There are three parts in this exam (50% +20% +30%)
... molecules; (B) ATP is one of the building blocks of DNAs of living cells; (C) ATP occupies the top of the phosphoryl group transfer scale, which makes it a universal donor of the phosphoryl group; (D) ATP has a position roughly at the bottom of the phosphoryl group transfer scale, which allows it to ...
... molecules; (B) ATP is one of the building blocks of DNAs of living cells; (C) ATP occupies the top of the phosphoryl group transfer scale, which makes it a universal donor of the phosphoryl group; (D) ATP has a position roughly at the bottom of the phosphoryl group transfer scale, which allows it to ...
BioMI 2900
... They are red in color due to a heme molecule. There environments are largely anoxic, due to the heme molecule. ...
... They are red in color due to a heme molecule. There environments are largely anoxic, due to the heme molecule. ...
Chapter 03 Lecture PowerPoint - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Proteins We now know about the building blocks of proteins (amino
... substrate binds and is released from an “active site” Chemistry C483 ...
... substrate binds and is released from an “active site” Chemistry C483 ...
(codons) make a specific amino acid
... • Fatal mutations can kill a cell immediately and end the cell genetic contribution of the cell to the body. • Deleterious mutations to DNA can change the proteins produced by a cell and cause cellular dysfunction….i.e. Cancer – Why are they passed to cell in same body but not next generation? ...
... • Fatal mutations can kill a cell immediately and end the cell genetic contribution of the cell to the body. • Deleterious mutations to DNA can change the proteins produced by a cell and cause cellular dysfunction….i.e. Cancer – Why are they passed to cell in same body but not next generation? ...
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDES (BIO MEDICAL IMPORTANCE)
... Ornithine and Citrulline have important role in liver during safe disposal of Ammonia (Urea Cycle) -Alanine →synthesis of Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) Carnitine is employed in lipid transport within cells. ...
... Ornithine and Citrulline have important role in liver during safe disposal of Ammonia (Urea Cycle) -Alanine →synthesis of Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) Carnitine is employed in lipid transport within cells. ...
Amino Acids
... Ornithine and Citrulline have important role in liver during safe disposal of Ammonia (Urea Cycle) -Alanine →synthesis of Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) Carnitine is employed in lipid transport within cells. ...
... Ornithine and Citrulline have important role in liver during safe disposal of Ammonia (Urea Cycle) -Alanine →synthesis of Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) Carnitine is employed in lipid transport within cells. ...
Inborn error in metabolism of amino acids
... population are affected by this enzyme defect leading to ketoaciduria. When untreated this condition may lead to both physical and mental retardation of the newborn and a distinct maple syrup odor of the urine. This defect can be partially managed with a low protein or modified diet. In some instanc ...
... population are affected by this enzyme defect leading to ketoaciduria. When untreated this condition may lead to both physical and mental retardation of the newborn and a distinct maple syrup odor of the urine. This defect can be partially managed with a low protein or modified diet. In some instanc ...
The Molecules of Life Biochem! - Belle Vernon Area School District
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
Biochemistry Test w/Answers
... and any volume or concentration. 2. The enzymes that catalyze cellular reactions are macromolecules made of organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. These types of macromolecules are known as: (9A, 9C) A. Starches B. Sugars C. Proteins D. Fats 3. Like complex carbohydrat ...
... and any volume or concentration. 2. The enzymes that catalyze cellular reactions are macromolecules made of organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. These types of macromolecules are known as: (9A, 9C) A. Starches B. Sugars C. Proteins D. Fats 3. Like complex carbohydrat ...
AMINO ACIDS COMPLEX Factsheet
... contain approximately 16% nitrogen, which differentiates them from the other two primary nutrients, sugars and fatty acids, which do not contain nitrogen. Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins are not obtained directly from human diet, instead they are broken down from ...
... contain approximately 16% nitrogen, which differentiates them from the other two primary nutrients, sugars and fatty acids, which do not contain nitrogen. Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins are not obtained directly from human diet, instead they are broken down from ...
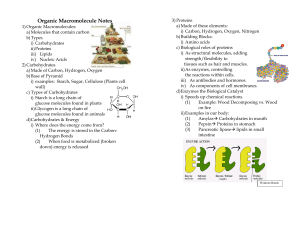
Organic Macromolecule Notes
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
ReviewExamIII
... that we studied in the Enzyme lab. How does pH and temperature affect enzymatic rate (velocity)? How does a graph of enzymatic rate look versus pH and temperature? How do catabolic and anabolic reactions differ with respect to energy requirements or use, and which is a "build-up" and which a "break- ...
... that we studied in the Enzyme lab. How does pH and temperature affect enzymatic rate (velocity)? How does a graph of enzymatic rate look versus pH and temperature? How do catabolic and anabolic reactions differ with respect to energy requirements or use, and which is a "build-up" and which a "break- ...
Table 1 The Essential Amino Acids and Their Plant Sources
... molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and transported to cells via the bloodstream. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. Urea is what gives your urine its yellow color. Why protein is needed Dietary pr ...
... molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and transported to cells via the bloodstream. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. Urea is what gives your urine its yellow color. Why protein is needed Dietary pr ...
Name
... 2. How can you tell if a molecule is organic or inorganic? 3. What are the four categories of organic macromolecules? 4. Which three atoms are found in all of the organic macromolecules? 5. Explain dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. 6. Draw the following molecules: fats, nucleotide, ami ...
... 2. How can you tell if a molecule is organic or inorganic? 3. What are the four categories of organic macromolecules? 4. Which three atoms are found in all of the organic macromolecules? 5. Explain dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. 6. Draw the following molecules: fats, nucleotide, ami ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.