Cell Powerpoint used in class
... • Nutrients needed for life dissolved inside cell • Includes organelles ...
... • Nutrients needed for life dissolved inside cell • Includes organelles ...
7.3 Structures and Organelles
... moving substances within the cell. Microfilaments are thin protein threads that help give the cell shape and enable part or the entire cell to move. ...
... moving substances within the cell. Microfilaments are thin protein threads that help give the cell shape and enable part or the entire cell to move. ...
Cell Organelle Powerpoint
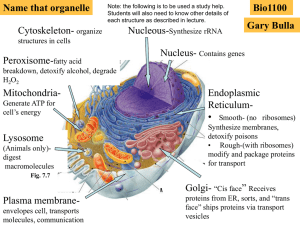
... NUCLEUS Contains DNA Function: control center of cell Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are ...
... NUCLEUS Contains DNA Function: control center of cell Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are ...
Study Guide
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) It is a double protein layer with floating lipid molecules. 3. Which structures are found in every living cell? ...
... B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) It is a double protein layer with floating lipid molecules. 3. Which structures are found in every living cell? ...
Cells
... • Nucleus-houses the genetic material • Cytoplasm-surrounds the nucleus and contains all the other organelles • Cell Membrane-surrounds the cytoplasm and controls what goes in and out, also communicates with other cells • Organelles-specialized structures that perform specific functions which divide ...
... • Nucleus-houses the genetic material • Cytoplasm-surrounds the nucleus and contains all the other organelles • Cell Membrane-surrounds the cytoplasm and controls what goes in and out, also communicates with other cells • Organelles-specialized structures that perform specific functions which divide ...
Cell Organelle Chart
... DNA RNA amino acids proteins Instructions, messenger, building blocks These proteins are used in your cells’ membranes for building muscles, creating blood cells, enzymes, etc. ...
... DNA RNA amino acids proteins Instructions, messenger, building blocks These proteins are used in your cells’ membranes for building muscles, creating blood cells, enzymes, etc. ...
The Cell - Community College of Rhode Island
... bilayer (with pores) Bilayers surround the fluid part of nucleus (nucleoplasm) Continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum ...
... bilayer (with pores) Bilayers surround the fluid part of nucleus (nucleoplasm) Continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum ...
Nucleus - JeongAPbiology
... • Centrioles are located in centrosomes and are important in cell division • 2 types of microtubles -flagella is a long tail used to help cell propel through water (unicellular) -cilia are “hairs” that also help cell move • 3 types of intercellular junctions (connections to neihbor cells) - tight ju ...
... • Centrioles are located in centrosomes and are important in cell division • 2 types of microtubles -flagella is a long tail used to help cell propel through water (unicellular) -cilia are “hairs” that also help cell move • 3 types of intercellular junctions (connections to neihbor cells) - tight ju ...
Cell Organelles
... replicate independently. They are most commonly found in bacteria as small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. ...
... replicate independently. They are most commonly found in bacteria as small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. ...
Unit 5 Cells Study Guide
... 17. What is a flagella? How does it differ in size and number from cilia? What is the function of each of these organelles? (bottom of p.181) 18. How is the composition of cilia and flagella different with reference to microtubules? Sketch that difference below. p.499 & p.501 ...
... 17. What is a flagella? How does it differ in size and number from cilia? What is the function of each of these organelles? (bottom of p.181) 18. How is the composition of cilia and flagella different with reference to microtubules? Sketch that difference below. p.499 & p.501 ...
Cell Organelles - Mayfield City Schools
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.