Persian Wars - Mrs. Helmer
... The Greek politician, Themistocles, convinced the Athenians otherwise. o So while Persia delayed through the 480's, Themistocles and the Athenians began a navybuilding project of epic proportions. o Themistocles convinced the Athenians to invest the profits from a newly discovered silver mine into t ...
... The Greek politician, Themistocles, convinced the Athenians otherwise. o So while Persia delayed through the 480's, Themistocles and the Athenians began a navybuilding project of epic proportions. o Themistocles convinced the Athenians to invest the profits from a newly discovered silver mine into t ...
Name Day/Block ______ Ancient Greece Notes
... Resulted in the slowing of cultural advance and weakening of political power e) characterizing life in Athens during the Golden Age of Pericles f) citing contributions in drama, poetry, history, sculpture, architecture, science, math, and philosophy Golden Age of Pericles (between Persian and Pelo ...
... Resulted in the slowing of cultural advance and weakening of political power e) characterizing life in Athens during the Golden Age of Pericles f) citing contributions in drama, poetry, history, sculpture, architecture, science, math, and philosophy Golden Age of Pericles (between Persian and Pelo ...
GREECE
... Outlawed slavery, elite held office but all could participate in assembly $ Cleisthenes ...
... Outlawed slavery, elite held office but all could participate in assembly $ Cleisthenes ...
Ancient Greece
... Peloponnesian War 431-404 BCE • Thucydides wrote History of the Peloponnesian Wars • Began as a competition for allies • Spart and Atens went to war – fought off and on for 27 years • Plague swept through Athens killing ¼ of the population (including Pericles) • 4ll BCE Athens suffered internal rev ...
... Peloponnesian War 431-404 BCE • Thucydides wrote History of the Peloponnesian Wars • Began as a competition for allies • Spart and Atens went to war – fought off and on for 27 years • Plague swept through Athens killing ¼ of the population (including Pericles) • 4ll BCE Athens suffered internal rev ...
Slide 1
... Described the Persian Wars and many other events “These are the Researches of Herodotus of Halicarnassus set down to preserve the memory of the past, and to prevent the great and wonderful achievements of the Greeks and the Barbarians from losing their glory, and in particular, to show how the two ...
... Described the Persian Wars and many other events “These are the Researches of Herodotus of Halicarnassus set down to preserve the memory of the past, and to prevent the great and wonderful achievements of the Greeks and the Barbarians from losing their glory, and in particular, to show how the two ...
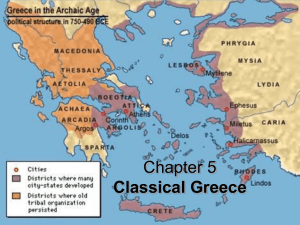
Classical Greece Section 1
... Shift from bronze to iron weapons did what to the army? The phalanx, formed by hoplites, became a fierce fighting force. ...
... Shift from bronze to iron weapons did what to the army? The phalanx, formed by hoplites, became a fierce fighting force. ...
Regents Review - Ancient Greece
... –Aristocracy = Rule by landholding elite –Oligarchy = Small, powerful elite business class rule –Phalanx= formation of heavily armed soldiers ...
... –Aristocracy = Rule by landholding elite –Oligarchy = Small, powerful elite business class rule –Phalanx= formation of heavily armed soldiers ...
It`s Greek to Me
... The citizens of Sparta didn’t want to trade or exchange ideas, so they used iron bars for money and didn’t accept other currency. Outsiders were not welcome. Spartans did not want wealth because they believed it led to laziness and weakness. Weak or ill citizens were useless to the Spartans. They we ...
... The citizens of Sparta didn’t want to trade or exchange ideas, so they used iron bars for money and didn’t accept other currency. Outsiders were not welcome. Spartans did not want wealth because they believed it led to laziness and weakness. Weak or ill citizens were useless to the Spartans. They we ...
Ancient Greece Test Review
... 24. What do Spartan men spend all of their time doing? ____________________________________________________ 25. Describe what happens to boys when they are born in Sparta? What if they don’t make the cut? ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
... 24. What do Spartan men spend all of their time doing? ____________________________________________________ 25. Describe what happens to boys when they are born in Sparta? What if they don’t make the cut? ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
Popular government - bugilsocialstudies
... • - Democritus all matter made up of small atoms. - Hippocrates “Father of Medicine” ...
... • - Democritus all matter made up of small atoms. - Hippocrates “Father of Medicine” ...
Ancient Greece: The Development of Athenian Democracy
... Thermopylae and Salamis • In 480 B.C., Persians launch new invasion of Greece • Greeks are divided; many stay neutral or side with Persians • Greek forces hold Thermopylae for three days before retreating • Athenians defeat Persians at sea, near island of Salamis • Victories at Salamis and Plataea f ...
... Thermopylae and Salamis • In 480 B.C., Persians launch new invasion of Greece • Greeks are divided; many stay neutral or side with Persians • Greek forces hold Thermopylae for three days before retreating • Athenians defeat Persians at sea, near island of Salamis • Victories at Salamis and Plataea f ...
Ancient Greece - MrsGaunasWiki
... Sparta vs. Athens, 431 – 404 BC Athens surrendered in 404 BC Long war left Greece economically weak, politically unstable, and with a decrease in population. This left Greece vulnerable to attack. ...
... Sparta vs. Athens, 431 – 404 BC Athens surrendered in 404 BC Long war left Greece economically weak, politically unstable, and with a decrease in population. This left Greece vulnerable to attack. ...
Greece and Iran - Willis High School
... • Attack on Athens foiled when Athenian forces defeated Persians at Marathon. – A messenger named Philippidès ran from Marathon to Athens to tell of the victory. He died from exhaustion. • The marathon is now run to celebrate his heroism. ...
... • Attack on Athens foiled when Athenian forces defeated Persians at Marathon. – A messenger named Philippidès ran from Marathon to Athens to tell of the victory. He died from exhaustion. • The marathon is now run to celebrate his heroism. ...
Test Review WS
... HOPLITE 6. The form of government used by Sparta OLIGARCHY 7. Built by Pericles, taking 15 years and 20,000 tons of marble PARTHENON 8. A body of land with oceans on three sides PENINSULA 9. He made Athens more democratic ...
... HOPLITE 6. The form of government used by Sparta OLIGARCHY 7. Built by Pericles, taking 15 years and 20,000 tons of marble PARTHENON 8. A body of land with oceans on three sides PENINSULA 9. He made Athens more democratic ...
Ancient Greece Greek Gods and Goddesses
... ____________ to sailing his navy to the channel by_______________. ...
... ____________ to sailing his navy to the channel by_______________. ...
Student 1
... Marathon not been won it is fair to say that the battles that followed would not have been the same or maybe not even existed as Greece would have struggled to resist the Persian army any further and ended up as a part of the Persian empire. After the Battle of Marathon, Athens was overjoyed at thei ...
... Marathon not been won it is fair to say that the battles that followed would not have been the same or maybe not even existed as Greece would have struggled to resist the Persian army any further and ended up as a part of the Persian empire. After the Battle of Marathon, Athens was overjoyed at thei ...
Greek Unit Test Review
... A. The leader of Athens who brought about the Golden Age of Athens and made the Delian League B. The beautiful woman who had a war fought over her. C. A goddess who Athens was named after D. The famous Greek thinker who asked others to think for themselves and question their beliefs. He was killed f ...
... A. The leader of Athens who brought about the Golden Age of Athens and made the Delian League B. The beautiful woman who had a war fought over her. C. A goddess who Athens was named after D. The famous Greek thinker who asked others to think for themselves and question their beliefs. He was killed f ...
File
... i. Darius, king of Persia, is dead. Son Xerxes has taken throne 1. Decides to avenge his father’s greatest defeat and again attacks Greece a. Went over land this time, attacking from the North b. Greece divided over how to handle the invasion i. Some wanted to fight, some wanted to wait ii. Xerxes c ...
... i. Darius, king of Persia, is dead. Son Xerxes has taken throne 1. Decides to avenge his father’s greatest defeat and again attacks Greece a. Went over land this time, attacking from the North b. Greece divided over how to handle the invasion i. Some wanted to fight, some wanted to wait ii. Xerxes c ...
p. 152, Translation of Latin Passage - Bolchazy
... where Themistocles and Eurybiades forced a naval batt le in the Straits there before the very eyes of Xerxes, who had been so confident of victory that he set up a golden throne on the promontory to watch the batt le. Needless to say, he promptly retreated to Asia but left an army under Mardonius. U ...
... where Themistocles and Eurybiades forced a naval batt le in the Straits there before the very eyes of Xerxes, who had been so confident of victory that he set up a golden throne on the promontory to watch the batt le. Needless to say, he promptly retreated to Asia but left an army under Mardonius. U ...
The Greeks at War!
... Athens faced a serious geographic disadvantage from the start. Sparta was located inland, the Athenian navy was no good against them. When Sparta invaded Athens, Pericles allowed people from the countryside to move inside the city. Overcrowding led to a plague that killed a third of the people. ...
... Athens faced a serious geographic disadvantage from the start. Sparta was located inland, the Athenian navy was no good against them. When Sparta invaded Athens, Pericles allowed people from the countryside to move inside the city. Overcrowding led to a plague that killed a third of the people. ...
Empires: The Greeks
... the world’s first democracy, Ancient Athens, through the life of an Athenian nobleman, Cleisthenes. In the brutal world of the fifth century, B.C., the Athenians struggle against a series of tyrants and their greatest rival, Sparta, to create a new “society of equals.” The program closes on the eve ...
... the world’s first democracy, Ancient Athens, through the life of an Athenian nobleman, Cleisthenes. In the brutal world of the fifth century, B.C., the Athenians struggle against a series of tyrants and their greatest rival, Sparta, to create a new “society of equals.” The program closes on the eve ...
Peloponnesian War

The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. In the first phase, the Archidamian War, Sparta launched repeated invasions of Attica, while Athens took advantage of its naval supremacy to raid the coast of the Peloponnese attempting to suppress signs of unrest in its empire. This period of the war was concluded in 421 BC, with the signing of the Peace of Nicias. That treaty, however, was soon undermined by renewed fighting in the Peloponnese. In 415 BC, Athens dispatched a massive expeditionary force to attack Syracuse in Sicily; the attack failed disastrously, with the destruction of the entire force, in 413 BC. This ushered in the final phase of the war, generally referred to either as the Decelean War, or the Ionian War. In this phase, Sparta, now receiving support from Persia, supported rebellions in Athens' subject states in the Aegean Sea and Ionia, undermining Athens' empire, and, eventually, depriving the city of naval supremacy. The destruction of Athens' fleet at Aegospotami effectively ended the war, and Athens surrendered in the following year. Corinth and Thebes demanded that Athens should be destroyed and all its citizens should be enslaved but Sparta refused.The Peloponnesian War reshaped the ancient Greek world. On the level of international relations, Athens, the strongest city-state in Greece prior to the war's beginning, was reduced to a state of near-complete subjection, while Sparta became established as the leading power of Greece. The economic costs of the war were felt all across Greece; poverty became widespread in the Peloponnese, while Athens found itself completely devastated, and never regained its pre-war prosperity. The war also wrought subtler changes to Greek society; the conflict between democratic Athens and oligarchic Sparta, each of which supported friendly political factions within other states, made civil war a common occurrence in the Greek world. Greek warfare, meanwhile, originally a limited and formalized form of conflict, was transformed into an all-out struggle between city-states, complete with atrocities on a large scale. Shattering religious and cultural taboos, devastating vast swathes of countryside, and destroying whole cities, the Peloponnesian War marked the dramatic end to the fifth century BC and the golden age of Greece.