* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Taxonomy - starting with the Domain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
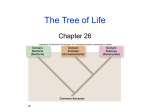
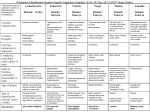
Name: __________________ Period:___ TAXONOMY Classification is the process of sorting and organizing things into groups having similar characteristics. Grouping objects together allows scientist to easily observe similarities within groups and differences between groups. Scientists then seek to explain why these similarities and differences exist. Taxonomy is the special name given to the science and practice of classification. Biological classification is a form of Taxonomy in which Biologist attempt to group and categorize all living organisms. Recent advances in microscope technology, understanding cellular chemistry, and discoveries about the nature of genetic material found in cells (DNA) have changed the field of Taxonomy. Up until the last 50 years or so it was thought that all life fit into two categories…plant or animal. Taxonomy is much more complex than that now. Today Taxonomy begins by looking at the smallest unit of life…the cell. Based on the characteristic of cells, all life forms are now placed into one of three groups…called Domains. These three domains…Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya are the broadest categories of life classification…they contain all known life forms. Life Cell Structure = Nucleus? No - Yes Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Energy? Domain Domain Domain Archaea Bacteria Eukarya Characteristics Autotrophic Prokaryotic Unicellular Asexual Reproduction Extreme Habitats Ancient Characteristics Heterotrophic Decomposers! Prokaryotic Unicellular Asexual Reproduction Possibly Pathogenic (cause disease) Most biomass on planet Characteristics Eukaryotic = NUCLEUS! Multicellular or Unicellular Sexual Reproduction Heterotrophic or Autotrophic Examples Halophiles – Successful in – salt (NaCl) Thermoacidophiles – Successful in acid / extreme heat Examples Cyanobacteria Examples All plants, algae, animals, and fungi. These are further split into the Kingdoms – Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, & Protista