cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
animal cells
... All living things are made of cells Cells are the smallest units that can carry out the activities of life All cells must obtain energy, remove waste products, and reproduce in order to stay alive The development of the microscope helped create the cell theory. Know the function of each or ...
... All living things are made of cells Cells are the smallest units that can carry out the activities of life All cells must obtain energy, remove waste products, and reproduce in order to stay alive The development of the microscope helped create the cell theory. Know the function of each or ...
Earth Liberation Front Leadership and Organizational Structure
... Leaders? •No identifiable leaders or chain of command •ELF used as an ideological standard •Leaderless Resistance •Earth Liberation Front Press Office ...
... Leaders? •No identifiable leaders or chain of command •ELF used as an ideological standard •Leaderless Resistance •Earth Liberation Front Press Office ...
Ch. 25 Terms
... in flatworms, a cilia-lined, bulblike cell that moves water and certain substances into excretory tubules for elimination outside the body. ...
... in flatworms, a cilia-lined, bulblike cell that moves water and certain substances into excretory tubules for elimination outside the body. ...
Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
Document
... Supplemental Methods Stimulation of Cell Lines The same concentrations of TLR agonists were used to stimulate reactivation of the J-Lat 10.6, ACH-2 and U1 HIV-1 latently cell lines, and in order to induce expression of IL-8 cytokine in THP-1 cells. Cells were maintained in culture medium made of RPM ...
... Supplemental Methods Stimulation of Cell Lines The same concentrations of TLR agonists were used to stimulate reactivation of the J-Lat 10.6, ACH-2 and U1 HIV-1 latently cell lines, and in order to induce expression of IL-8 cytokine in THP-1 cells. Cells were maintained in culture medium made of RPM ...
Chapter 5
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
7th Grade Review for Benchmark
... All body systems work together to make the organism function within an environment. The endocrine system in an organism is the system responsible for producing chemicals in the body such as insulin, sex hormones and adrenaline. Animal Adaptations Over time, as an environment changes, organisms must ...
... All body systems work together to make the organism function within an environment. The endocrine system in an organism is the system responsible for producing chemicals in the body such as insulin, sex hormones and adrenaline. Animal Adaptations Over time, as an environment changes, organisms must ...
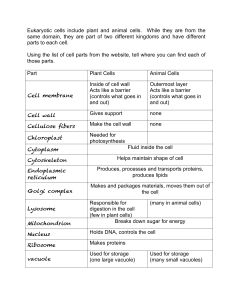
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
Cell Unit Test Review Sheet 1. What are the three parts of the cell
... 11. Draw an example of mitochondria. Explain where you would find it and its function within the cell. ...
... 11. Draw an example of mitochondria. Explain where you would find it and its function within the cell. ...
Subcellular Organelles and Structures
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
Sc 8 Unit 2 Topic 3 Notes WD
... -Cannot grow very large, must take in all materials they need through cell membranes so most can only live in watery, food-rich surroundings Multicellular (many-celled): -Made up of 2 or more cells -Bigger and more complex -May look different because they are specialized for specific functions -Can ...
... -Cannot grow very large, must take in all materials they need through cell membranes so most can only live in watery, food-rich surroundings Multicellular (many-celled): -Made up of 2 or more cells -Bigger and more complex -May look different because they are specialized for specific functions -Can ...
Unit 1 Test Review Guide: 5 pts Extra Credit on Summative Category
... 11. ________ Breaks food down into a usable, absorbable form 12. ________ Removal of cellular wastes from body tissues and the blood. 13. ________ Internal protect against microorganisms and foreign proteins. Homeostasis & Feedback 14. What is homeostasis? What is one mechanism our body uses to main ...
... 11. ________ Breaks food down into a usable, absorbable form 12. ________ Removal of cellular wastes from body tissues and the blood. 13. ________ Internal protect against microorganisms and foreign proteins. Homeostasis & Feedback 14. What is homeostasis? What is one mechanism our body uses to main ...
Chapter 9/10 Short Answer questions
... b. What can you infer about the other 600 cells the biology student photographed? 2. A white blood cell from a female golden retriever was found to contain a total of 78 chromosomes. How many different kinds (sizes and shapes) of chromosomes would you expect to find in the cell? Justify your answer. ...
... b. What can you infer about the other 600 cells the biology student photographed? 2. A white blood cell from a female golden retriever was found to contain a total of 78 chromosomes. How many different kinds (sizes and shapes) of chromosomes would you expect to find in the cell? Justify your answer. ...
Honors Biology Midterm Chapters and Topics 2014
... Properties of water Hydrogen bonds Identifying reactants and products in a chemical equation pH Chapter 3 The Molecules of Cells Organic verses inorganic Polymers and monomers Dehydration and hydrolysis reactions Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids o Monomers of each molecule o Structures ...
... Properties of water Hydrogen bonds Identifying reactants and products in a chemical equation pH Chapter 3 The Molecules of Cells Organic verses inorganic Polymers and monomers Dehydration and hydrolysis reactions Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids o Monomers of each molecule o Structures ...
Cell Power Point Questions
... 12) The __________________ regulates movement of materials into and out of the cell. 13) The ________________ contains DNA and chromosomes. 14) The ________________ is the energy powerhouse of the eukaryotic cell. 15) The cell wall is absent in _________________. 16) Chloroplasts are found in ______ ...
... 12) The __________________ regulates movement of materials into and out of the cell. 13) The ________________ contains DNA and chromosomes. 14) The ________________ is the energy powerhouse of the eukaryotic cell. 15) The cell wall is absent in _________________. 16) Chloroplasts are found in ______ ...
1.3-2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Student
... Belong to the __________________ Domain Most eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular Eukaryotic cells have _____________________. ...
... Belong to the __________________ Domain Most eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular Eukaryotic cells have _____________________. ...
Cell Size Limitations
... Most cells are between 2µm and 200µm A micrometer is 1 millionth of a meter! Too small to be seen with naked eye ...
... Most cells are between 2µm and 200µm A micrometer is 1 millionth of a meter! Too small to be seen with naked eye ...