Levels of Organization in Living Things How living things are organized
... Response to their environment (stimuli) to maintain balance (homeostasis) Adapt to their environment over time (as a species, not individual) ...
... Response to their environment (stimuli) to maintain balance (homeostasis) Adapt to their environment over time (as a species, not individual) ...
Test Review: Unit 4 Cells and microscopes What is a prokaryote
... 18. While using a microscope, you are asked for the total magnification of a specimen. How do you find the total magnification? ...
... 18. While using a microscope, you are asked for the total magnification of a specimen. How do you find the total magnification? ...
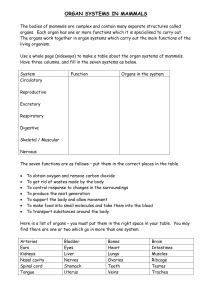
doc Organ systems table Table to fill in which will
... Skeletal / Muscular Nervous The seven functions are as follows – put them in the correct places in the table. ...
... Skeletal / Muscular Nervous The seven functions are as follows – put them in the correct places in the table. ...
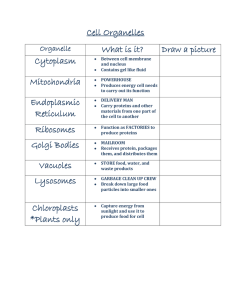
Chapter 7 The Cell
... Nucleus-Brain of cell/controls all cell activities. Cell division. Chromatin-DNA spread out in nucleus Nucleolus-Dark spot. Makes ribosomes. ...
... Nucleus-Brain of cell/controls all cell activities. Cell division. Chromatin-DNA spread out in nucleus Nucleolus-Dark spot. Makes ribosomes. ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. They prevent excessive cell growth and keep the tissues of the body from disrupting ...
... a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. They prevent excessive cell growth and keep the tissues of the body from disrupting ...
Cell: The Basic Unit of Life
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which is the only kingdom of life that is made from prokaryotic cells? _______ ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which is the only kingdom of life that is made from prokaryotic cells? _______ ...
Cells - Wsfcs
... The liquid environment of the cell. The cytoplasm contains the organelles of ...
... The liquid environment of the cell. The cytoplasm contains the organelles of ...
Six Kingdoms of Life
... S7L1. Students will investigate the diversity of living organisms and how they can be compared scientifically. b. Classify organisms based on physical characteristics using a dichotomous key of the six kingdom system (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals). ...
... S7L1. Students will investigate the diversity of living organisms and how they can be compared scientifically. b. Classify organisms based on physical characteristics using a dichotomous key of the six kingdom system (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals). ...
Semester 1 Exam Study Guide with answers
... 11. What is mitosis? The cell divides into 2 new cells Why is it important? It’s how cells reproduce 12. Which organelle is the control center of a cell? Nucleus 13. Which organelles store food and other materials needed by the cell? Vacuoles 14. What is the function of a cell membrane? To control w ...
... 11. What is mitosis? The cell divides into 2 new cells Why is it important? It’s how cells reproduce 12. Which organelle is the control center of a cell? Nucleus 13. Which organelles store food and other materials needed by the cell? Vacuoles 14. What is the function of a cell membrane? To control w ...
Starter Activity
... Starter Activity • Name 4 differences between plant and animal cells. ANSWERS 1. Shape (plant cells are rectangular and animal cells are generally round) 2. Plant cells have a large vacuole 3. Plant cells have a cell wall (to provide extra structure) 4. Plant cells have chroloplasts (where photosynt ...
... Starter Activity • Name 4 differences between plant and animal cells. ANSWERS 1. Shape (plant cells are rectangular and animal cells are generally round) 2. Plant cells have a large vacuole 3. Plant cells have a cell wall (to provide extra structure) 4. Plant cells have chroloplasts (where photosynt ...
science unit A chpt 2 lesson 2
... Plants also use hormones that may cause the stem to bend toward ______________, or could direct a plant to grow taller instead of wider. ...
... Plants also use hormones that may cause the stem to bend toward ______________, or could direct a plant to grow taller instead of wider. ...
Planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) are made up of a repeating
... Planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) are made up of a repeating sequence of thin layers of energy producing ceramics. For electro-chemical reasons it is best to keep these layers as thin as possible, which also means that the cells are more mechanically susceptible to damage during production and/or ...
... Planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) are made up of a repeating sequence of thin layers of energy producing ceramics. For electro-chemical reasons it is best to keep these layers as thin as possible, which also means that the cells are more mechanically susceptible to damage during production and/or ...
Chapter 16: Section 1 The World of Cells
... Why are cells important? They help us do what we do Breakdown food Move Grow Reproduce ...
... Why are cells important? They help us do what we do Breakdown food Move Grow Reproduce ...
Studying Life
... – Molecules make up Cells (basic unit of life) Approach to – Cells make up Tissues (a group of cells serving a particular purpose) Biology – Tissues make up organs (group of organs working together) – Organs make up the organism (multi-cellular) – A group of similar organisms make up a population (o ...
... – Molecules make up Cells (basic unit of life) Approach to – Cells make up Tissues (a group of cells serving a particular purpose) Biology – Tissues make up organs (group of organs working together) – Organs make up the organism (multi-cellular) – A group of similar organisms make up a population (o ...
cells: The living units
... Polar heads are attracted to water so they lie on the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane Nonpolar tails avoid water and line up in the center of the membrane ...
... Polar heads are attracted to water so they lie on the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane Nonpolar tails avoid water and line up in the center of the membrane ...
Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1
... Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum – folded membrane where cell materials are made (proteins, lipids) and moved to different places in the cell Mitochondria – power source of a c ...
... Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum – folded membrane where cell materials are made (proteins, lipids) and moved to different places in the cell Mitochondria – power source of a c ...
Unit 5 Anatomy and Physiology Cells
... • The human body is made up of millions of tiny cells • These can only be seen under a microscope • They appear in many different shapes and sizes and have different functions • Each cell has a nucleus which contains the genetic coding called DNA • Cells cannot function by themselves The Function of ...
... • The human body is made up of millions of tiny cells • These can only be seen under a microscope • They appear in many different shapes and sizes and have different functions • Each cell has a nucleus which contains the genetic coding called DNA • Cells cannot function by themselves The Function of ...
Important organells in a Cell 2
... Unicellular organisms: Made of only one cell. Multicellular: Made up of more than one cell eg Humans. ...
... Unicellular organisms: Made of only one cell. Multicellular: Made up of more than one cell eg Humans. ...
logcsscibap_2_1_2_d_..
... Spirogyra is an alga. It is made up of cells joined by their cell walls to form long filaments. If a single cell is detached from the filament it can survive and grow to form a new filament. a ...
... Spirogyra is an alga. It is made up of cells joined by their cell walls to form long filaments. If a single cell is detached from the filament it can survive and grow to form a new filament. a ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...