells 9. What aspects of protein structure are stabilized or assisted by hydroge ...
... 5. Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water? 6. Humans can digest starch but not cellulose because. Explain? 7. How does RNA differ from DNA? 8. Explain how ATP functions as the primary energy transfer molecule in living cells 9. What aspects of protein structure are stabilized or assisted by hydroge ...
Slide 1
... 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
... 2. Translation – the mRNA, with the help of the ribosome, forms a chain of amino acids (eventually forming a protein) based on the information contained on the mRNA. ...
Biochem notes
... Phospholipids have both polar and nonpolar sections. As a result, they are able to dissolve in both type of solvents as well. They are important for living things because they form the borders of all cells (cell membranes) and also participate in forming many cell organelles. ...
... Phospholipids have both polar and nonpolar sections. As a result, they are able to dissolve in both type of solvents as well. They are important for living things because they form the borders of all cells (cell membranes) and also participate in forming many cell organelles. ...
1. Important Features
... f. Major step is the synthesis of the coded "messenger" molecule – mRNA g. mRNA is "transcribed" from DNA by complementary base pairing (mRNA has no thymine, which is replaced by uracil) h. mRNA passes out to cytoplasm to the ribosome ...
... f. Major step is the synthesis of the coded "messenger" molecule – mRNA g. mRNA is "transcribed" from DNA by complementary base pairing (mRNA has no thymine, which is replaced by uracil) h. mRNA passes out to cytoplasm to the ribosome ...
Main concepts Carbohydrates Fats, Proteins and Enzymes
... 2. Carbohydrates are composed of the three elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. 3. Carbohydrates include monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. 4. The molecular formulas for carbohydrates can be represented as Cx(H2O)y. 5. Monosaccharides form the basis of all other carbohydrates. 6. D ...
... 2. Carbohydrates are composed of the three elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. 3. Carbohydrates include monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. 4. The molecular formulas for carbohydrates can be represented as Cx(H2O)y. 5. Monosaccharides form the basis of all other carbohydrates. 6. D ...
Practice - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... Normal human blood plasma contains all the amino acids require for the synthesis of body proteins, but not in equal concentration. Alanine and glutamine are present in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. Suggest why? Answer : Muscle tissue can convert amino acids to their keto acids p ...
... Normal human blood plasma contains all the amino acids require for the synthesis of body proteins, but not in equal concentration. Alanine and glutamine are present in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. Suggest why? Answer : Muscle tissue can convert amino acids to their keto acids p ...
Nervous System
... Structure: single chain folded into “cloverleaf” shape. Has an anticodon on one end and binds an amino acid on the opposite end. Function: to transfer (deliver) the correct amino acids to the ribosome. There are many different tRNAs; each carries a different a.a. ...
... Structure: single chain folded into “cloverleaf” shape. Has an anticodon on one end and binds an amino acid on the opposite end. Function: to transfer (deliver) the correct amino acids to the ribosome. There are many different tRNAs; each carries a different a.a. ...
Biological Macromolecules
... Polymers made of amino acids, which are joined by peptide bonds - proteins are also called polypeptides Amino acids form a wide variety of structures, mainly building blocks for living tissue Also used for: ...
... Polymers made of amino acids, which are joined by peptide bonds - proteins are also called polypeptides Amino acids form a wide variety of structures, mainly building blocks for living tissue Also used for: ...
Completed Note
... Long fatty acid chain linked to alcohol or carbon rings * Not a true monomer… Fatty acid chains ...
... Long fatty acid chain linked to alcohol or carbon rings * Not a true monomer… Fatty acid chains ...
Chapter Summary - OHS General Biology
... • RNA and DNA are the molecules that enable living organisms to reproduce their complex components from generation to generation. • The flow of genetic information is DNA RNA protein. A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides. • Nucleic acids are polymers made of nucleotide monomers orga ...
... • RNA and DNA are the molecules that enable living organisms to reproduce their complex components from generation to generation. • The flow of genetic information is DNA RNA protein. A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides. • Nucleic acids are polymers made of nucleotide monomers orga ...
Chapter 22 (Part 1) - University of Nevada, Reno
... • But aminoacyl-tRNAs do something else: activate the amino acid for transfer to peptide • Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases do the critical job - linking the right amino acid with "cognate" tRNA ...
... • But aminoacyl-tRNAs do something else: activate the amino acid for transfer to peptide • Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases do the critical job - linking the right amino acid with "cognate" tRNA ...
Chapter 4
... DNA Template (3’ to 5’ strand) No primer required Nucleoside triphosphates: ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP Synthesis is 5’ to 3’ ...
... DNA Template (3’ to 5’ strand) No primer required Nucleoside triphosphates: ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP Synthesis is 5’ to 3’ ...
Supporting text S1
... amino acid-catabolizing enzymes common in other bacteria, and many were lacking. For example, both histidine and serine ammonia-lyase are absent. Enzymes necessary for histidine degradation via urocanate or histamine are all absent. Aromatic amino acids cannot be degraded, based on the lack of genes ...
... amino acid-catabolizing enzymes common in other bacteria, and many were lacking. For example, both histidine and serine ammonia-lyase are absent. Enzymes necessary for histidine degradation via urocanate or histamine are all absent. Aromatic amino acids cannot be degraded, based on the lack of genes ...
002 Chapter 2
... A. hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, sulfur C. hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen B. carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, iron D. sulfur, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen 2. Which statement is NOT true about elements? A. An element cannot be broken down into substances with different properties. B. An element consists of at ...
... A. hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, sulfur C. hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen B. carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, iron D. sulfur, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen 2. Which statement is NOT true about elements? A. An element cannot be broken down into substances with different properties. B. An element consists of at ...
CP Biology
... 16 Regulatory protein 17 The part of tRNA that lines up with the correct codon 20 "Many Bodies" 21 Organelle responsible for protein production 24 What the Golgi Apparatus makes 25 Going from DNA to mRNA 27 A non-metal bonded to a metal 30 Oxygen Dependant 31 "Batteries" that all life runs on 32 Har ...
... 16 Regulatory protein 17 The part of tRNA that lines up with the correct codon 20 "Many Bodies" 21 Organelle responsible for protein production 24 What the Golgi Apparatus makes 25 Going from DNA to mRNA 27 A non-metal bonded to a metal 30 Oxygen Dependant 31 "Batteries" that all life runs on 32 Har ...
Protein mteabolism
... Removal of α-amino group: Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield α-keto acid of the original amino acid and a new amino acid. The enzymes that catalyze transamination are called transaminases or ...
... Removal of α-amino group: Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield α-keto acid of the original amino acid and a new amino acid. The enzymes that catalyze transamination are called transaminases or ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.