160 GLUCOSE DECREASES DURING AMINO ACID
... The application of FU in the treatment of colon cancer is limited because of myeloid and gastrointestinal toxicity. It has been demonstrated that UR is able to rescue mice from the toxic effects of FU, which precludes the use of higher FU doses. Antitumor effect and toxicity were studied in two muri ...
... The application of FU in the treatment of colon cancer is limited because of myeloid and gastrointestinal toxicity. It has been demonstrated that UR is able to rescue mice from the toxic effects of FU, which precludes the use of higher FU doses. Antitumor effect and toxicity were studied in two muri ...
Exam I Cell and Molecular Biology September 26, 2007 This exam
... 6. Triacylglycerol and cholesterol esters are nonpolar; in contrast, phospholipids are amphipathic molecules. Biomembranes are based on phospholipids rather than on triacylglycerols. Why? Biomembranes are based on phospholipids rather than on triacylglycerols because phospholipids as amphipathic mol ...
... 6. Triacylglycerol and cholesterol esters are nonpolar; in contrast, phospholipids are amphipathic molecules. Biomembranes are based on phospholipids rather than on triacylglycerols. Why? Biomembranes are based on phospholipids rather than on triacylglycerols because phospholipids as amphipathic mol ...
Macromolecules - Dickinson ISD
... These carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double or triple covalent bonds. Chains can close up on themselves and form rings. ...
... These carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double or triple covalent bonds. Chains can close up on themselves and form rings. ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Types of Fatty Acids • Unsaturated fatty acids have less than the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (a double bond between carbons) Saturated fatty acids have the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (all single bonds between carbons) ...
... Types of Fatty Acids • Unsaturated fatty acids have less than the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (a double bond between carbons) Saturated fatty acids have the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons (all single bonds between carbons) ...
The CENTRAL DOGMA in Biology:
... 1. Summarize the ‘Central Dogma’ of biology. 2. Describe the structure of a protein (what are the sub-components of a protein? What makes proteins different from each other? How is its final structure formed?) 3. Differentiate the places in a cell where DNA is stored in a cell and where proteins are ...
... 1. Summarize the ‘Central Dogma’ of biology. 2. Describe the structure of a protein (what are the sub-components of a protein? What makes proteins different from each other? How is its final structure formed?) 3. Differentiate the places in a cell where DNA is stored in a cell and where proteins are ...
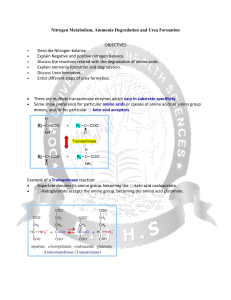
Nitrogen Metabolism, Ammonia Degradation and Urea Formation
... Terrestrial vertebrates synthesize urea (excreted by the kidneys) - ureotelic organisms Birds, reptiles synthesize uric acid Urea formation takes place in the liver ...
... Terrestrial vertebrates synthesize urea (excreted by the kidneys) - ureotelic organisms Birds, reptiles synthesize uric acid Urea formation takes place in the liver ...
Protein Sequence WKS - Kenton County Schools
... M.C. Hammerase Protein If this protein is made it causes the organism to start singing “You Can’t Touch This” over and over until it manages to score a goal on the soccer field. This organism will also grow a mullet and have the uncontrollable urge to wear hammer pants. methionine – valine – glutami ...
... M.C. Hammerase Protein If this protein is made it causes the organism to start singing “You Can’t Touch This” over and over until it manages to score a goal on the soccer field. This organism will also grow a mullet and have the uncontrollable urge to wear hammer pants. methionine – valine – glutami ...
PowerPoint- Protein Shape
... 2) How is replication different from transcription? 3) What are the steps of protein synthesis? 4) Compare transcription and translation. 5) How is DNA different from mRNA? ...
... 2) How is replication different from transcription? 3) What are the steps of protein synthesis? 4) Compare transcription and translation. 5) How is DNA different from mRNA? ...
Amino acids & proteins part 2
... – Identify the structural units of the protein backbone. – Explain why some backbone conformations are “forbidden”, i.e. not found in natural proteins. – Name properties on which the amino acids can be grouped. – Name more amino acids than you could before One and three letter codes ...
... – Identify the structural units of the protein backbone. – Explain why some backbone conformations are “forbidden”, i.e. not found in natural proteins. – Name properties on which the amino acids can be grouped. – Name more amino acids than you could before One and three letter codes ...
Macromolecules
... • Made from amino acids chains • The polymer protein is made up of the monomer amino acids • 20 different amino acids • bonded together by peptide bonds • Even though there are only 20 amino acids, many different types of proteins exist because the sequence and number of amino acids in a chain can v ...
... • Made from amino acids chains • The polymer protein is made up of the monomer amino acids • 20 different amino acids • bonded together by peptide bonds • Even though there are only 20 amino acids, many different types of proteins exist because the sequence and number of amino acids in a chain can v ...
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters
... • http://what-whenhow.com/neuroscience/neurotransmitters-theneuron-part-1/ ...
... • http://what-whenhow.com/neuroscience/neurotransmitters-theneuron-part-1/ ...
Sample exam 1
... 1. The enzyme that acts on ketone bodies to convert them into a form that can be broken down into acetyl CoA is present in brain, but not in liver. What type of reaction is catalyzed by this enzyme? a. Oxidation. b. Dehydration. c. Transfer of CoA. d. Hydroxylation. e. Decarboxylation. 2. Erucic aci ...
... 1. The enzyme that acts on ketone bodies to convert them into a form that can be broken down into acetyl CoA is present in brain, but not in liver. What type of reaction is catalyzed by this enzyme? a. Oxidation. b. Dehydration. c. Transfer of CoA. d. Hydroxylation. e. Decarboxylation. 2. Erucic aci ...
Macromolecules
... Chemical Reactions • Chemical Reaction – changes one set of chemicals (reactants) into another set of chemicals (products) ...
... Chemical Reactions • Chemical Reaction – changes one set of chemicals (reactants) into another set of chemicals (products) ...
Study guide
... Strands of nucleotides held together by sugar-phosphate backbone. Two strands are paired together with hydrogen bonds between paired bases. One strand is the template for the other (base pairing rules— this property gives DNA its unique quality of being able to self-replicate) DNA replication DNA tr ...
... Strands of nucleotides held together by sugar-phosphate backbone. Two strands are paired together with hydrogen bonds between paired bases. One strand is the template for the other (base pairing rules— this property gives DNA its unique quality of being able to self-replicate) DNA replication DNA tr ...
Bio-Macromolecules Worksheet
... Nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P). Nucleic acids carry the genetic information in a cell. DNA or deoxyribose nucleic acid contains all the instructions for making every protein nee ...
... Nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P). Nucleic acids carry the genetic information in a cell. DNA or deoxyribose nucleic acid contains all the instructions for making every protein nee ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.