Ch 9 chapter summary
... • High-energy electrons are passed to the electron carrier NAD+, forming two molecules of NADH. • 4 ATP are synthesized during glycolysis for a net gain of 2 ATP. The Krebs Cycle The second stage of cellular respiration is the Krebs cycle, which operates only when oxygen is available. The Krebs cycl ...
... • High-energy electrons are passed to the electron carrier NAD+, forming two molecules of NADH. • 4 ATP are synthesized during glycolysis for a net gain of 2 ATP. The Krebs Cycle The second stage of cellular respiration is the Krebs cycle, which operates only when oxygen is available. The Krebs cycl ...
ppt - University of Illinois Urbana
... • Once differentiated, a cell cannot change from one type to another • Yet, all cells of an organism have exactly the same genetic code • Differences come from differences in gene expression, that is whether or not the product a gene codes for is produced and how much is produced ...
... • Once differentiated, a cell cannot change from one type to another • Yet, all cells of an organism have exactly the same genetic code • Differences come from differences in gene expression, that is whether or not the product a gene codes for is produced and how much is produced ...
Macromolecule Molecular Structure Carbohydrates
... showed that the material is distributed at 50% between A- and B-chains. In addition it is worth noting the molecule of glycogenin, a protein that acts as a primer, at the centre of the structure.” ...
... showed that the material is distributed at 50% between A- and B-chains. In addition it is worth noting the molecule of glycogenin, a protein that acts as a primer, at the centre of the structure.” ...
Discuss on Cellular Respiration Submitted by WWW
... of enzyme-catalyzed conversions. The conversions, which involve up to 10 chemical reactions, are all brought about by enzymes. In many of the steps, high-energy electrons are released to NAD. The NAD molecule also acquires a hydrogen ion and becomes NADH. In one of the steps, FAD serves as the elec ...
... of enzyme-catalyzed conversions. The conversions, which involve up to 10 chemical reactions, are all brought about by enzymes. In many of the steps, high-energy electrons are released to NAD. The NAD molecule also acquires a hydrogen ion and becomes NADH. In one of the steps, FAD serves as the elec ...
Blank Jeopardy
... The lactic acid cycle (lactic acid fermentation) uses this sugar to get started, what is it? ...
... The lactic acid cycle (lactic acid fermentation) uses this sugar to get started, what is it? ...
aerobic vs anerobic ws - Hicksville Public Schools
... III. Cellular Respiration: 13. Is cellular respiration aerobic or anaerobic? Explain. They both are because they both produce ATP. ____________________________________________ ...
... III. Cellular Respiration: 13. Is cellular respiration aerobic or anaerobic? Explain. They both are because they both produce ATP. ____________________________________________ ...
The BIG FOUR!
... Amino acids link together in a process called ________________. Amino acids are linked by a special covalent bond called a ____________. The first amino acid set down in every protein is _____________. Five important functions of my favorite organic compound are _____________, _________________, ___ ...
... Amino acids link together in a process called ________________. Amino acids are linked by a special covalent bond called a ____________. The first amino acid set down in every protein is _____________. Five important functions of my favorite organic compound are _____________, _________________, ___ ...
Anaerobic respiration
... There are two types of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen is called Aerobic respiration. Aerobic Respiration occurs in a cell's mitochondria, the energy source of the cell. Cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen is called Anaerobic res ...
... There are two types of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen is called Aerobic respiration. Aerobic Respiration occurs in a cell's mitochondria, the energy source of the cell. Cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen is called Anaerobic res ...
Organic Molecules Worksheet: Review
... are very valuable because they provide a quick form of energy for the body. The second is glycogen. Glycogen is used for food storage in animals. The third is cellulose. Cellulose is used for structural support in plants (stems, leaves). 15. What are the three classes of carbohydrates? a. __________ ...
... are very valuable because they provide a quick form of energy for the body. The second is glycogen. Glycogen is used for food storage in animals. The third is cellulose. Cellulose is used for structural support in plants (stems, leaves). 15. What are the three classes of carbohydrates? a. __________ ...
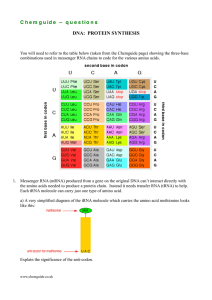
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Yeast Nutrition and Fermentation Progression
... Degradation may depend upon availability of other components: vitamins and oxygen Utilization impacted by other environmental factors such as pH and ethanol ...
... Degradation may depend upon availability of other components: vitamins and oxygen Utilization impacted by other environmental factors such as pH and ethanol ...
Unit 2 - kehsscience.org
... 13. Which of the following types of molecules provides building blocks for tissues, transports other molecules, and helps to regulate certain reactions in the human body? a. lipids c. carbohydrates b. fats (lipids) d. proteins 14. Which of the following is the correct equation for photosynthesis? a. ...
... 13. Which of the following types of molecules provides building blocks for tissues, transports other molecules, and helps to regulate certain reactions in the human body? a. lipids c. carbohydrates b. fats (lipids) d. proteins 14. Which of the following is the correct equation for photosynthesis? a. ...
cellular respiration - Aurora City Schools
... How does energy flow through an ecosystem? Can energy be recycled? How do producers get their energy? In which cell organelle does most of this take place? Draw and label it. ...
... How does energy flow through an ecosystem? Can energy be recycled? How do producers get their energy? In which cell organelle does most of this take place? Draw and label it. ...
comprehensive biochemistry
... B. Lateral extensions on the glycolytic pathway 18. Chitin pathway a. Chitin biosynthesis b. Regressive evolution of chitin biosynthesis c. Physiological radiations of chitin d. Regressive evolution in chitinolysis 19. Trehalose biosynthesis 20. Sustained flight in bees and flies 21. Glycerol produc ...
... B. Lateral extensions on the glycolytic pathway 18. Chitin pathway a. Chitin biosynthesis b. Regressive evolution of chitin biosynthesis c. Physiological radiations of chitin d. Regressive evolution in chitinolysis 19. Trehalose biosynthesis 20. Sustained flight in bees and flies 21. Glycerol produc ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 12 Notes
... PO4 nucleophilic attack on succinyl CoA releasing CoA. His cleaves PO4 off of succinate. PO4 transfers from His(enzyme) to GDP forming GTP ...
... PO4 nucleophilic attack on succinyl CoA releasing CoA. His cleaves PO4 off of succinate. PO4 transfers from His(enzyme) to GDP forming GTP ...
The Damaged Cell Surgery
... The Coming of Lysosomes • The Mitochondria cannot be fixed. • So a vesicle encloses the Mitochondria and lysosomes bump into the vesicle and pour enzymes into them. • Useful amino acids and fatty acids will be returned to the cytoplasm and waste particles are removed from the cell. • The cell can m ...
... The Coming of Lysosomes • The Mitochondria cannot be fixed. • So a vesicle encloses the Mitochondria and lysosomes bump into the vesicle and pour enzymes into them. • Useful amino acids and fatty acids will be returned to the cytoplasm and waste particles are removed from the cell. • The cell can m ...
Introduction to Cellular Respiration •ATP is needed in order for cells
... •Chemiosmosis is a process involving electron transport chain and ATP synthases. The electron transport chain temporarily produces potential energy in the form of an increase in H+ concentration on one side of a membrane; the ATP synthases use potential energy to generate ATP (from ADP and phosphate ...
... •Chemiosmosis is a process involving electron transport chain and ATP synthases. The electron transport chain temporarily produces potential energy in the form of an increase in H+ concentration on one side of a membrane; the ATP synthases use potential energy to generate ATP (from ADP and phosphate ...
Introduction to Cellular Respiration •ATP is needed in order for cells
... •Chemiosmosis is a process involving electron transport chain and ATP synthases. The electron transport chain temporarily produces potential energy in the form of an increase in H+ concentration on one side of a membrane; the ATP synthases use potential energy to generate ATP (from ADP and phosphate ...
... •Chemiosmosis is a process involving electron transport chain and ATP synthases. The electron transport chain temporarily produces potential energy in the form of an increase in H+ concentration on one side of a membrane; the ATP synthases use potential energy to generate ATP (from ADP and phosphate ...
The Obesity Epidemic: Are Our Tastebuds to Blame? Timothy Gilbertson, Ph.D.
... survival of those individuals who could store as many calories as possible, then burn them as slowly as possible. ...
... survival of those individuals who could store as many calories as possible, then burn them as slowly as possible. ...
The Origin of Life - The University of Texas at Dallas
... of higher or lower energy, with a preference for lower. Can we apply the same reasoning to the chemistry of life? For real hills, we understand not only that the water will flow downward but also many things about how it will do so. Molecules of water will not each flow down a random path. Instead t ...
... of higher or lower energy, with a preference for lower. Can we apply the same reasoning to the chemistry of life? For real hills, we understand not only that the water will flow downward but also many things about how it will do so. Molecules of water will not each flow down a random path. Instead t ...
For lecture notes click here
... STEP 2: In peripheral capillaries, lipoprotein lipase removes many of the triglycerides from VLDLs, leaving IDLs; the triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and monoglycerides. STEP 3: When IDLs reach the liver, additional triglycerides are removed and the protein content is altered. This pr ...
... STEP 2: In peripheral capillaries, lipoprotein lipase removes many of the triglycerides from VLDLs, leaving IDLs; the triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and monoglycerides. STEP 3: When IDLs reach the liver, additional triglycerides are removed and the protein content is altered. This pr ...
Respiration II
... cellular respiration most of the energy in glucose ends up in two acetyl groups. ...
... cellular respiration most of the energy in glucose ends up in two acetyl groups. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.