cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
Biology - cloudfront.net
... crenate, plasmolysis, turgor pressure, facilitated diffusion, equilibrium, cytolosis 2) Know functions of: vacuole, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cell wall, chloroplast, cilia, cytoskeleton, Cytosol, Lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, plasma membrane, rough ER, smooth ER 3) Know disc ...
... crenate, plasmolysis, turgor pressure, facilitated diffusion, equilibrium, cytolosis 2) Know functions of: vacuole, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cell wall, chloroplast, cilia, cytoskeleton, Cytosol, Lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, plasma membrane, rough ER, smooth ER 3) Know disc ...
Cell Structure and Function
... cell membrane for exocytosis • Produces lysosomes • Cis and trans face ...
... cell membrane for exocytosis • Produces lysosomes • Cis and trans face ...
Reproduction
... 5) The manufactured protein enters the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 6) A vesicle forms at the end of the ER, and carries the protein to the Golgi body. 7) The Golgi body repackages the protein for transport out of the cell. 8) A vesicle forms off the end of the Golgi body to carry the protein to the ...
... 5) The manufactured protein enters the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 6) A vesicle forms at the end of the ER, and carries the protein to the Golgi body. 7) The Golgi body repackages the protein for transport out of the cell. 8) A vesicle forms off the end of the Golgi body to carry the protein to the ...
Chapter 4 Eukaryotic Cell
... Free in the cytoplasm Show up as dots in a micrograph. Made up of two subunits. Each subunit is made up of proteins and ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
... Free in the cytoplasm Show up as dots in a micrograph. Made up of two subunits. Each subunit is made up of proteins and ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
Cells and Tissues - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy of the Cell Cells are not all the same All cells share general structures Cells are organized into three main regions Nucleus Cytoplasm Plasma membrane ...
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy of the Cell Cells are not all the same All cells share general structures Cells are organized into three main regions Nucleus Cytoplasm Plasma membrane ...
Practice Cell Organelle Quiz
... ______ Found inside the nucleus; Makes ribosomes ______ Finishes and Packages molecules to be released to the outside of the cell ______ Whip-like projection on outside of cell ...
... ______ Found inside the nucleus; Makes ribosomes ______ Finishes and Packages molecules to be released to the outside of the cell ______ Whip-like projection on outside of cell ...
Cell parts practice
... and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
... and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
Curtis Science Dept. Biology Name: Period: Date: Chapter 10: Cell
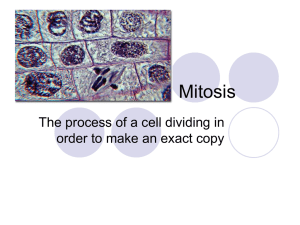
... The first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus. ...
... The first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus. ...
Grade 6 Spelling
... algae, and some bacteria 5. Cellular respiration- process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen 6. Fermentation- process by which cells release energy by breaking down food molecules without using oxygen 7. Interphase- first stage of the cel ...
... algae, and some bacteria 5. Cellular respiration- process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen 6. Fermentation- process by which cells release energy by breaking down food molecules without using oxygen 7. Interphase- first stage of the cel ...
Plant Cell
... Within the nucleus is the DNA responsible for providing the cell with its unique characteristics. The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus to positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they are critical in protei ...
... Within the nucleus is the DNA responsible for providing the cell with its unique characteristics. The prominent structure in the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus to positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they are critical in protei ...
Microscopes allow us to see inside the cell
... membrane where most of the cell work is done. • EUKARYOTIC cells have a nucleus containing its genetic material. (most multicellular) • PROKARYOTIC cells have its genetic material float throughout the cytoplasm with no nucleus. (most unicellular are prokaryotes) • ORGANELLES are any part of a cell e ...
... membrane where most of the cell work is done. • EUKARYOTIC cells have a nucleus containing its genetic material. (most multicellular) • PROKARYOTIC cells have its genetic material float throughout the cytoplasm with no nucleus. (most unicellular are prokaryotes) • ORGANELLES are any part of a cell e ...
Ch. 7 GN - Jamestown Public Schools
... - Facilitated diffusion - _____________ that can’t __________ across the ______ lipid bilayer on their own, move through ___________ channels instead ...
... - Facilitated diffusion - _____________ that can’t __________ across the ______ lipid bilayer on their own, move through ___________ channels instead ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.