Criterion
... SNC2D: Biology – Cells, Tissues and Living Systems Name _____________ Microviewer Lab Activity Make scientific drawings for 2 different cells. Choose one red blood cell and one respiration cell. The drawing must be done to scale. Draw only a few cells. Use solid lines, no shading but stippling is en ...
... SNC2D: Biology – Cells, Tissues and Living Systems Name _____________ Microviewer Lab Activity Make scientific drawings for 2 different cells. Choose one red blood cell and one respiration cell. The drawing must be done to scale. Draw only a few cells. Use solid lines, no shading but stippling is en ...
Plant and Animal Cells
... goes in and out of the cell. Ribosomes are found in the nucleus where they carry out photosynthesis. Plant cells are irregular in shape. They have a cell membrane that gives support to the cell. Like animal cells, they have vacuoles where energy is produced for use by the cell. We use methylene blue ...
... goes in and out of the cell. Ribosomes are found in the nucleus where they carry out photosynthesis. Plant cells are irregular in shape. They have a cell membrane that gives support to the cell. Like animal cells, they have vacuoles where energy is produced for use by the cell. We use methylene blue ...
Cells - Weebly
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. ...
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. ...
Everybody`s Made From Cells
... on ribosomes Then they’re transported through the endoplasmic reticulum To the Golgi where they’re packed in a bubble To keep them out of trouble But when you eat, they’re released on the double To turn your food into monomer rubble. ...
... on ribosomes Then they’re transported through the endoplasmic reticulum To the Golgi where they’re packed in a bubble To keep them out of trouble But when you eat, they’re released on the double To turn your food into monomer rubble. ...
The Cell Cycle - Haiku Learning
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
Structures and Organelles
... digest excess organelles and/or food particles also digest bacteria and viruses ...
... digest excess organelles and/or food particles also digest bacteria and viruses ...
Unit_biology_2_Cells
... b) Plant and algal cells also have a cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell. Plant cells often have: ■ chloroplasts, which absorb light energy to make food ■ a permanent vacuole filled with cell sap. c) A bacterial cell consists of cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall; ...
... b) Plant and algal cells also have a cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell. Plant cells often have: ■ chloroplasts, which absorb light energy to make food ■ a permanent vacuole filled with cell sap. c) A bacterial cell consists of cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall; ...
12-1 pm Location: Room HSW1057 UCSF
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
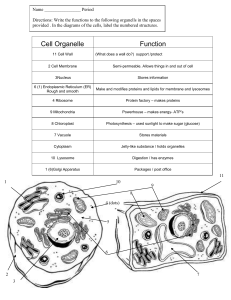
Cell Organelle
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
Body Systems REVIEW
... 1. The process by which organ systems maintain relatively constant internal conditions is called ___________________. 2. Which system coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment? __________________ 3. What provides support for the body, attachment sites for mu ...
... 1. The process by which organ systems maintain relatively constant internal conditions is called ___________________. 2. Which system coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment? __________________ 3. What provides support for the body, attachment sites for mu ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... I’m a series of tubes Found throughout the cell. I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
... I’m a series of tubes Found throughout the cell. I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
l2 biology: topics covered on the midterm exam and what to study
... diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport Differing concentrations: if a cell is put into higher/lower salt concentration what happens Membrane structure! Cells: ...
... diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport Differing concentrations: if a cell is put into higher/lower salt concentration what happens Membrane structure! Cells: ...
013368718X_CH02_015
... B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
... B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
013368718X_CH02_015
... B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
... B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
Ch.1 Notes - Green Local Schools
... Doing it all means not doing any one thing really well. Example of tradeoff Fully-featured Swiss Army knife does many jobs, but each tool can be awkward to use. ...
... Doing it all means not doing any one thing really well. Example of tradeoff Fully-featured Swiss Army knife does many jobs, but each tool can be awkward to use. ...
First Grade Portfolio
... common. (Nucleus, Mitochondria, Membrane) Nucleus-the “brain” of the cell. -Contains genetic information - controls the cell’s activity by directing protein synthesis -( a combination or mixture) Mitochondria- carries out cellular respiration in eurakaryotic cells -Converts nutrients into energy in ...
... common. (Nucleus, Mitochondria, Membrane) Nucleus-the “brain” of the cell. -Contains genetic information - controls the cell’s activity by directing protein synthesis -( a combination or mixture) Mitochondria- carries out cellular respiration in eurakaryotic cells -Converts nutrients into energy in ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...