Overview
... Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism 1. Explain the role of catabolic and anabolic pathways in cellular metabolism. 2. Distinguish between potential and kinetic energy. 3. Explain the first and second laws of thermodynamics. 4. Write and define each component of the equation for change in free e ...
... Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism 1. Explain the role of catabolic and anabolic pathways in cellular metabolism. 2. Distinguish between potential and kinetic energy. 3. Explain the first and second laws of thermodynamics. 4. Write and define each component of the equation for change in free e ...
Midterm Review Notes
... – Proteins have 1000’s of amino acids joined together – But there are only 20 different amino acids – The order you place them determine what protein you make ...
... – Proteins have 1000’s of amino acids joined together – But there are only 20 different amino acids – The order you place them determine what protein you make ...
PPT_Biochemistry_Short_Course
... Polysaccharides Storage forms of sugars (cellular fuel & some structural components) = larger size so lower solubility (doesn’t break down as easily) Starch • Type of polysaccharide found in Plants • Cellulose & lignin indigestible by humans • Used for FIBER (drink lots of water!!) ...
... Polysaccharides Storage forms of sugars (cellular fuel & some structural components) = larger size so lower solubility (doesn’t break down as easily) Starch • Type of polysaccharide found in Plants • Cellulose & lignin indigestible by humans • Used for FIBER (drink lots of water!!) ...
Bio Honors Review Packet
... 2. Which element is not required in order for a compound to be organic? A) carbon b) oxygen c) hydrogen d) all must be present 3. Which element is usually found in proteins but not in triglyerides? A) calcium b) phosphorus c) nitrogen d) oxygen 4. Structurally lipids are a very diverse group but the ...
... 2. Which element is not required in order for a compound to be organic? A) carbon b) oxygen c) hydrogen d) all must be present 3. Which element is usually found in proteins but not in triglyerides? A) calcium b) phosphorus c) nitrogen d) oxygen 4. Structurally lipids are a very diverse group but the ...
A1984SZ47200001
... acid pattern when fresh, after two weeks’ diet who responded biochemically to pharstorage, revealed large spots in the cysteic macological doses of B~,thus establishing acid position. The urine was also found to the original form of homocystinuria as an give a positive nitroprussidelcyanide test, ea ...
... acid pattern when fresh, after two weeks’ diet who responded biochemically to pharstorage, revealed large spots in the cysteic macological doses of B~,thus establishing acid position. The urine was also found to the original form of homocystinuria as an give a positive nitroprussidelcyanide test, ea ...
Stabilization of Low Affinity Protein-Protein Interactions by
... The introduction of new chemical functionalities into proteins represents a promising approach for investigating and manipulating diverse biological processes. Among a number of different approaches, the expansion of the genetic code has emerged as an eminent tool for in vivo site-specific incorpora ...
... The introduction of new chemical functionalities into proteins represents a promising approach for investigating and manipulating diverse biological processes. Among a number of different approaches, the expansion of the genetic code has emerged as an eminent tool for in vivo site-specific incorpora ...
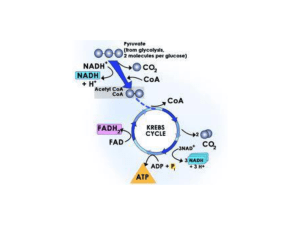
4 ADP + 4 Pi are converted to 2 ATP to produce a net gain of 2 ATP
... be harnessed in a controlled fashion to generate high energy bonds in the form of ATP) The cells can then allow the protons to re-enter the cell in a controlled fashion, and the energy derived from this movement can be used to do work. This is analogous to water stored behind a dam How does the cell ...
... be harnessed in a controlled fashion to generate high energy bonds in the form of ATP) The cells can then allow the protons to re-enter the cell in a controlled fashion, and the energy derived from this movement can be used to do work. This is analogous to water stored behind a dam How does the cell ...
SOME Important Points About Cellular Energetics by Dr. Ty C.M.
... The citric acid cycle receives acetyl (a two-‐carbon compound) and combines it with oxaloacetate (a four-‐carbon compound) to produce citrate (a six-‐ carbon compound). This six carbon compound is then broken ...
... The citric acid cycle receives acetyl (a two-‐carbon compound) and combines it with oxaloacetate (a four-‐carbon compound) to produce citrate (a six-‐ carbon compound). This six carbon compound is then broken ...
Proseminar 3: Questions and Answers
... tissue is triggered, so free fatty acids are massively released. The situation in the liver cells then simply reflects substrate-level regulation (i.e. control by substrate availability): The 2 possible fates of free fatty acids in the liver are: synthesis of TAG or β-oxidation. Under conditions of ...
... tissue is triggered, so free fatty acids are massively released. The situation in the liver cells then simply reflects substrate-level regulation (i.e. control by substrate availability): The 2 possible fates of free fatty acids in the liver are: synthesis of TAG or β-oxidation. Under conditions of ...
Stable Isotope and Metabolomics Core Facility
... test hypotheses about the metabolic consequences of various changes in gene expression and protein function, in order to guide further integrative systems biology analyses of the underlying mechanisms in diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetic complications. The Core objectives includes ...
... test hypotheses about the metabolic consequences of various changes in gene expression and protein function, in order to guide further integrative systems biology analyses of the underlying mechanisms in diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetic complications. The Core objectives includes ...
Glycolysis Animation
... Learning Targets 5. Compare and contrast substrate level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, and photophosphorylation. ...
... Learning Targets 5. Compare and contrast substrate level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, and photophosphorylation. ...
Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Protein Catabolism Figure 27.7 Overview of Protein catabolism. ...
... Protein Catabolism Figure 27.7 Overview of Protein catabolism. ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
... ENTNER-DUDOROFF PATHWAY • The Entner-Doudoroff pathway yields one ATP and two NADPH molecules from one glucose molecule. • Uses 4 enzymes that are different from EMP 1 Glucose 2 pyruvate + 1 ATP + 1 NADH + 1 NADPH Bacteria: Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Agrobacterium, Enterococcus faecalis ...
... ENTNER-DUDOROFF PATHWAY • The Entner-Doudoroff pathway yields one ATP and two NADPH molecules from one glucose molecule. • Uses 4 enzymes that are different from EMP 1 Glucose 2 pyruvate + 1 ATP + 1 NADH + 1 NADPH Bacteria: Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Agrobacterium, Enterococcus faecalis ...
Chemical digestion
... (finger like projections). Absorbed by blood. Absorption of fats occurs at the villi; absorbed into lymph system. ...
... (finger like projections). Absorbed by blood. Absorption of fats occurs at the villi; absorbed into lymph system. ...
Honors
... - Video: Why is carbon such a tramp? - Notes on Macromolecules - FedUp Article and Questions ...
... - Video: Why is carbon such a tramp? - Notes on Macromolecules - FedUp Article and Questions ...
Review Book Topic D: Evolution - wfs
... a. Life as we know it is based on organic molecules such as amino acids, yet early Earth had only inorganic matter. b. In order to build more complex molecules like proteins, monomers (single molecules like amino acids, simple sugars, and nucleotides) need to be connected together into polymers (lon ...
... a. Life as we know it is based on organic molecules such as amino acids, yet early Earth had only inorganic matter. b. In order to build more complex molecules like proteins, monomers (single molecules like amino acids, simple sugars, and nucleotides) need to be connected together into polymers (lon ...
Question Report - FM Faculty Web Pages
... mitochondria and chloroplasts are about the same size as prokaryotic cells mitochondria have their own DNA ...
... mitochondria and chloroplasts are about the same size as prokaryotic cells mitochondria have their own DNA ...
Extracellular Enzymes Lab
... Enzymes • Enzymes are large proteins that all organisms synthesize to catalyze metabolic reactions. • Enzymes are typically highly specific, converting only one substrate to one product. • Almost all reactions that occur within the cell, including energy production (catabolism) and biosynthesis (a ...
... Enzymes • Enzymes are large proteins that all organisms synthesize to catalyze metabolic reactions. • Enzymes are typically highly specific, converting only one substrate to one product. • Almost all reactions that occur within the cell, including energy production (catabolism) and biosynthesis (a ...
The 6 Essential Nutrients
... CHOLESTEROL - A waxy, fat like substance produced by the body that is used to build cells and make other substances. ...
... CHOLESTEROL - A waxy, fat like substance produced by the body that is used to build cells and make other substances. ...
macromolecules
... nitrogen and phosphorus Monomer: Nucleotide (sugar, phosphate & nitrogen base) Polymer: Nucleic Acid Structure: Long chains of nucleotides found in a twisted or folded structure ...
... nitrogen and phosphorus Monomer: Nucleotide (sugar, phosphate & nitrogen base) Polymer: Nucleic Acid Structure: Long chains of nucleotides found in a twisted or folded structure ...
Glossary
... A waxy substance, technically a steroid alcohol, found only in animal fats and oil; used in making cell membranes, as a building block for some hormones, in the fatty sheath around nerve fibers, and in other necessary substances. ...
... A waxy substance, technically a steroid alcohol, found only in animal fats and oil; used in making cell membranes, as a building block for some hormones, in the fatty sheath around nerve fibers, and in other necessary substances. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.