Sparta and Athens: Totalitarianism vs. Democracy
... • You will be given two quotes to read. • Discuss amongst your group and determine which civilization – Athens or Sparta – that influenced the quote and why. • Take a guess where or who stated this quote. ...
... • You will be given two quotes to read. • Discuss amongst your group and determine which civilization – Athens or Sparta – that influenced the quote and why. • Take a guess where or who stated this quote. ...
Persian War - Canyon ISD
... Marches down Eastern coast Greeks were ÷ Persian’s had Greeks fighting w/ them 7,000 Greeks, including 500 Spartans fight Xerxes @ Battle of Thermopylae ...
... Marches down Eastern coast Greeks were ÷ Persian’s had Greeks fighting w/ them 7,000 Greeks, including 500 Spartans fight Xerxes @ Battle of Thermopylae ...
Classical Greece The High Point of Greek civilization is the time
... forming a defensive alliance against the Persians called the Delian league. Its main headquarters was on the island of Delos, but its chief officials were from Athens. Eventually the Greek states wanted to leave the league because they saw that the Persian threat was over. However, the Athenians for ...
... forming a defensive alliance against the Persians called the Delian league. Its main headquarters was on the island of Delos, but its chief officials were from Athens. Eventually the Greek states wanted to leave the league because they saw that the Persian threat was over. However, the Athenians for ...
Athens and Sparta: Two very different cities
... officials and killed. Healthy boys were trained to be soldiers. ◦ Sent to military training schools. ...
... officials and killed. Healthy boys were trained to be soldiers. ◦ Sent to military training schools. ...
Clash of the Titans: The Persian Wars - WLPCS Middle School
... “You hateful water, our master lays his judgment on you ...
... “You hateful water, our master lays his judgment on you ...
The Greeks at War
... strength & sheer will of the Athenian soldiers. After several days the Persians decided to attack by sea, but they were no match for the Athenian navy. ***Story of Pheidippides… VICTORY: Athens ...
... strength & sheer will of the Athenian soldiers. After several days the Persians decided to attack by sea, but they were no match for the Athenian navy. ***Story of Pheidippides… VICTORY: Athens ...
Greece—404 to 338 bc
... Aftermath of Peloponnesian War — Battle of Chaeronea After Athens’s defeat at the end of the Peloponnesian War, Sparta became the undisputed first power among the Greek city-states. The Spartan general Lysander had Athens’s walls pulled down and appointed thirty loyal Spartans to run the city. These ...
... Aftermath of Peloponnesian War — Battle of Chaeronea After Athens’s defeat at the end of the Peloponnesian War, Sparta became the undisputed first power among the Greek city-states. The Spartan general Lysander had Athens’s walls pulled down and appointed thirty loyal Spartans to run the city. These ...
Greek Civilization
... Solon (630? – 560? BC): Athenian poet and statesman who introduced reforms to Athens. Aristocrats chose him on account of his excellent reputation to solve single handedly, the political and social problems facing Athens. Reforms (beginning 594 BC): 1. Cancelled debts of the poor 2. Slavery for debt ...
... Solon (630? – 560? BC): Athenian poet and statesman who introduced reforms to Athens. Aristocrats chose him on account of his excellent reputation to solve single handedly, the political and social problems facing Athens. Reforms (beginning 594 BC): 1. Cancelled debts of the poor 2. Slavery for debt ...
Greece Test Review Power Point
... Athens was the cultural center of Greece, it had its golden age under the ruler Pericles. The thing that set Athens apart from the other city-states was its government. Athens was a democracy. The government of Athens, however, went through several stages before reaching democracy. ...
... Athens was the cultural center of Greece, it had its golden age under the ruler Pericles. The thing that set Athens apart from the other city-states was its government. Athens was a democracy. The government of Athens, however, went through several stages before reaching democracy. ...
The Beginnings of Democracy
... Everyone is equal under the law State ruled by citizens Rule based on citizenship Majority decides vote ...
... Everyone is equal under the law State ruled by citizens Rule based on citizenship Majority decides vote ...
The Greeks: Victory and Defeat
... was about 25 miles northeast of Athens. The Persian army was much bigger than the Athenian army, and the outnumbered Athenians had no one to help them. But while the Persians were loading their ships, the Athenians attacked and defeated them. Pheidippides ran 25 miles from Marathon to Athens to anno ...
... was about 25 miles northeast of Athens. The Persian army was much bigger than the Athenian army, and the outnumbered Athenians had no one to help them. But while the Persians were loading their ships, the Athenians attacked and defeated them. Pheidippides ran 25 miles from Marathon to Athens to anno ...
File - Ms lukas` classes
... Phillipides – ran to Sparta to request aid (marathon) Sparta could not send help for ten days – “full moon” ...
... Phillipides – ran to Sparta to request aid (marathon) Sparta could not send help for ten days – “full moon” ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR GREEK QUIZ II Answer the following questions
... The Greeks fought in a formation called a 22. _____ The Spartans had this symbol on “Flank”. their shields... S 7. _____ The Persians had a more diverse army than 23. _____ The Spartan’s leader and king was the Greeks at Marathon. Miltiades. 8. _____ The Athenians were saved by the Spartans. 2 ...
... The Greeks fought in a formation called a 22. _____ The Spartans had this symbol on “Flank”. their shields... S 7. _____ The Persians had a more diverse army than 23. _____ The Spartan’s leader and king was the Greeks at Marathon. Miltiades. 8. _____ The Athenians were saved by the Spartans. 2 ...
Ch. 5 Sec. 4 - J Go World History
... learn to run a household (wealthy girls learn to read & write) ...
... learn to run a household (wealthy girls learn to read & write) ...
File
... Alexander the Great (384-322 BC). 2. Philosopher who taught that good conduct meant following a moderate course between extremes Athens Golden Age is the Greek city-state of Athens in the time from 480 BC-404 BC. This was a period of Athenian political hegemony, economic growth and cultural flourish ...
... Alexander the Great (384-322 BC). 2. Philosopher who taught that good conduct meant following a moderate course between extremes Athens Golden Age is the Greek city-state of Athens in the time from 480 BC-404 BC. This was a period of Athenian political hegemony, economic growth and cultural flourish ...
ANCIENT GREECE REVIEW - Hauppauge School District / …
... Where the wealthiest citizens make decisions. They also had a strong Navy. They became very wealthy during the “Golden Age” Colonies paid their navy for protection. Sparta had a strong military and once joined with Athens to defeat the Persians but eventually became jealous of Athens’ power and defe ...
... Where the wealthiest citizens make decisions. They also had a strong Navy. They became very wealthy during the “Golden Age” Colonies paid their navy for protection. Sparta had a strong military and once joined with Athens to defeat the Persians but eventually became jealous of Athens’ power and defe ...
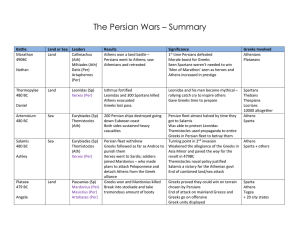
The Persian Wars – Summary Battle Land or Sea Leaders Results
... Greeks followed as far as Andros to punish them Xerxes went to Sardis; soldiers joined Mardonius – who made plans to attack Peloponnese and detach Athens from the Greek alliance Greeks won and Mardonius killed Break into stockade and take tremendous amount of booty ...
... Greeks followed as far as Andros to punish them Xerxes went to Sardis; soldiers joined Mardonius – who made plans to attack Peloponnese and detach Athens from the Greek alliance Greeks won and Mardonius killed Break into stockade and take tremendous amount of booty ...
Greek Review Answers
... Athens – Women received no educaon, could not serve in the government, own property, or even leave their homes. 10.b) Compare and Contrast; How was the educaon of Spartan boys different from the educaon of Athenian boys? What did the educaon of both groups have in common? Sparta – Trained from an ...
... Athens – Women received no educaon, could not serve in the government, own property, or even leave their homes. 10.b) Compare and Contrast; How was the educaon of Spartan boys different from the educaon of Athenian boys? What did the educaon of both groups have in common? Sparta – Trained from an ...
Warring City States
... • 7,000 Greeks and 300 Spartans • Blocked Xerxes troops for three days • Traitor told of secret path • Spartans held back the Persians, while other Greeks retreated ...
... • 7,000 Greeks and 300 Spartans • Blocked Xerxes troops for three days • Traitor told of secret path • Spartans held back the Persians, while other Greeks retreated ...
post- words study guide - Germantown School District
... defeated would mix with Greek culture A philosopher that taught using a method of asking questions ...
... defeated would mix with Greek culture A philosopher that taught using a method of asking questions ...
Greek Warfare - Little Miami Schools
... was joined by forces from other Greek city-states to defend the pass. • Leonidas and his men held back the Persians, including the elite Immortals, frontal attacks for the first 2 days, losing very few of their own. On the third day, a traitor named Ephialtes led the Persians to a mountain track to ...
... was joined by forces from other Greek city-states to defend the pass. • Leonidas and his men held back the Persians, including the elite Immortals, frontal attacks for the first 2 days, losing very few of their own. On the third day, a traitor named Ephialtes led the Persians to a mountain track to ...
Classical Greece Minoan Civilization (1750-1400 BC)
... • Leader of Athens • Made Athens a direct democracy where every citizen had a say in government • Rebuilt Athens into a beautiful, rich, and powerful city • Went to war with Athens and its allies in the Peloponnesian War ...
... • Leader of Athens • Made Athens a direct democracy where every citizen had a say in government • Rebuilt Athens into a beautiful, rich, and powerful city • Went to war with Athens and its allies in the Peloponnesian War ...
PERSIAN WARS What empire was the strongest in the world at the
... SPARTA BLOCKED OFF THEIR PORT AND THEY COULDN’T GET ANY SUPPLIES IN AND COULDN’T GET OUT OF THE CITY – THE WALLS TRAPPED THEM INSIDE AND THEY STARVED 30. What city-state declared war on Athens? SPARTA 31. How many years did the Peloponnesian War last? 27 YEARS 32. Why is the Peloponnesian War consid ...
... SPARTA BLOCKED OFF THEIR PORT AND THEY COULDN’T GET ANY SUPPLIES IN AND COULDN’T GET OUT OF THE CITY – THE WALLS TRAPPED THEM INSIDE AND THEY STARVED 30. What city-state declared war on Athens? SPARTA 31. How many years did the Peloponnesian War last? 27 YEARS 32. Why is the Peloponnesian War consid ...
Peloponnesian War

The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought by Athens and its empire against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. In the first phase, the Archidamian War, Sparta launched repeated invasions of Attica, while Athens took advantage of its naval supremacy to raid the coast of the Peloponnese attempting to suppress signs of unrest in its empire. This period of the war was concluded in 421 BC, with the signing of the Peace of Nicias. That treaty, however, was soon undermined by renewed fighting in the Peloponnese. In 415 BC, Athens dispatched a massive expeditionary force to attack Syracuse in Sicily; the attack failed disastrously, with the destruction of the entire force, in 413 BC. This ushered in the final phase of the war, generally referred to either as the Decelean War, or the Ionian War. In this phase, Sparta, now receiving support from Persia, supported rebellions in Athens' subject states in the Aegean Sea and Ionia, undermining Athens' empire, and, eventually, depriving the city of naval supremacy. The destruction of Athens' fleet at Aegospotami effectively ended the war, and Athens surrendered in the following year. Corinth and Thebes demanded that Athens should be destroyed and all its citizens should be enslaved but Sparta refused.The Peloponnesian War reshaped the ancient Greek world. On the level of international relations, Athens, the strongest city-state in Greece prior to the war's beginning, was reduced to a state of near-complete subjection, while Sparta became established as the leading power of Greece. The economic costs of the war were felt all across Greece; poverty became widespread in the Peloponnese, while Athens found itself completely devastated, and never regained its pre-war prosperity. The war also wrought subtler changes to Greek society; the conflict between democratic Athens and oligarchic Sparta, each of which supported friendly political factions within other states, made civil war a common occurrence in the Greek world. Greek warfare, meanwhile, originally a limited and formalized form of conflict, was transformed into an all-out struggle between city-states, complete with atrocities on a large scale. Shattering religious and cultural taboos, devastating vast swathes of countryside, and destroying whole cities, the Peloponnesian War marked the dramatic end to the fifth century BC and the golden age of Greece.