Model - Sitka School District
... Plant and Animal Cells GLE SC2.1 Diversity of Life The student demonstrates an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles and diversity of living organisms by describing the basic structure and function of plant and animal cells. ...
... Plant and Animal Cells GLE SC2.1 Diversity of Life The student demonstrates an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles and diversity of living organisms by describing the basic structure and function of plant and animal cells. ...
CHAPTER 3: CELLS
... Why is there this arrangement of lipids? Cytoplasm and outside of cell is _________________ Molecules on the Plasma Membrane ...
... Why is there this arrangement of lipids? Cytoplasm and outside of cell is _________________ Molecules on the Plasma Membrane ...
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 3: Anatomy of
... Chapter 3: Anatomy of Cells Simply stated, cell theory asserts that the cell is the fundamental organizational unit of life. Common cell structures and their functions are examined in this chapter. The approach is general, and the model of the "composite cell" is useful for an overall understanding. ...
... Chapter 3: Anatomy of Cells Simply stated, cell theory asserts that the cell is the fundamental organizational unit of life. Common cell structures and their functions are examined in this chapter. The approach is general, and the model of the "composite cell" is useful for an overall understanding. ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... DNA molecule attached to the inner cell membrane • They divide through a simple form of division called Binary Fission ...
... DNA molecule attached to the inner cell membrane • They divide through a simple form of division called Binary Fission ...
A cell is like a human body because the both contain things that are
... The vacuole is like a stomach because the stomach stores food and water for the body like the vacuole stores food and water for the cell ...
... The vacuole is like a stomach because the stomach stores food and water for the body like the vacuole stores food and water for the cell ...
Cell Reproduction Notes
... In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough ____________________ and __________ across its cell membrane – Activity Surface Area to volume ratio ...
... In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough ____________________ and __________ across its cell membrane – Activity Surface Area to volume ratio ...
Slide 1
... - Chromosome (thread) segregation during mitosis (i.e. precise partitioning/transport of defined cell structures) ...
... - Chromosome (thread) segregation during mitosis (i.e. precise partitioning/transport of defined cell structures) ...
Taxonomy - starting with the Domain
... Classification is the process of sorting and organizing things into groups having similar characteristics. Grouping objects together allows scientist to easily observe similarities within groups and differences between groups. Scientists then seek to explain why these similarities and differences ex ...
... Classification is the process of sorting and organizing things into groups having similar characteristics. Grouping objects together allows scientist to easily observe similarities within groups and differences between groups. Scientists then seek to explain why these similarities and differences ex ...
Bacteria - Auburn City Schools
... “stuffed” inside the cell, along with free floating ribosomes (which help make proteins and have RNA). Reproduces by binary fission Since the cell’s DNA is not concentrated in one area all the bacteria cell has to do is double it’s genetic material, and split in half. ...
... “stuffed” inside the cell, along with free floating ribosomes (which help make proteins and have RNA). Reproduces by binary fission Since the cell’s DNA is not concentrated in one area all the bacteria cell has to do is double it’s genetic material, and split in half. ...
Biology EOC Review
... 2) Lipids – composed of fatty acids joined to glycerol and sometimes phosphate groups, can also include the steroids 3) Proteins – composed of amino acids (20 different types) – do most of the work in organisms and are major structural components 4) Nucleic Acids – are composed of nucleotides – eith ...
... 2) Lipids – composed of fatty acids joined to glycerol and sometimes phosphate groups, can also include the steroids 3) Proteins – composed of amino acids (20 different types) – do most of the work in organisms and are major structural components 4) Nucleic Acids – are composed of nucleotides – eith ...
The Cell - Blass Wiki
... All cells share certain structures that make them a cell All cells must contain at least 3 basic structures to be considered a living cell ...
... All cells share certain structures that make them a cell All cells must contain at least 3 basic structures to be considered a living cell ...
Diffusion and osmosis notes
... a. Hypotonic environment – occurs in fresh water with single-celled organisms. They often have contractile vacuoles to push out the excess water b. Hypotonic environment for plants – The cell wall prevents the cell from ...
... a. Hypotonic environment – occurs in fresh water with single-celled organisms. They often have contractile vacuoles to push out the excess water b. Hypotonic environment for plants – The cell wall prevents the cell from ...
Document
... The cell membrane has a two-layered structure mainly made of protein, lipid and carbohydrate molecules Protein molecules are embedded in the lipid bilayer Carbohydrate molecules may branch out from the external surface of the membrane ...
... The cell membrane has a two-layered structure mainly made of protein, lipid and carbohydrate molecules Protein molecules are embedded in the lipid bilayer Carbohydrate molecules may branch out from the external surface of the membrane ...
Cell Structures and Functions
... – Protein filaments in a 9+2 arrangement embedded in the membrane ...
... – Protein filaments in a 9+2 arrangement embedded in the membrane ...
Structure and Function of Cells – Glossary
... large sac like structure in a plant cell that regulates water content of the cell ...
... large sac like structure in a plant cell that regulates water content of the cell ...
What Makes Up A Living Thing
... Mitochondrion Small double-membrane organelle; called the power plant of the cell because it converts energy from food to energy the cell can use through the process of cellular respiration Nucleus Directs all the cell’s activities; contains genetic material called DNA ...
... Mitochondrion Small double-membrane organelle; called the power plant of the cell because it converts energy from food to energy the cell can use through the process of cellular respiration Nucleus Directs all the cell’s activities; contains genetic material called DNA ...
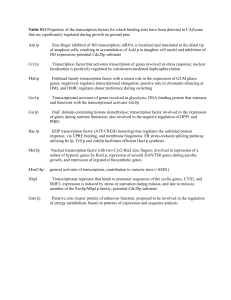
Table S11 Properties of the transcription factors for which binding
... Table S11 Properties of the transcription factors for which binding sites have been detected in CAZymes that are significantly regulated during growth on ground pine Ash1p ...
... Table S11 Properties of the transcription factors for which binding sites have been detected in CAZymes that are significantly regulated during growth on ground pine Ash1p ...
Cell - My Teacher Pages
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
Gated ion channels
... Cytoplasm • Cytoplasm: gel-like internal substance of cells that includes many organelles suspended in watery intracellular fluid called cytosol • Cellular material outside nucleus but inside plasma membrane • Two major groups of organelles (Table 3-3) – Membranous organelles are sacs or canals mad ...
... Cytoplasm • Cytoplasm: gel-like internal substance of cells that includes many organelles suspended in watery intracellular fluid called cytosol • Cellular material outside nucleus but inside plasma membrane • Two major groups of organelles (Table 3-3) – Membranous organelles are sacs or canals mad ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.