* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SPECIALIZED CELLS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
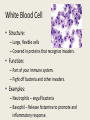
Epithelial Cells form Epithelial Tissue • Structure: – Epithelial Cells pack tightly together and form continuous sheets that line different parts of the body. • Function: – Protection, secretion, absorption, and transport • Examples: – Inside the mouth (cheek cells) – Line organs like the stomach – Surround the outside of organs – Make the outer layer of skin MUSCLE TISSUE • Structure: – Muscle cells make specialized tissue that can contract. – Muscle tissue contains the specialized proteins actin and myosin that slide past one another. • Function: – Allows for movement of limbs and contraction. • Examples: – Heart – Cardiac Muscle – Body Movement—Skeletal Muscle – Digestive Tract, Veins/Arteries, Bladder—Smooth Muscle NERVE TISSUE • Structure: – Elongated cells with many branches. • Function: – Has the ability to generate and conduct electrical signals in the body. – These signals are managed by the brain and transmitted down the spinal cord to the body. White Blood Cell • Structure: – Large, flexible cells – Covered in proteins that recognize invaders. • Function: – Part of your immune system. – Fight off bacteria and other invaders. • Examples: – Neutrophils – engulf bacteria – Basophil – Release histamine to promote and inflammatory response. Plant Leaf vs. Plant Stem • Leaf – Contains Guard Cells that open and close to allow for gas exchange – Lined with Chloroplasts • Stem – Contain Xylem and Phloem that carry food and water up the stem of the plant. Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. Tissues – groups of individual cells 3. Organs – groups of tissues working together 4. Organ Systems – groups of organs that work together for a specific function 5. Organism