vocab flip chart - Effingham County Schools
... found in all the cells of all living things, the blueprint for life, is the instructions for proteins ...
... found in all the cells of all living things, the blueprint for life, is the instructions for proteins ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... microscope? Explain your answer. With a light microscope you could easily distinguish the prokaryotic bacteria from the other cell types. The prokaryotic bacteria would not have a nucleus, the other cell types would. The yeast cell wall would distinguish yeast cells from human and insect cells. Dist ...
... microscope? Explain your answer. With a light microscope you could easily distinguish the prokaryotic bacteria from the other cell types. The prokaryotic bacteria would not have a nucleus, the other cell types would. The yeast cell wall would distinguish yeast cells from human and insect cells. Dist ...
CELL TEST REVIEW:
... Know what is passive transport and active transport Know why passive transport is different from active transport (concentration gradients and energy use) Types of passive transport (osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion) and how they differ Examples of each type of passive transport P ...
... Know what is passive transport and active transport Know why passive transport is different from active transport (concentration gradients and energy use) Types of passive transport (osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion) and how they differ Examples of each type of passive transport P ...
Unit 4 Cells Practice Exam
... 5. In all organisms, which microscopic structures carry out the major life functions? (1) chloroplasts (2) cells (3) cytoplasm (4) nucleus 6. What is the outermost structure in a plant cell? (1) cell membrane (2) cytoplasm ...
... 5. In all organisms, which microscopic structures carry out the major life functions? (1) chloroplasts (2) cells (3) cytoplasm (4) nucleus 6. What is the outermost structure in a plant cell? (1) cell membrane (2) cytoplasm ...
Oct. 5, 2015 Cells - AP Biology Study Guide
... 1. Understand the basic tenets of the cell theory. 2. Understand the implications of how the surface-to-volume ratio constrains cell size. 3. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Be able to distinguish the organelles and structures typical of eukaryotic plant and ani ...
... 1. Understand the basic tenets of the cell theory. 2. Understand the implications of how the surface-to-volume ratio constrains cell size. 3. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Be able to distinguish the organelles and structures typical of eukaryotic plant and ani ...
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
... Smallest unit of an element that still retains the properties of that element, made of subatomic particles One Atom of ...
... Smallest unit of an element that still retains the properties of that element, made of subatomic particles One Atom of ...
3 The cell as the basic unit of life
... (d) Mitochondria. Respiration occurs in mitochondria to release energy. ...
... (d) Mitochondria. Respiration occurs in mitochondria to release energy. ...
Cellular Hierarchy - Bibb County Schools
... S7L2c Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems and systems into organisms. ...
... S7L2c Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems and systems into organisms. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Draw at least three different types of specialized cells on separate paper and label the cell type (animal or plant) and any recognizable cell structures. Then compare the different cells and describe how their structures are related to their functions. ...
... Draw at least three different types of specialized cells on separate paper and label the cell type (animal or plant) and any recognizable cell structures. Then compare the different cells and describe how their structures are related to their functions. ...
Cell Processes Study Guide
... Photosynthesis – this process takes place in the Chloroplast of the cell Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the ...
... Photosynthesis – this process takes place in the Chloroplast of the cell Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the ...
Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is
... move) cells (like sperm cells or some protists) 4) Organelle that controls and manages cell functions in eukaryotic cells 5) Fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are found 6) Produces a usable form of energy (ATP) for the cell 7) Stack of membranes that modifies and packages proteins and ot ...
... move) cells (like sperm cells or some protists) 4) Organelle that controls and manages cell functions in eukaryotic cells 5) Fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are found 6) Produces a usable form of energy (ATP) for the cell 7) Stack of membranes that modifies and packages proteins and ot ...
Organ Systems and Homeostasis
... 9. What happens if part of an organ system fails? • Failure of any part can affect the entire system, potentially causing organ system failure • Example: heart attack ...
... 9. What happens if part of an organ system fails? • Failure of any part can affect the entire system, potentially causing organ system failure • Example: heart attack ...
I. Organization of Living Things TISSUE CELL
... ______________________ System: breaks down food so it can be used by cells for growth and energy. ______________________ System: carries food and oxygen to cells ______________________ System: brings in oxygen and gets rid of harmful gases ______________________ System: protects the body, helps cont ...
... ______________________ System: breaks down food so it can be used by cells for growth and energy. ______________________ System: carries food and oxygen to cells ______________________ System: brings in oxygen and gets rid of harmful gases ______________________ System: protects the body, helps cont ...
Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Eukaryotic cells can differ from each other depending on their jobs Structure is the arrangement of parts Function is the activity the parts carry out Ex: plant and animal cells differ, cells in a single organism can be different depending on function Most cells in multicellular organisms have a spe ...
... Eukaryotic cells can differ from each other depending on their jobs Structure is the arrangement of parts Function is the activity the parts carry out Ex: plant and animal cells differ, cells in a single organism can be different depending on function Most cells in multicellular organisms have a spe ...
Study Guide for Science Test
... Diffusion: Process by which particles of a substance move from an area where there are many particles of the substance to an area where there are fewer particles of the substance. Chloroplast: Organelle that contains chlorophyll, and is found only in plant cells. Cell: Basic unit of structure and fu ...
... Diffusion: Process by which particles of a substance move from an area where there are many particles of the substance to an area where there are fewer particles of the substance. Chloroplast: Organelle that contains chlorophyll, and is found only in plant cells. Cell: Basic unit of structure and fu ...
Objectives Cell unit
... 13. produce labeled drawings of each type of cell 14. list three differences between plant and animal cells. Include: (i) plant cells have chloroplasts (ii) plant cells have cell walls, therefore they have a regular shape (iii) plant cells have fewer, and larger, vacuoles ...
... 13. produce labeled drawings of each type of cell 14. list three differences between plant and animal cells. Include: (i) plant cells have chloroplasts (ii) plant cells have cell walls, therefore they have a regular shape (iii) plant cells have fewer, and larger, vacuoles ...
01 - Cobb Learning
... 3. the fluid inside a cell 7. the world’s smallest cells 10. the chemical control center of a cell 11. organelle containing digestive enzymes 12. kind of cell that does not have a nucleus 13. organelle that packages and transport materials out of the cell 17. describes an organism that exists as a g ...
... 3. the fluid inside a cell 7. the world’s smallest cells 10. the chemical control center of a cell 11. organelle containing digestive enzymes 12. kind of cell that does not have a nucleus 13. organelle that packages and transport materials out of the cell 17. describes an organism that exists as a g ...
ch-3-crossword-puzzle
... 3. the fluid inside a cell 7. the world’s smallest cells 10. the chemical control center of a cell 11. organelle containing digestive enzymes 12. kind of cell that does not have a nucleus 13. organelle that packages and transport materials out of the cell 17. describes an organism that exists as a g ...
... 3. the fluid inside a cell 7. the world’s smallest cells 10. the chemical control center of a cell 11. organelle containing digestive enzymes 12. kind of cell that does not have a nucleus 13. organelle that packages and transport materials out of the cell 17. describes an organism that exists as a g ...
19th May 2015 - Prof Robert Brown
... substrates and require slow, problematic cell seeding while native protein 3D substrates are cell friendly but frequently (always?) are exceedingly weak, over-hydrated hydrogels. Plastic compression is now in use within two separate families of applications; namely for en mass fabrication of 3D livi ...
... substrates and require slow, problematic cell seeding while native protein 3D substrates are cell friendly but frequently (always?) are exceedingly weak, over-hydrated hydrogels. Plastic compression is now in use within two separate families of applications; namely for en mass fabrication of 3D livi ...
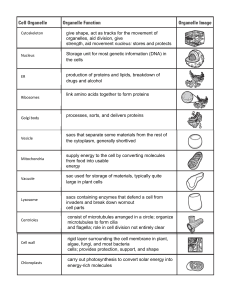
carry out photosynthesis to convert solar energy into energy
... give shape, act as tracks for the movement of organelles, aid division, give strength, aid movement nucleus: stores and protects the DNA Storage unit for most genetic information (DNA) in the cells production of proteins and lipids, breakdown of drugs and alcohol link amino acids together to form pr ...
... give shape, act as tracks for the movement of organelles, aid division, give strength, aid movement nucleus: stores and protects the DNA Storage unit for most genetic information (DNA) in the cells production of proteins and lipids, breakdown of drugs and alcohol link amino acids together to form pr ...