Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
... States of matter: (fill in by class response) Definite volume (V)? ...
... States of matter: (fill in by class response) Definite volume (V)? ...
Test: "Chemical Equations" (General Chemistry)
... General Chemistry: Chapter 7 Test 1. In endothermic reactions: a. energy is released b. products have less energy than reactants ...
... General Chemistry: Chapter 7 Test 1. In endothermic reactions: a. energy is released b. products have less energy than reactants ...
Chapter 11
... ► Combination combines two to form one ► Decomposition breaks one into two ► Single replacement has one compound and one element on both sides of the equation. ► Double replacement involves two compounds on both sides of the equation. ...
... ► Combination combines two to form one ► Decomposition breaks one into two ► Single replacement has one compound and one element on both sides of the equation. ► Double replacement involves two compounds on both sides of the equation. ...
(s) If 5.00 moles of zinc is placed into 1.50 L... 34. solution,what is the mass of the hydrogen gas produced?
... Base your answers to questions 34 through 32 on on the following chemical reaction: ...
... Base your answers to questions 34 through 32 on on the following chemical reaction: ...
12 Chemical Potential
... Here we derive the probability that a system with accessible energy levels E1, E2,... and particle numbers N1, N2,... at temperature T is in any particular state with an energy level Ei and particle number Nj. Again define the Helmholtz free energy F as the average work required to assemble the syst ...
... Here we derive the probability that a system with accessible energy levels E1, E2,... and particle numbers N1, N2,... at temperature T is in any particular state with an energy level Ei and particle number Nj. Again define the Helmholtz free energy F as the average work required to assemble the syst ...
Syllabus - Harrison County BOE
... during the first year of college. AP Chemistry will review the content of Chemistry I and II and focus on higher level questioning. Five major topics will be discussed, redox, acid/base, equilibrium, thermochemistry, and kinetics. This course will focus on preparation for the AP exam. Materials Used ...
... during the first year of college. AP Chemistry will review the content of Chemistry I and II and focus on higher level questioning. Five major topics will be discussed, redox, acid/base, equilibrium, thermochemistry, and kinetics. This course will focus on preparation for the AP exam. Materials Used ...
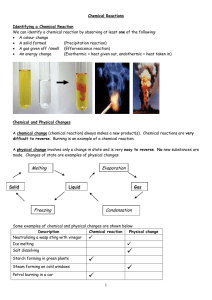
Chemical Reactions
... The reactants are separated from each other by a plus sign and the products are separated from each other by a plus sign. There should be an arrow in the middle. Examples: When sodium is mixed with water, a purple alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide is produced and hydrogen gas is evolved. Sodium ...
... The reactants are separated from each other by a plus sign and the products are separated from each other by a plus sign. There should be an arrow in the middle. Examples: When sodium is mixed with water, a purple alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide is produced and hydrogen gas is evolved. Sodium ...
Chemical Thermodynamics
... 1. Use the First Law of Thermodynamics to relate heat, work and energy changes. 2. Use bond energies to estimate heats of reaction for gas phase reactions; use ΔH values for gas phase reactions to find bond energies. 3. Discuss changes in Internal Energy, E, and its relationship to heat and work. 4 ...
... 1. Use the First Law of Thermodynamics to relate heat, work and energy changes. 2. Use bond energies to estimate heats of reaction for gas phase reactions; use ΔH values for gas phase reactions to find bond energies. 3. Discuss changes in Internal Energy, E, and its relationship to heat and work. 4 ...
Chapter 11.1: Describing Chemical Reactions
... catalyst is a substance that can be added to speed up the reaction but is not used up in a reaction. It is neither a product or a reactant. ...
... catalyst is a substance that can be added to speed up the reaction but is not used up in a reaction. It is neither a product or a reactant. ...
Lecture 6 Free Energy
... same, the entropy of water does not change. However, the solutes still want to maximize entropy by expansion, just like an ideal gas. ...
... same, the entropy of water does not change. However, the solutes still want to maximize entropy by expansion, just like an ideal gas. ...
Thermochemistry www.AssignmentPoint.com Thermochemistry is
... reactions and/or physical transformations. A reaction may release or absorb energy, and a phase change may do the same, such as in melting and boiling. Thermochemistry focuses on these energy changes, particularly on the system's energy exchange with its surroundings. Thermochemistry is useful in pr ...
... reactions and/or physical transformations. A reaction may release or absorb energy, and a phase change may do the same, such as in melting and boiling. Thermochemistry focuses on these energy changes, particularly on the system's energy exchange with its surroundings. Thermochemistry is useful in pr ...
KEY CONCEPT Enzymes are catalysts for chemical
... A catalyst lowers activation energy. • Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. – decrease activation energy – increase reaction rate ...
... A catalyst lowers activation energy. • Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. – decrease activation energy – increase reaction rate ...
Chemical Thermodynamic
... Ans1. A process which is carried out infinitesimally slowly so that changes occurring in the direct process can be exactly reversed without disturbing the equilibrium. Q2. What is the main limitation of the first law of thermodynamics? Ans2. It cannot predict the spontaneity of a process. Q3. Define ...
... Ans1. A process which is carried out infinitesimally slowly so that changes occurring in the direct process can be exactly reversed without disturbing the equilibrium. Q2. What is the main limitation of the first law of thermodynamics? Ans2. It cannot predict the spontaneity of a process. Q3. Define ...
Chemistry Claims Unit 1: Alchemy: Matter, Atomic Structure, and
... Exothermic/Endothermic reactions are the most useful/dangerous types of reactions The first/second law is the most important Law of Thermodynamics. Bread/Potato chips/ Walnuts/ Coca-Cola is/are the best source of “fuel”. Hydrogen/Carbon bonds are hard/easy bonds to break. Steam engines/Int ...
... Exothermic/Endothermic reactions are the most useful/dangerous types of reactions The first/second law is the most important Law of Thermodynamics. Bread/Potato chips/ Walnuts/ Coca-Cola is/are the best source of “fuel”. Hydrogen/Carbon bonds are hard/easy bonds to break. Steam engines/Int ...
Double Replacement Reactions
... 1. Write the formula for one s’more: _____________________ 2. Write the formula for two s’mores: _______________________ On your formula above, draw a square around the coefficient. Draw a circle around the subscripts. 3. If you have two s’mores how many of each type of “atom” do you have? _____ Gc ...
... 1. Write the formula for one s’more: _____________________ 2. Write the formula for two s’mores: _______________________ On your formula above, draw a square around the coefficient. Draw a circle around the subscripts. 3. If you have two s’mores how many of each type of “atom” do you have? _____ Gc ...
ACS_Thermodynamics_Exam_1981
... From these data, estimate the temperature at which the equilibrium constant for this reaction is approximately unity. a) ...
... From these data, estimate the temperature at which the equilibrium constant for this reaction is approximately unity. a) ...
Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry 2012 – 2013 Ramsay High
... vaporization and fusion; calorimetry ...
... vaporization and fusion; calorimetry ...
SCH3U Course Review
... decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
... decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
Chemical Synthesis (sat6)
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.