Name: Date: Block: Science 8 Chapter 1 Review Answer the
... Answer the following questions in full sentences on a separate piece of lined paper. 1. What are the 5 characteristics of living things? 2. What is the cell theory? 3. What is the field of view? Which objective lens will show you the greatest field of view? 4. What is the nucleus of a cell? 5. Expla ...
... Answer the following questions in full sentences on a separate piece of lined paper. 1. What are the 5 characteristics of living things? 2. What is the cell theory? 3. What is the field of view? Which objective lens will show you the greatest field of view? 4. What is the nucleus of a cell? 5. Expla ...
First Six Weeks Test Corrections The cell membrane controls what
... 2. The mitochondria releases chemical energy for the cell’s activities. 3. Plant cells are usually rectangular in shape. 4. The thick-jelly like substance that holds organelles in place inside a cell is the cytoplasm. 5. Central vacuole is used as storage in the cell. 6. The porous holes in the cell ...
... 2. The mitochondria releases chemical energy for the cell’s activities. 3. Plant cells are usually rectangular in shape. 4. The thick-jelly like substance that holds organelles in place inside a cell is the cytoplasm. 5. Central vacuole is used as storage in the cell. 6. The porous holes in the cell ...
Cardiovascular System
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function In all living cells Human cells have characteristics for carrying out special functions ...
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function In all living cells Human cells have characteristics for carrying out special functions ...
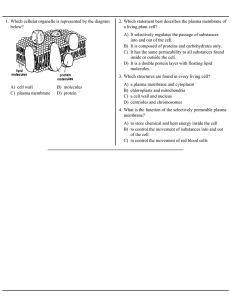
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
Human Body Vocabulary
... Human Body Vocabulary GLE 0507.4.1 Describe how genetic information is passed from parents to offspring during reproduction ...
... Human Body Vocabulary GLE 0507.4.1 Describe how genetic information is passed from parents to offspring during reproduction ...
Plant and Animal Cells www
... Part A: Plant Cells Draw a diagram of a plant cell and using the illustration on the web page to label your diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
... Part A: Plant Cells Draw a diagram of a plant cell and using the illustration on the web page to label your diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
sci 7 study guide
... Genus-group of species; when a scientist discovers a new species, it is placed with the species with which it shares the most characteristics Structure and Function of Living Organisms: From Cells to Organisms Cells: smallest, or lowest, level of organization of the human body Organelles/parts: nucl ...
... Genus-group of species; when a scientist discovers a new species, it is placed with the species with which it shares the most characteristics Structure and Function of Living Organisms: From Cells to Organisms Cells: smallest, or lowest, level of organization of the human body Organelles/parts: nucl ...
CELL PARTS MATCHING - SD43 Teacher Sites
... PACKAGES PROTEIN AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE TO THE CELL ...
... PACKAGES PROTEIN AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE TO THE CELL ...
Plant and Animal Cells www
... Part A: Plant Cells Draw a diagram of a plant cell and using the illustration on the web page to label your diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
... Part A: Plant Cells Draw a diagram of a plant cell and using the illustration on the web page to label your diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
6.2.02i - UC CEAS
... a) Organs are made from one type of tissue. b) Tissues are made from one type of organ. c) Tissues are made from one different types of organs. d) Organs are made from different types of tissues. 4) Which is an example of a group of cells with a common structure and function? a) Kidney b) Kidney tis ...
... a) Organs are made from one type of tissue. b) Tissues are made from one type of organ. c) Tissues are made from one different types of organs. d) Organs are made from different types of tissues. 4) Which is an example of a group of cells with a common structure and function? a) Kidney b) Kidney tis ...
Cell Structure and Function Highlight Packet
... 2. The main difference between the structure of the smooth ER versus the rough ER is that the rough ER has ___________________ on its surface. 3. The central _____________________ in a plant is used to store water, nutrients and wastes. 4. Eukaryotic cells have ___________________ bound ____________ ...
... 2. The main difference between the structure of the smooth ER versus the rough ER is that the rough ER has ___________________ on its surface. 3. The central _____________________ in a plant is used to store water, nutrients and wastes. 4. Eukaryotic cells have ___________________ bound ____________ ...
Chapter review p 83-84 Model answers Cell Function Organelles
... 19. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of folded membranes within a cell where many proteins, lipids, and other materials are made in the cell. The smooth ER also helps break down toxic materials. The ER is the part of the internal delivery system in a cell. The Golgi complex modifies, packa ...
... 19. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of folded membranes within a cell where many proteins, lipids, and other materials are made in the cell. The smooth ER also helps break down toxic materials. The ER is the part of the internal delivery system in a cell. The Golgi complex modifies, packa ...
Introduction: Apoptosis – programmed cell death significantly
... Apoptosis – programmed cell death significantly participates in maintaining of tissue homeostasis. Its alteration is leading to cancer disease. Inositolhexaphosphate (IP6) is naturally occurring substance that is present in most legumes, cereals and seems. IP6 and its lower phosphorylated forms are ...
... Apoptosis – programmed cell death significantly participates in maintaining of tissue homeostasis. Its alteration is leading to cancer disease. Inositolhexaphosphate (IP6) is naturally occurring substance that is present in most legumes, cereals and seems. IP6 and its lower phosphorylated forms are ...
Part 2: EOC Review Questions
... Describe the structure of a cell membrane? Why are some membranes considered selectively permeable? What is the function of proteins found within the cell membrane? What type of cellular transport does not require energy? What type of cellular transport requires energy What is meant by a concentrati ...
... Describe the structure of a cell membrane? Why are some membranes considered selectively permeable? What is the function of proteins found within the cell membrane? What type of cellular transport does not require energy? What type of cellular transport requires energy What is meant by a concentrati ...
01A004 - Proliferated Cell Lines and Uses Thereof
... Despite the promising potential of cellular therapies, one fundamental problem that has long hindered implementation is the fact that most cells are only capable of replicating a finite number of times. As this technique can be employed on virtually any adult cell type, potential applications where ...
... Despite the promising potential of cellular therapies, one fundamental problem that has long hindered implementation is the fact that most cells are only capable of replicating a finite number of times. As this technique can be employed on virtually any adult cell type, potential applications where ...
levels of organization directed reading
... Organism is the name of the independent living thing. It can carry out the basic functions of life. Organisms can be made of a single cell or of multiple cells. The definition of "living thing" is still debated in scientific circles (a virus, for example, is considered by some to be living, but othe ...
... Organism is the name of the independent living thing. It can carry out the basic functions of life. Organisms can be made of a single cell or of multiple cells. The definition of "living thing" is still debated in scientific circles (a virus, for example, is considered by some to be living, but othe ...
Print here - Ecosystemforkids.com
... Identify an organism below that has cells that have a cell wall. a. ...
... Identify an organism below that has cells that have a cell wall. a. ...
Human Structure and Function (HUMB1000) – UNIT NOTES
... b) regional: body is studied area by area (region by region) – studying anatomy of specific region 2) Surface Anatomy: study of the external for of the body and its relation to deeper structures. (is gross macroscopic anatomy) eg: sternum and ribs (surface landmark)) 3) Microscopic: structures exami ...
... b) regional: body is studied area by area (region by region) – studying anatomy of specific region 2) Surface Anatomy: study of the external for of the body and its relation to deeper structures. (is gross macroscopic anatomy) eg: sternum and ribs (surface landmark)) 3) Microscopic: structures exami ...
cells alive webquest
... when you are ready to learn about another organelle. f) Read and answer the questions below. ...
... when you are ready to learn about another organelle. f) Read and answer the questions below. ...