TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.1
... 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at different rates Rates of cell division vary widely and are linked to the body’s need. The length of ga ...
... 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at different rates Rates of cell division vary widely and are linked to the body’s need. The length of ga ...
chapter 40 basic principles of animal form and function
... •Responsible for nearly all types of body movement •Muscle filaments are made of the proteins actin (thin) and myosin (thick) •Muscle fibers contract when stimulated by a nerve impulse •Most abundant tissue in most animals •Three types of muscle: skeletal (voluntary), cardiac ...
... •Responsible for nearly all types of body movement •Muscle filaments are made of the proteins actin (thin) and myosin (thick) •Muscle fibers contract when stimulated by a nerve impulse •Most abundant tissue in most animals •Three types of muscle: skeletal (voluntary), cardiac ...
Postassessment Study Guide
... ______________ is a type of material that is made from specialized cells. ______________ is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus. ______________ the process where dead organism are broken down and important materials are returned to the environment. ______________ is an organism that is mad ...
... ______________ is a type of material that is made from specialized cells. ______________ is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus. ______________ the process where dead organism are broken down and important materials are returned to the environment. ______________ is an organism that is mad ...
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... _B__10. Carry out every activity associated with living things Lysosome Chloroplast Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Ribosome plasma membrane vacuole WHO AM I? Directions: Choose which type of organelle best fits each description. Write the correct organelle in the blank provided next to each clue. _m ...
... _B__10. Carry out every activity associated with living things Lysosome Chloroplast Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Ribosome plasma membrane vacuole WHO AM I? Directions: Choose which type of organelle best fits each description. Write the correct organelle in the blank provided next to each clue. _m ...
CELL: the smallest unit of life. CHLOROPHYLL: a material in plants
... CHLOROPHYLL: a material in plants that helps them takes in sunlight. BIOTIC FACTOR: a living part of the ecosystem. ABIOTIC FACTORS: a nonliving part of the ecosystem ENVIRONMENT: all the living and nonliving things that surround an organism. TISSUE: similar cells acting to perform a specific functi ...
... CHLOROPHYLL: a material in plants that helps them takes in sunlight. BIOTIC FACTOR: a living part of the ecosystem. ABIOTIC FACTORS: a nonliving part of the ecosystem ENVIRONMENT: all the living and nonliving things that surround an organism. TISSUE: similar cells acting to perform a specific functi ...
Cell culture on high-extension surfaces
... Cell culture on high-extension surfaces: Novel technology in support of regenerative medicine Thomas M. Quinn and Derek H. Rosenzweig While seeking ways for improved culture of chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering, we have developed novel technology for cell culture on extendable surfaces. ...
... Cell culture on high-extension surfaces: Novel technology in support of regenerative medicine Thomas M. Quinn and Derek H. Rosenzweig While seeking ways for improved culture of chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering, we have developed novel technology for cell culture on extendable surfaces. ...
6.1.01a - UC CEAS
... a) Organs are made from one type of tissue. b) Tissues are made from one type of organ. c) Tissues are made from one different types of organs. d) Organs are made from different types of tissues. 4) Which is an example of a group of cells with a common structure and function? a) Kidney b) Kidney tis ...
... a) Organs are made from one type of tissue. b) Tissues are made from one type of organ. c) Tissues are made from one different types of organs. d) Organs are made from different types of tissues. 4) Which is an example of a group of cells with a common structure and function? a) Kidney b) Kidney tis ...
Cells: basic unit of Life
... Some organisms consist of only one cell These are called unicellular or single celled Other organisms are made of many cells They are multicellular We are multicellular organisms ...
... Some organisms consist of only one cell These are called unicellular or single celled Other organisms are made of many cells They are multicellular We are multicellular organisms ...
How Cell Structure Fits Function
... Can change shape to fit between tissues to find and fight infections. ...
... Can change shape to fit between tissues to find and fight infections. ...
Name - Humble ISD
... 1. Describe the structure of a “typical cell” 2. Describe the molecular structure and function of the plasma membrane. 3. Describe the structure and function of the following: endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton (cell fibers, centroso ...
... 1. Describe the structure of a “typical cell” 2. Describe the molecular structure and function of the plasma membrane. 3. Describe the structure and function of the following: endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton (cell fibers, centroso ...
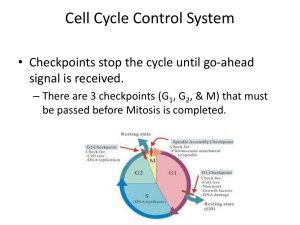
Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
... • Checkpoints stop the cycle until go-ahead signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
... • Checkpoints stop the cycle until go-ahead signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
cell structure review sheet
... Fill in the chart and be able to identify the organelles on a plant or animal cell diagram: CELL ORGANELLE ...
... Fill in the chart and be able to identify the organelles on a plant or animal cell diagram: CELL ORGANELLE ...
cells cells - Springwater River Otters
... can float around for hours Running round with chloroplasts, lovin' sunlight showers Cells, cells, they're made of organelles First things first, there's two different typesanimal and plant cells that make up all life. The little things that make up microscopic cells, The main structures- yeah, we ca ...
... can float around for hours Running round with chloroplasts, lovin' sunlight showers Cells, cells, they're made of organelles First things first, there's two different typesanimal and plant cells that make up all life. The little things that make up microscopic cells, The main structures- yeah, we ca ...
Cellular Structure
... M. Site of protein production N. Non-living part of a plant cell that provides support O. Green pigment 1n plant cells used in photosynthesis P. Special plastids in plant cells that contain the chlorophyll Q. "Powerhouse" of the cell because it releases energy for the cell's use R. Contain genetic i ...
... M. Site of protein production N. Non-living part of a plant cell that provides support O. Green pigment 1n plant cells used in photosynthesis P. Special plastids in plant cells that contain the chlorophyll Q. "Powerhouse" of the cell because it releases energy for the cell's use R. Contain genetic i ...
1st Q Life Science
... h. Meosis: The special kind of cell division in which sex cells are produced with half as many chromosomes as in other cells. i. ...
... h. Meosis: The special kind of cell division in which sex cells are produced with half as many chromosomes as in other cells. i. ...
No Slide Title
... Which situation BEST represents active transport in a cell? a. clothes are pushed into a hamper that is already filled b. lemonade is poured out of a full pitcher c. sugar is dissolved in a glass of hot tea d. one student is placed at each desk ...
... Which situation BEST represents active transport in a cell? a. clothes are pushed into a hamper that is already filled b. lemonade is poured out of a full pitcher c. sugar is dissolved in a glass of hot tea d. one student is placed at each desk ...
Cell Content Statement 1 Study Guide
... Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. All cells are made of the same basic chemicals. All energy flow of life occurs within cells. ...
... Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. All cells are made of the same basic chemicals. All energy flow of life occurs within cells. ...
Excretory notes
... the filtrate. They move up the distal tubule, through the collecting duct which joins the ureter. ...
... the filtrate. They move up the distal tubule, through the collecting duct which joins the ureter. ...
Test 1 Study Guide
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...