CHAPTER - 8 CELL – STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
... The cell membrane gives shape to the cell, protects the inner parts of the cell and allows movement of materials in and out of the cell. In plant cells the cell membrane is covered by another thick covering called cell wall. The cytoplasm is a jelly like substance between the cell membrane ad nucleu ...
... The cell membrane gives shape to the cell, protects the inner parts of the cell and allows movement of materials in and out of the cell. In plant cells the cell membrane is covered by another thick covering called cell wall. The cytoplasm is a jelly like substance between the cell membrane ad nucleu ...
Year 9 Biological Principles word sheet
... Smallest change that can be measured by an instrument. For example, in a microscope it is the smallest distance between two points that can be seen as two points and not blurred into one point. A dye used to colour parts of a cell to make them easier to see. ...
... Smallest change that can be measured by an instrument. For example, in a microscope it is the smallest distance between two points that can be seen as two points and not blurred into one point. A dye used to colour parts of a cell to make them easier to see. ...
CHAPTER - 8 CELL – STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
... The cell membrane gives shape to the cell, protects the inner parts of the cell and allows movement of materials in and out of the cell. In plant cells the cell membrane is covered by another thick covering called cell wall. The cytoplasm is a jelly like substance between the cell membrane ad nucleu ...
... The cell membrane gives shape to the cell, protects the inner parts of the cell and allows movement of materials in and out of the cell. In plant cells the cell membrane is covered by another thick covering called cell wall. The cytoplasm is a jelly like substance between the cell membrane ad nucleu ...
(endosymbiotic) origin of the nucleus - Université Paris-Sud
... manner in which the nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm’’. This is true, but the question is also whether we should expect, after many hundred millions years of evolution, to find a nuclear membrane remaining identical to that of a free-living prokaryote. We think this is highly improbable. On t ...
... manner in which the nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm’’. This is true, but the question is also whether we should expect, after many hundred millions years of evolution, to find a nuclear membrane remaining identical to that of a free-living prokaryote. We think this is highly improbable. On t ...
Why is the cell membrane so important?
... Why? 1. Channels are made out protein; “likes” both water and lipids ...
... Why? 1. Channels are made out protein; “likes” both water and lipids ...
Function
... – Have other membrane-enclosed structures (ORGANELLES) – Larger – Structurally more complex ...
... – Have other membrane-enclosed structures (ORGANELLES) – Larger – Structurally more complex ...
The World of Biology
... division is the formation of two cells from an existing cell. In unicellular organisms, cell division results in more organisms. Newly divided cells enlarge until they are the size of a mature cell. In multicellular organisms, however, organisms grow and mature through cell division, cell enlargemen ...
... division is the formation of two cells from an existing cell. In unicellular organisms, cell division results in more organisms. Newly divided cells enlarge until they are the size of a mature cell. In multicellular organisms, however, organisms grow and mature through cell division, cell enlargemen ...
Eukaryotic Notes
... Function: Gives the cells shape and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. ...
... Function: Gives the cells shape and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. ...
Vocabulary from the 1 st 6 weeks
... support that it needs. To help cell wall is the vacuole, a large pocket of mostly water enclosed in a membrane. This exerts pressure on the cell wall to give additional strength. Function: Chloroplast is an organelle where sugar is made during photosynthesis (found only in plants). Mitochondria are ...
... support that it needs. To help cell wall is the vacuole, a large pocket of mostly water enclosed in a membrane. This exerts pressure on the cell wall to give additional strength. Function: Chloroplast is an organelle where sugar is made during photosynthesis (found only in plants). Mitochondria are ...
Name
... cells to gain or lose water helps maintain their shapes, which contribute to their function to open or close the stomata. ...
... cells to gain or lose water helps maintain their shapes, which contribute to their function to open or close the stomata. ...
Topic Thiteen - Science - Miami
... Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Identify basic structures that most cells share Compare and contrast the structure and function of the major organelles of plant and animal cells Distinguish plant cells from animal cells using the differences in organelles Develop a mo ...
... Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Identify basic structures that most cells share Compare and contrast the structure and function of the major organelles of plant and animal cells Distinguish plant cells from animal cells using the differences in organelles Develop a mo ...
1 - Lone Star College
... Cholesterol molecules stabilize the membrane Glycoproteins and glycolipids attached to outer surface of some protein and lipid molecules mark cells as belonging to a particular individual ...
... Cholesterol molecules stabilize the membrane Glycoproteins and glycolipids attached to outer surface of some protein and lipid molecules mark cells as belonging to a particular individual ...
Unit Learning Goals - Mayfield City Schools
... Explain the cell as a functioning system highlighting how the organelles work together and depend on each other. This description includes situations where the lack of one organelle would impact the overall function of the specialized cell. Explain that the components of the cell are made of CHNOPS ...
... Explain the cell as a functioning system highlighting how the organelles work together and depend on each other. This description includes situations where the lack of one organelle would impact the overall function of the specialized cell. Explain that the components of the cell are made of CHNOPS ...
Molekuláris bionika és Infobionika Szakok tananyagának komplex
... PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members ...
... PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members ...
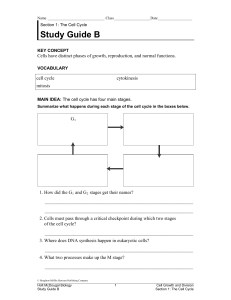
Study Guide B
... 9. Which typically increases faster as a cell grows, surface area or volume? _______________________________________________________________ 10. For cells to stay the same size from generation to generation, what two things must be coordinated? _______________________________________________________ ...
... 9. Which typically increases faster as a cell grows, surface area or volume? _______________________________________________________________ 10. For cells to stay the same size from generation to generation, what two things must be coordinated? _______________________________________________________ ...
Biosphere - Studentportalen
... With Ume, these molecules were concentrated, reacted with each other and formed more advanced molecules like proteins and nucleoUde bases ...
... With Ume, these molecules were concentrated, reacted with each other and formed more advanced molecules like proteins and nucleoUde bases ...
Biology
... f. properly apply all terms and concepts in describing/explaining real world examples g. make and interpret scientific graphs and diagrams h. teach someone else the concepts discussed i. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. relate advances i ...
... f. properly apply all terms and concepts in describing/explaining real world examples g. make and interpret scientific graphs and diagrams h. teach someone else the concepts discussed i. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. relate advances i ...
Basic cell notes
... • provides mechanical support and maintains cell shape • provides anchorage for many organelles and cytosolic enzymes • dynamic; dismantled in one part and reassembled in another (changes shape of cell) • major role in cell motility THREE MAIN CYTOSKELETAL FIBERS: 1) TUBULIN MICROTUBULES- thickest; ...
... • provides mechanical support and maintains cell shape • provides anchorage for many organelles and cytosolic enzymes • dynamic; dismantled in one part and reassembled in another (changes shape of cell) • major role in cell motility THREE MAIN CYTOSKELETAL FIBERS: 1) TUBULIN MICROTUBULES- thickest; ...
File
... A microscope allows scientists to study very small objects. It magnifies objects by focusing light or electrons. The chart below contains information about three kinds of microscopes. The middle column contains a description of each type of microscope. The third column describes ways each type of mi ...
... A microscope allows scientists to study very small objects. It magnifies objects by focusing light or electrons. The chart below contains information about three kinds of microscopes. The middle column contains a description of each type of microscope. The third column describes ways each type of mi ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.