Development of a Production Process of Viral Particles –Kinetic
... stability of the MV was carried out and it has been shown that the MV in the supernatant under culture conditions was very unstable due to temperature inactivation. After infection cell metabolism changed for MV production and therefore cells stopped growing but still consumed substrates. These kine ...
... stability of the MV was carried out and it has been shown that the MV in the supernatant under culture conditions was very unstable due to temperature inactivation. After infection cell metabolism changed for MV production and therefore cells stopped growing but still consumed substrates. These kine ...
National 4/5 Biology - Multicelluar Organisms
... Many living organisms are composed of only one cell - e.g. an amoeba Most living organisms are made of many millions of cells It would be inefficient if every cell performed exactly the same function ...
... Many living organisms are composed of only one cell - e.g. an amoeba Most living organisms are made of many millions of cells It would be inefficient if every cell performed exactly the same function ...
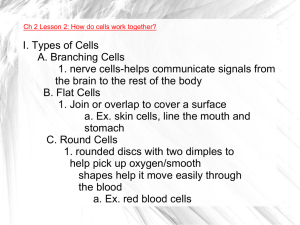
I. Types of Cells A. Branching Cells 1. nerve cells
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
Cellular specialization and differentiation
... § Research your assigned cell type. § Make a model. Pay attention to how the structure of the cell gives function to the cell. What tissue does your cell build? § You will present your model to the class! ...
... § Research your assigned cell type. § Make a model. Pay attention to how the structure of the cell gives function to the cell. What tissue does your cell build? § You will present your model to the class! ...
Cell Cycle regulation
... the cells at the site of the injury will grow until they fill in the empty space. • **These two examples show that there are controls on when cell division occurs. ...
... the cells at the site of the injury will grow until they fill in the empty space. • **These two examples show that there are controls on when cell division occurs. ...
Revision Poster
... photosynthesis. They are composed of grana (used during the light stage) and stroma (used during the dark stage) of photosynthesis. ...
... photosynthesis. They are composed of grana (used during the light stage) and stroma (used during the dark stage) of photosynthesis. ...
eukaryote: cell that has a membrane
... photosynthesis. They are composed of grana (used during the light stage) and stroma (used during the dark stage) of photosynthesis. ...
... photosynthesis. They are composed of grana (used during the light stage) and stroma (used during the dark stage) of photosynthesis. ...
Cells
... All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells ...
... All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells ...
eukaryote: cell that has a membrane
... photosynthesis. They are composed of grana (used during the light stage) and stroma (used during the dark stage) of photosynthesis. ...
... photosynthesis. They are composed of grana (used during the light stage) and stroma (used during the dark stage) of photosynthesis. ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Key
... Unit 3 Test: Study Guide Living Organisms 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular a ...
... Unit 3 Test: Study Guide Living Organisms 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular a ...
Cell Structure and Function
... We will look at the how the passage of water into a cell depends on the difference in concentration of solutes between cytoplasm and the surrounding ...
... We will look at the how the passage of water into a cell depends on the difference in concentration of solutes between cytoplasm and the surrounding ...
A - BEHS Science
... Answer each of the following questions on separate paper. All answers may be typed or handwritten… but do your OWN work. 1. Explain what happens to the surface area to volume ratio as the volume (size) of an object increases. How does this help to explain why cells are so tiny? 2. Explain the proces ...
... Answer each of the following questions on separate paper. All answers may be typed or handwritten… but do your OWN work. 1. Explain what happens to the surface area to volume ratio as the volume (size) of an object increases. How does this help to explain why cells are so tiny? 2. Explain the proces ...
Biology 109: Biology Today Laboratory 2 A literature review of cells
... Understand the differences between plant and animal cells. Have a full understanding of the (many) events involved in a typical cell life cycle. Have extra help to study for Exam One!! ...
... Understand the differences between plant and animal cells. Have a full understanding of the (many) events involved in a typical cell life cycle. Have extra help to study for Exam One!! ...
Cancer Cells - Answers - Iowa State University
... These cells were deemed ‘immortal’ because they never died - they just kept dividing and dividing. Almost all original caner testing and research were done on her cells because they lived on for so long. ...
... These cells were deemed ‘immortal’ because they never died - they just kept dividing and dividing. Almost all original caner testing and research were done on her cells because they lived on for so long. ...
7.2 Many organisms, including humans, have specialized organ
... • How are cells organized to perform specialized organ systems that specific functions in the human interact with each other to maintain body? homeostasis. • What does the structure of a cell tell (B) The cell is the basic unit of life for us about its function? all living things (except for viruses ...
... • How are cells organized to perform specialized organ systems that specific functions in the human interact with each other to maintain body? homeostasis. • What does the structure of a cell tell (B) The cell is the basic unit of life for us about its function? all living things (except for viruses ...
Supplementary Figure 4
... Supplementary figure 4. Aortic ring assays. a: overview of the culture. Scale bar, 0.5cm. b: quantification of cell movement. The distance of cell movement (pixel/2h1/2) was measured for each cell filmed (n=6 control, 8 Netrin-1, 16 Netrin-1/UNC5B-Fc). The mean±s.e.m. of all cells for each treatment ...
... Supplementary figure 4. Aortic ring assays. a: overview of the culture. Scale bar, 0.5cm. b: quantification of cell movement. The distance of cell movement (pixel/2h1/2) was measured for each cell filmed (n=6 control, 8 Netrin-1, 16 Netrin-1/UNC5B-Fc). The mean±s.e.m. of all cells for each treatment ...
Figure 1-21: Microtubules in a dividing cell.
... Figure 1-22: Some examples of the variety of cell shapes and sizes. (A) A nerve cell from the cerebellum (a part of the brain that controls movement). This cell has a huge branching tree of processes, through which it receives signals from as many as 100,000 other nerve cells. (B) Paramecium. This p ...
... Figure 1-22: Some examples of the variety of cell shapes and sizes. (A) A nerve cell from the cerebellum (a part of the brain that controls movement). This cell has a huge branching tree of processes, through which it receives signals from as many as 100,000 other nerve cells. (B) Paramecium. This p ...
Lecture 11: Cell proliferation, differentiation, and death
... Programmed cell death It is a normal physiological form of cell death with a distinct process known as apoptosis. It plays a key role both in the maintenance of adult tissues and in embryonic development. Renewal of 5 × 1011 blood cells a day elimination of nerve cells with faulty connection Elimin ...
... Programmed cell death It is a normal physiological form of cell death with a distinct process known as apoptosis. It plays a key role both in the maintenance of adult tissues and in embryonic development. Renewal of 5 × 1011 blood cells a day elimination of nerve cells with faulty connection Elimin ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... These are found only in plant cells and help protect and support them. (not large vacuole or chloroplast) ...
... These are found only in plant cells and help protect and support them. (not large vacuole or chloroplast) ...
Honors Biology Cell / Organelle Project
... You need to make a set of notes explaining the differences between different cell types and describe the organelles typically found in cells. For each term, you need to include a picture/drawing, and describe its structure and function. Here is a list of the cell types and organelles you must includ ...
... You need to make a set of notes explaining the differences between different cell types and describe the organelles typically found in cells. For each term, you need to include a picture/drawing, and describe its structure and function. Here is a list of the cell types and organelles you must includ ...