Grade 10 Academic Science – Biology
... prevention via that white blood cells that prevent pathogen activity. The digestive system breaks down food (…chemically and physically…) so the body can absorb and use the energy. The system includes many organs including the mouth, teeth, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas and large intesti ...
... prevention via that white blood cells that prevent pathogen activity. The digestive system breaks down food (…chemically and physically…) so the body can absorb and use the energy. The system includes many organs including the mouth, teeth, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas and large intesti ...
Organelle Notes #2
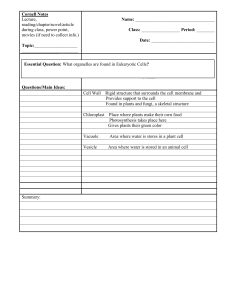
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
Nanotechnology and Heath: The use of nanostructure DDS
... underlying pathology. Most of the work developed until now are based on the use of engineered cells, tissues, associated with synthetic materials that can potentially extend and improve a patient’s life. Three basics approaches have been used, 1) organ transplants, 2) surgical reconstruction associa ...
... underlying pathology. Most of the work developed until now are based on the use of engineered cells, tissues, associated with synthetic materials that can potentially extend and improve a patient’s life. Three basics approaches have been used, 1) organ transplants, 2) surgical reconstruction associa ...
Name - Humble ISD
... Chapter 4 Physiology of Cells What are the similarities and differences between diffusion, dialysis, osmosis and filtration? What is the difference between active and passive transport? Describe the factors that determine potential osmotic pressure of electrolyte and non-electrolyte solutions. How d ...
... Chapter 4 Physiology of Cells What are the similarities and differences between diffusion, dialysis, osmosis and filtration? What is the difference between active and passive transport? Describe the factors that determine potential osmotic pressure of electrolyte and non-electrolyte solutions. How d ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Living Things
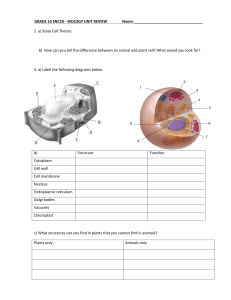
... 8. The chloroplast and the cell wall because they are only found in a plant cell. Vacuoles are much bigger in the plant cell. 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuol ...
... 8. The chloroplast and the cell wall because they are only found in a plant cell. Vacuoles are much bigger in the plant cell. 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuol ...
Biology Notes 3-2
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
... 1. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit(s) of life’s function and structure. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Most Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye: they are 5µm-20 µm (micrometers in diameter) Cells must have a high Surface Area-to-Volume ratio (S ...
Product Information
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for
... Cell membranes present a unique interface that governs numerous biological events in physiology as well as in disease pathogenesis; exploiting this interface for therapeutic development promises novel treatment modalities with biomimetic functionalities. Herein I report a nanoparticle functionalizat ...
... Cell membranes present a unique interface that governs numerous biological events in physiology as well as in disease pathogenesis; exploiting this interface for therapeutic development promises novel treatment modalities with biomimetic functionalities. Herein I report a nanoparticle functionalizat ...
Human Body Systems Review answers
... Human Body Systems Review 1. Put the following in order starting with the smallest: organs, organisms, organ systems, cells, tissues ...
... Human Body Systems Review 1. Put the following in order starting with the smallest: organs, organisms, organ systems, cells, tissues ...
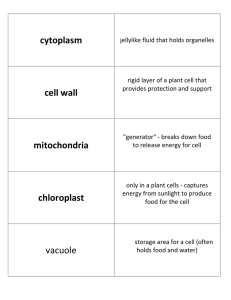
Organelles – Who Am I?
... 2. Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell and can break down a large molecule into a smaller one. 3. I am a jelly-like fluid that surrounds and supports organelles. 4. I am a series of tubes found throughout the cell. I transport proteins as they twist and form their shape, as we ...
... 2. Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell and can break down a large molecule into a smaller one. 3. I am a jelly-like fluid that surrounds and supports organelles. 4. I am a series of tubes found throughout the cell. I transport proteins as they twist and form their shape, as we ...
1. Cell The basic unit (or piece) of life. 2. Cell Theory All living
... Cell or organism that must eat food; cannot create its own food. (Example: animals eat food to survive.) ...
... Cell or organism that must eat food; cannot create its own food. (Example: animals eat food to survive.) ...
BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW
... 15. What is photosynthesis? Where does photosynthesis occur? 16. What is the hierarchy of cells? Give a specific example from one of the systems studied. 17. Label the diagram below in the spaces provided. ...
... 15. What is photosynthesis? Where does photosynthesis occur? 16. What is the hierarchy of cells? Give a specific example from one of the systems studied. 17. Label the diagram below in the spaces provided. ...
Label the organelles in the animal cell (see page 175
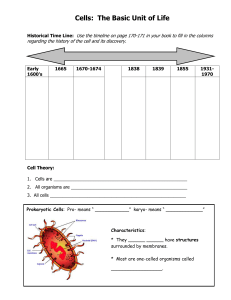
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
Biochemistry Review Sheet
... 10. What is diffusion? 11. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? 12. What is osmosis? 13. Draw three cells: one surrounded by hypotonic solution, one surrounded by hypertonic solution, and one surrounded by isotonic solution. Label the direction of solute movement and wate ...
... 10. What is diffusion? 11. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? 12. What is osmosis? 13. Draw three cells: one surrounded by hypotonic solution, one surrounded by hypertonic solution, and one surrounded by isotonic solution. Label the direction of solute movement and wate ...
7.3 From Cell To Organism
... a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood throughout the body ...
... a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood throughout the body ...
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
... Cilia and flagella are hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement. ...
... Cilia and flagella are hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement. ...
HW Chapter 4 HB
... Name: ________________________________________________ Homework Chapter 5 Biology of the Cell ...
... Name: ________________________________________________ Homework Chapter 5 Biology of the Cell ...
S3O1 Curr Map
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...